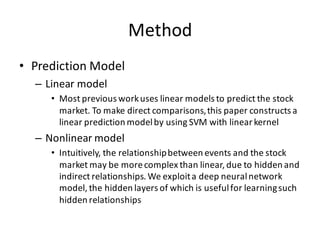
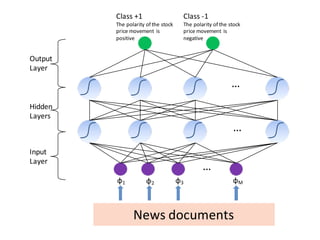
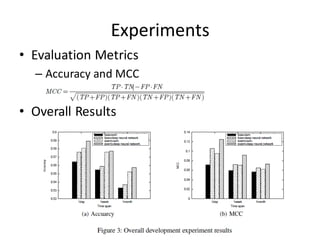
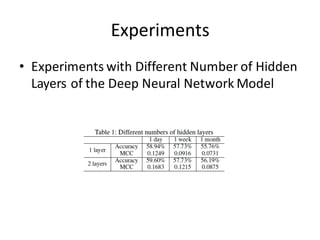
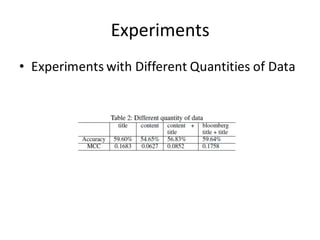
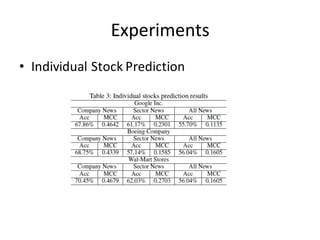
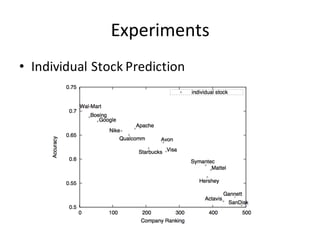
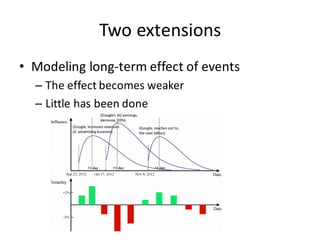
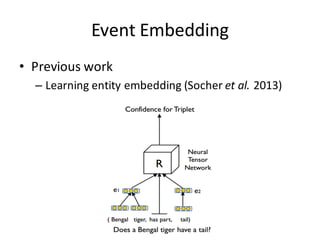
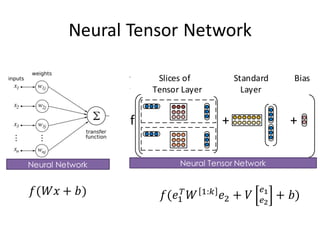
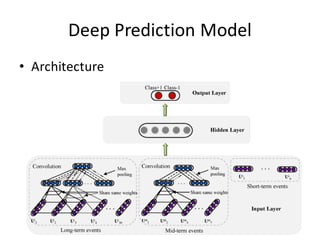
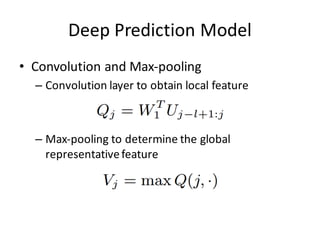
This document describes research on using deep learning models to predict stock market movements based on news events. It presents a method to extract event representations from news articles, generalize the events, embed the events, and feed the embedded events into deep learning models. Experimental results show that using embedded events as inputs to convolutional neural networks achieved more accurate stock market predictions than baseline methods, and modeling long, mid, and short-term event effects further improved performance. The research demonstrates that deep learning can effectively capture hidden relationships between news events and stock prices.










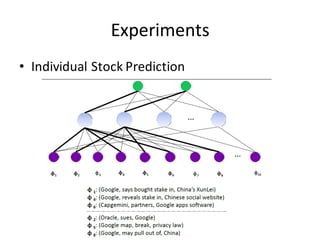



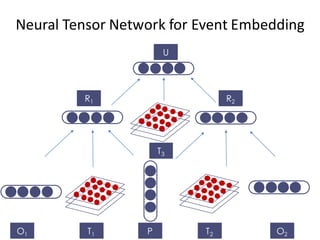
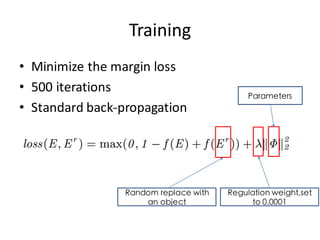
![O1 T1 P
R1
𝑅$ =
𝑓(𝑂$
%
𝑇$
[$:(]
𝑃 + 𝑉 :-
;
+ 𝑏)
Neural Tensor Network for Event Embedding](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/first-151022143649-lva1-app6892/85/Deep-Learning-for-Stock-Prediction-28-320.jpg)

![Experiments
• Baselines
Input Method
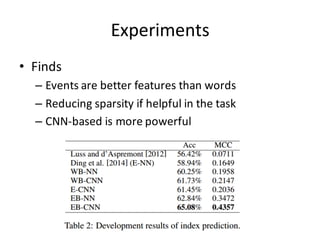
Luss and d’Aspremont [2012] Bag of words NN
Ding et al. [2014] (E-NN) Structured event NN
WB-NN Word embedding NN
WB-CNN Word embedding CNN
E-CNN Structured event CNN
EB-NN Event embedding NN
EB-CNN Event embedding CNN](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/first-151022143649-lva1-app6892/85/Deep-Learning-for-Stock-Prediction-33-320.jpg)