The document provides an overview of deep learning including:
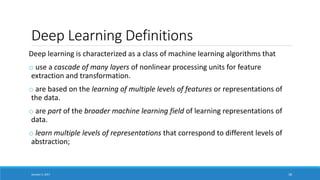
- Defining deep learning as a class of machine learning algorithms that use multiple levels of representation and nonlinear processing units.
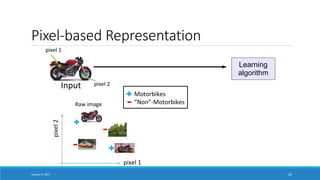
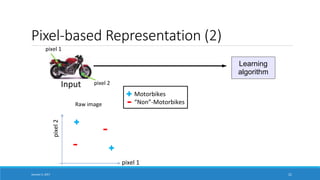
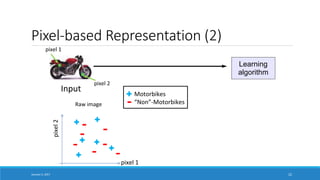
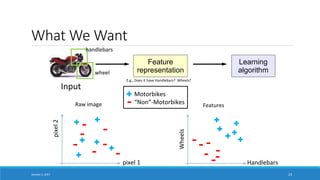
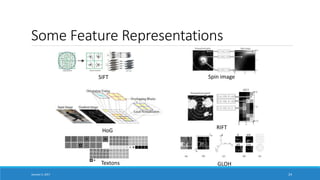
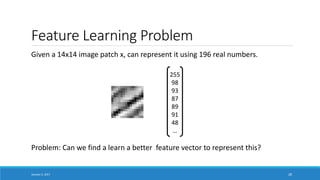
- Explaining that deep learning aims to learn representations of data without specifying features, in contrast to traditional machine learning which relies on human-engineered features.
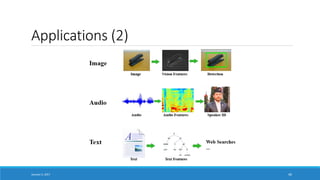
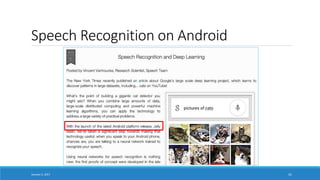
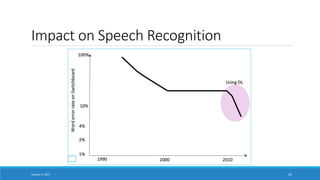
- Highlighting applications of deep learning like computer vision, speech recognition, machine translation and more which have achieved expert-level performance.















![The Brain:
Potential Motivation for Deep Learning
[Roe et al., 1992]
Auditory Cortex learns to see!
Auditory Cortex
January 5, 2017 26](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ai-deeplearning-er-170111031801/85/Deep-Learning-for-Artificial-Intelligence-AI-26-320.jpg)
![The Brain adapts!
[BrainPort; Welsh & Blasch, 1997; Nagel et al., 2005; Constantine-Paton & Law, 2009]
Seeing with your Tongue Human Echolocation (Sonar)
Haptic belt: Direction Sense Implanting a 3rd Eye
January 5, 2017 27](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ai-deeplearning-er-170111031801/85/Deep-Learning-for-Artificial-Intelligence-AI-27-320.jpg)
![Why Deep Learning?
Method Accuracy
Hessian + ESURF [Williems et al 2008] 38%
Harris3D + HOG/HOF [Laptev et al 2003,
2004]
45%
Cuboids + HOG/HOF [Dollar et al 2005,
Laptev 2004]
46%
Hessian + HOG/HOF [Laptev 2004, Williems
et al 2008]
46%
Dense + HOG / HOF [Laptev 2004] 47%
Cuboids + HOG3D [Klaser 2008, Dollar et al
2005]
46%
Unsupervised Feature Learning (DL) 52%
[Le, Zhou & Ng, 2011]
Task: Video Activity Recognition
January 5, 2017 29](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ai-deeplearning-er-170111031801/85/Deep-Learning-for-Artificial-Intelligence-AI-29-320.jpg)
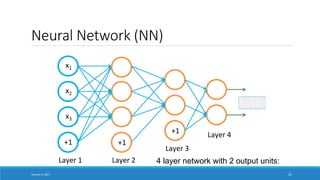
![Unsupervised Feature Learning with a NN
x4
x5
x6
+1
x1
x2
x3
+1
a1
a2
a3
+1
b1
b2
b3
+1
c1
c2
c3
New representation
for input.
Use [c1, c3, c3] as representation to feed to learning algorithm.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ai-deeplearning-er-170111031801/85/Deep-Learning-for-Artificial-Intelligence-AI-32-320.jpg)

![Deep Belief Network (2)
Input [x1, x2, x3, x4]
Layer 2. [a1, a2, a3]
Layer 3. [b1, b2, b3]
Similar to a sparse auto-encoder in many ways.
Stack RBMs on top of each other to get DBN.
January 5, 2017 34](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ai-deeplearning-er-170111031801/85/Deep-Learning-for-Artificial-Intelligence-AI-34-320.jpg)

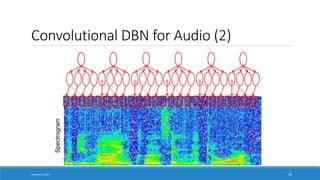
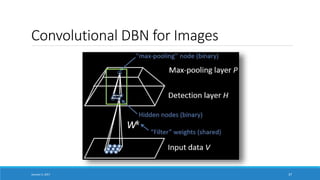
![Going Deep
Pixels
Object Models
[Honglak Lee]
Training Set: Aligned
images of faces.
January 5, 2017 38
Edges
Object Parts
(combination of edges)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ai-deeplearning-er-170111031801/85/Deep-Learning-for-Artificial-Intelligence-AI-38-320.jpg)