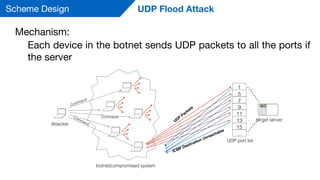
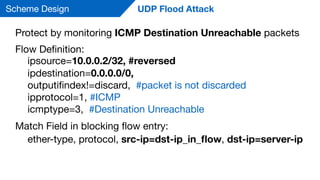
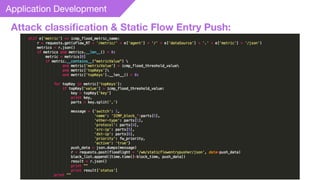
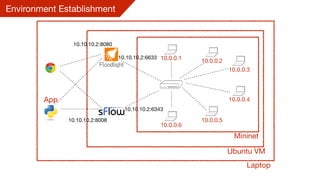
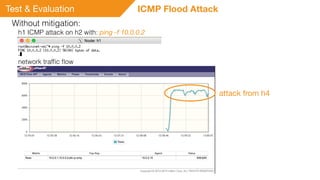
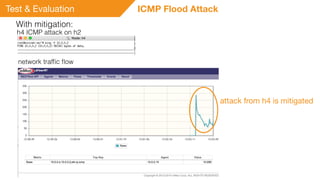
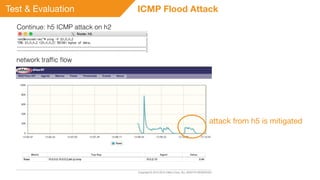
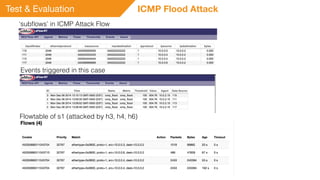
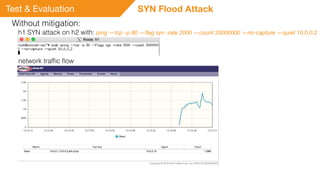
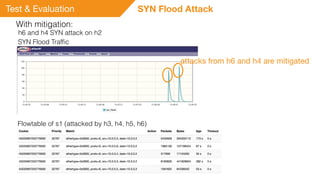
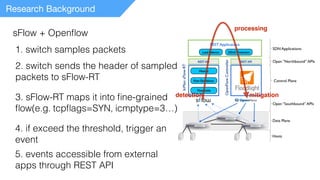
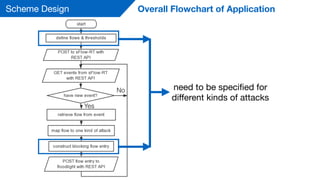
This document summarizes a presentation on detecting and mitigating distributed denial of service (DDoS) attacks in software-defined networks. It discusses using sFlow and the Floodlight controller to detect common DDoS attack types like ICMP floods, SYN floods, and DNS amplification. An application was developed in Python to classify attacks and push static flow entries to direct attack traffic to the sFlow collector for analysis. The scheme was tested in a Mininet virtual network and shown to successfully mitigate ICMP and SYN flood attacks. Future work includes testing DNS amplification and UDP floods, implementing adaptive sampling rates and thresholds, and designing an unblocking mechanism.








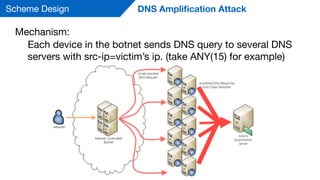
![Scheme Design DNS Amplification Attack
Flow Definition:
ipsource=0.0.0.0/0,
ipdestination=[10.0.0.1/32, 10.0.0.2/32], #suppose h1 and
h2 are the DNS servers
outputifindex!=discard, #packet is not discarded
dnsqr=false,
dnsqtype=255
Match Field in blocking flow entry:
ether-type, protocol, src-ip, dst-ip
Protect at the DNS servers (instead of the victim)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cc3736slides-150414170119-conversion-gate01/85/DDoS-Attack-Detection-Mitigation-in-SDN-14-320.jpg)