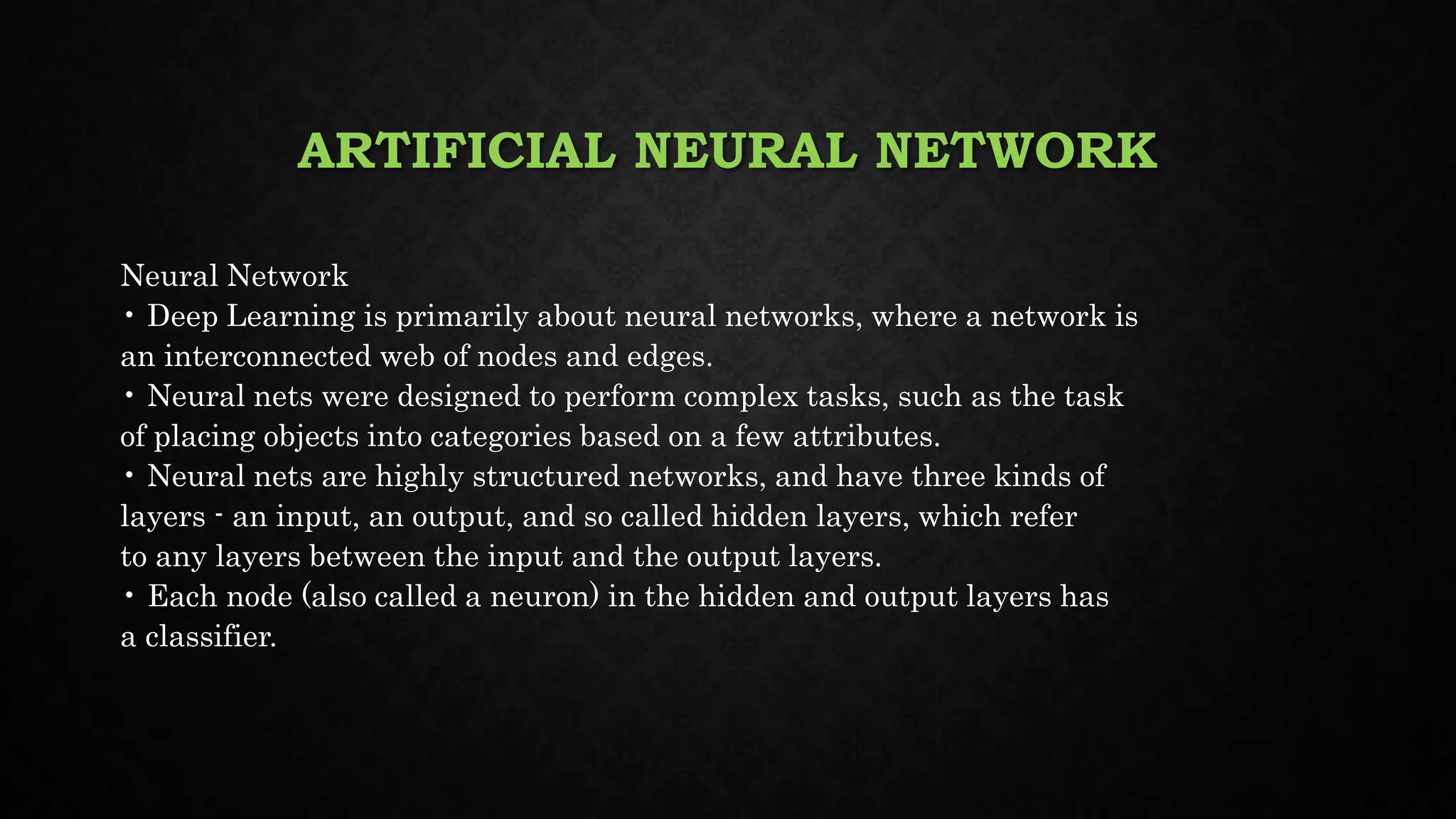
