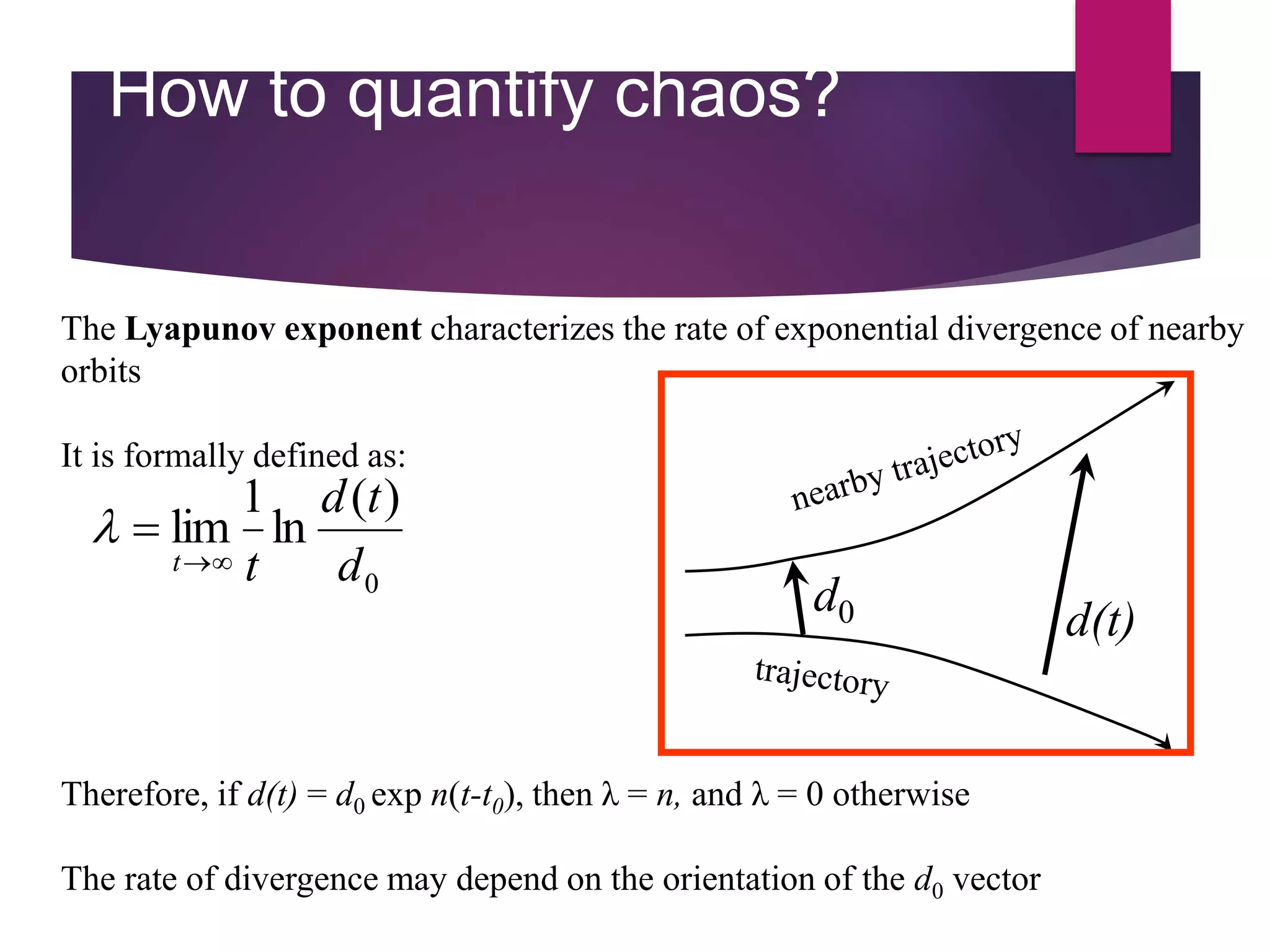
The document presents a seminar on chaotic systems, discussing key concepts such as sensitive dependence on initial conditions (the butterfly effect) and the deterministic nature of chaotic behavior. It explores various examples of chaotic systems, including weather patterns and population dynamics, and introduces methodologies for quantifying chaos using Lyapunov exponents. Additionally, the seminar highlights applications of chaos theory in cryptography, random number generation, and image encryption.




![Different Type Of Chaotic Maps
One dimensional and multi-dimensional,
Logistic map [One Dimensional]
With one parameter
𝑋 𝑁+1 = 𝑢𝑋 𝑁(1 − 𝑋 𝑁)
where
Sine map
𝑥 𝑛+1= f (r,x,n) = r x sin(π×𝑥 𝑛)
where r Ɛ (0,4]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/seminar1chaoticsystem-180406172848/75/Chaotic-system-and-its-Application-in-Cryptography-8-2048.jpg)
![Cont..
.
Chaotic Henon Map [2 dimensional]
The Henon map is a 2-D iterated map with chaotic solutions proposed
by Mchel Henon (1976).
2
1
1
1
(8)n n n
n n
X aX bY
Y X
0 0.2 0.4 0.6 0.8 1 1.2 1.4
-1.5
-1
-0.5
0
0.5
1
1.5
Bifurcation diagram for the Henon map,
b=0.3](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/seminar1chaoticsystem-180406172848/75/Chaotic-system-and-its-Application-in-Cryptography-10-2048.jpg)





![References
[1] Chanil Pak, Lilian Huang, A new color image encryption using
combination of 1D chaotic map, Signal Process.138 (2017) 129–137.
[2] Nigel Crook and Tjeerd olde Scheper, A Novel Chaotic Neural
Network Architecture
[3] Chaos and Time-Series Analysis, by J.C. Sprott, Oxford Press 2006
[4] S. M. Chang, M. C. Li and W. W. Lin, Asymptotic synchronization of
modified logistic hyper-chaotic systems and its applications. Nonlinear
Analysis: Real World Applications, Vol. 10, Issue 2 (2009), pp. 869–880.
[5] Nigel Crook and Tjeerd olde Scheper, A Novel Chaotic Neural
Network Architecture](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/seminar1chaoticsystem-180406172848/75/Chaotic-system-and-its-Application-in-Cryptography-22-2048.jpg)
