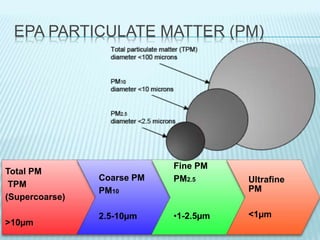
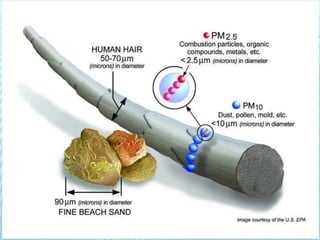
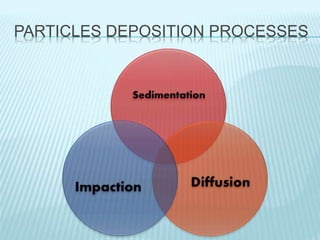
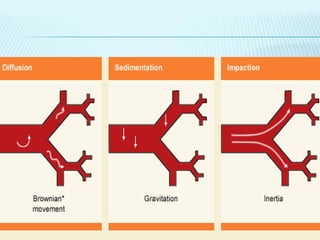
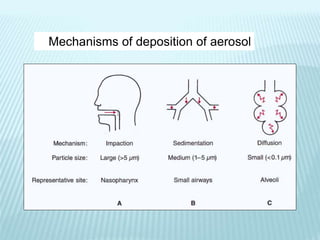
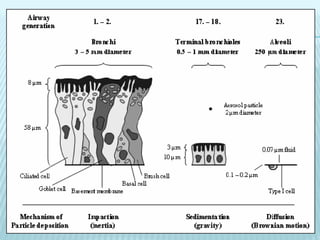
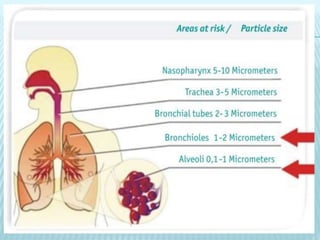
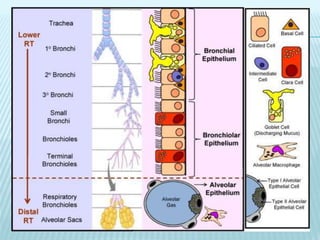
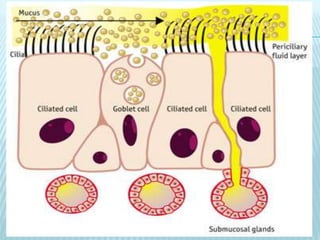
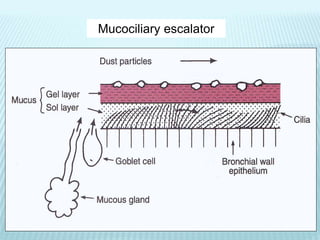
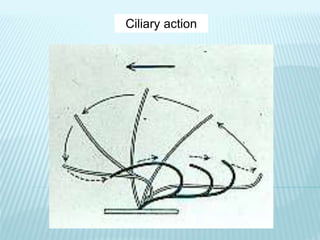
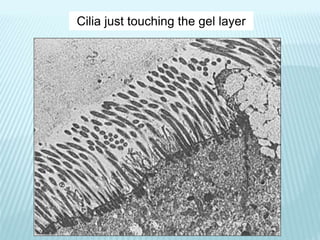
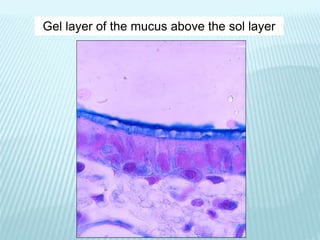
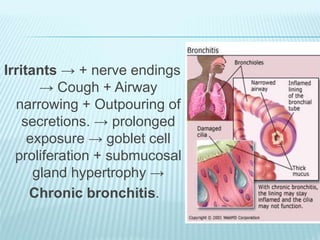
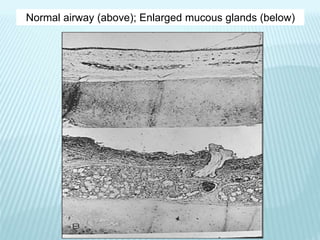
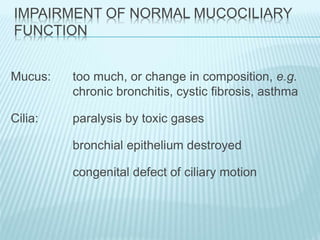
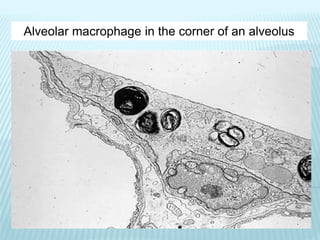
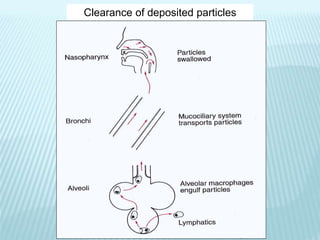
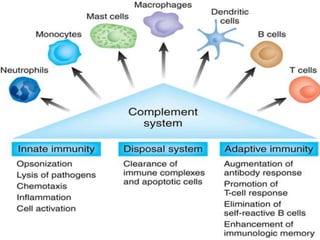
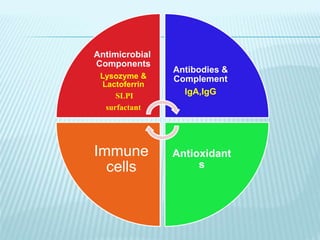
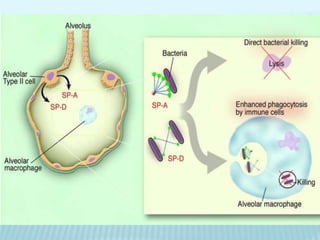
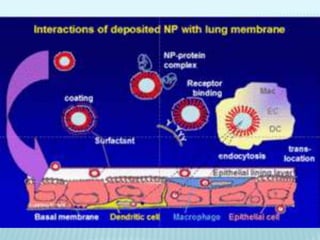
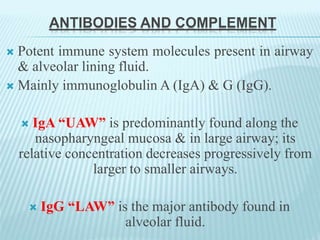
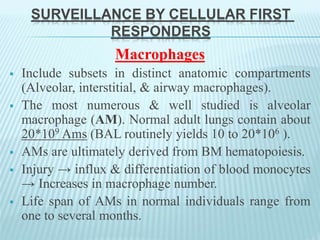
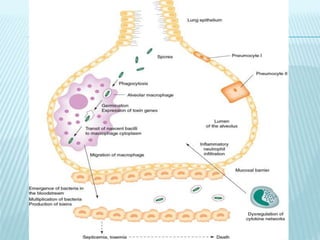
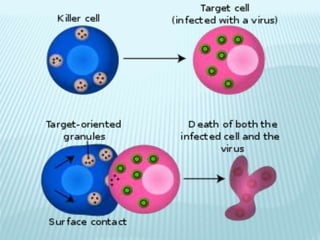
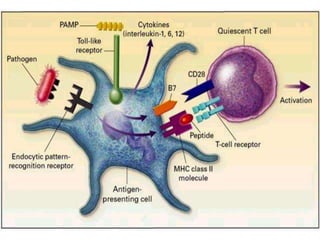
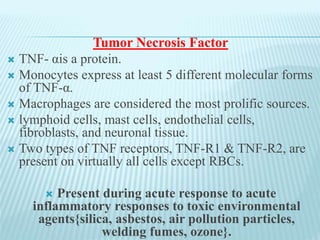
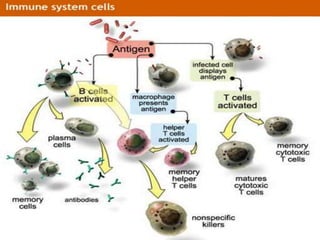
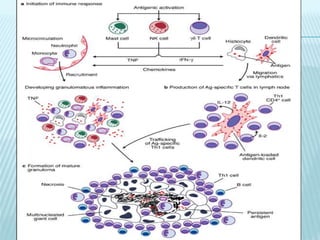
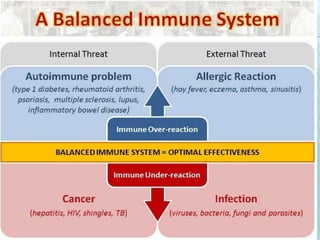
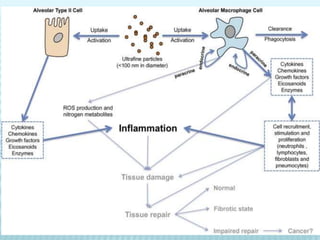
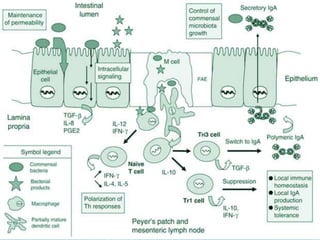
This document discusses pulmonary defense mechanisms against inhaled particles and pathogens. It describes several factors that affect particles' effects such as diameter, shape, and composition. It then covers the main deposition processes particles undergo in the lungs - impaction, sedimentation, and diffusion. The major lung defense mechanisms discussed are the upper and lower airway filters, macrophage clearance to and via lymphatics, and the immune defenses of the lungs including antimicrobial components, antibodies, complement, antioxidants, and immune cells like macrophages, epithelial cells, neutrophils, mast cells, NK cells, dendritic cells, and cytokines. The adaptive immune response of B and T lymphocytes in the lungs is also briefly mentioned.