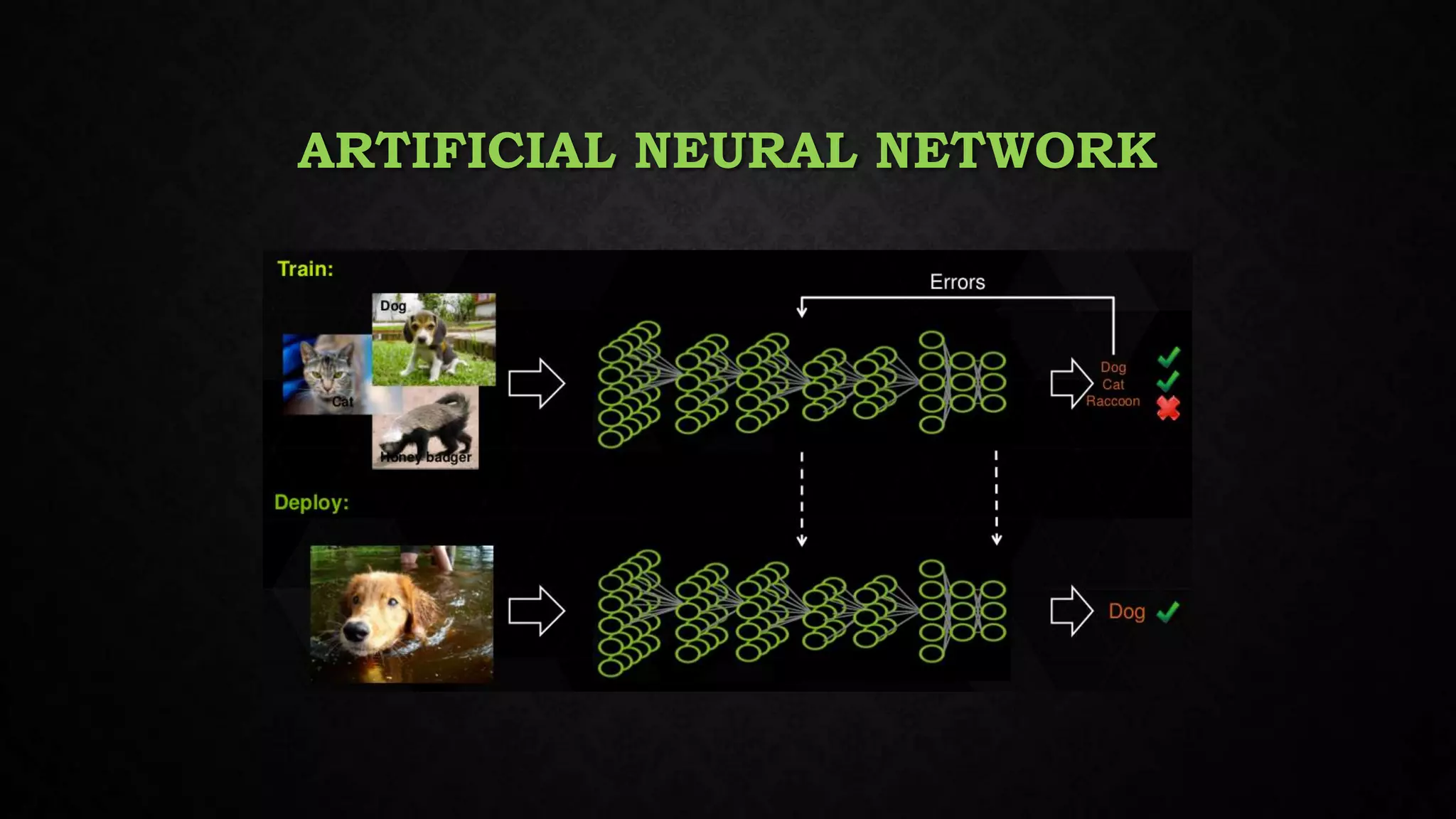
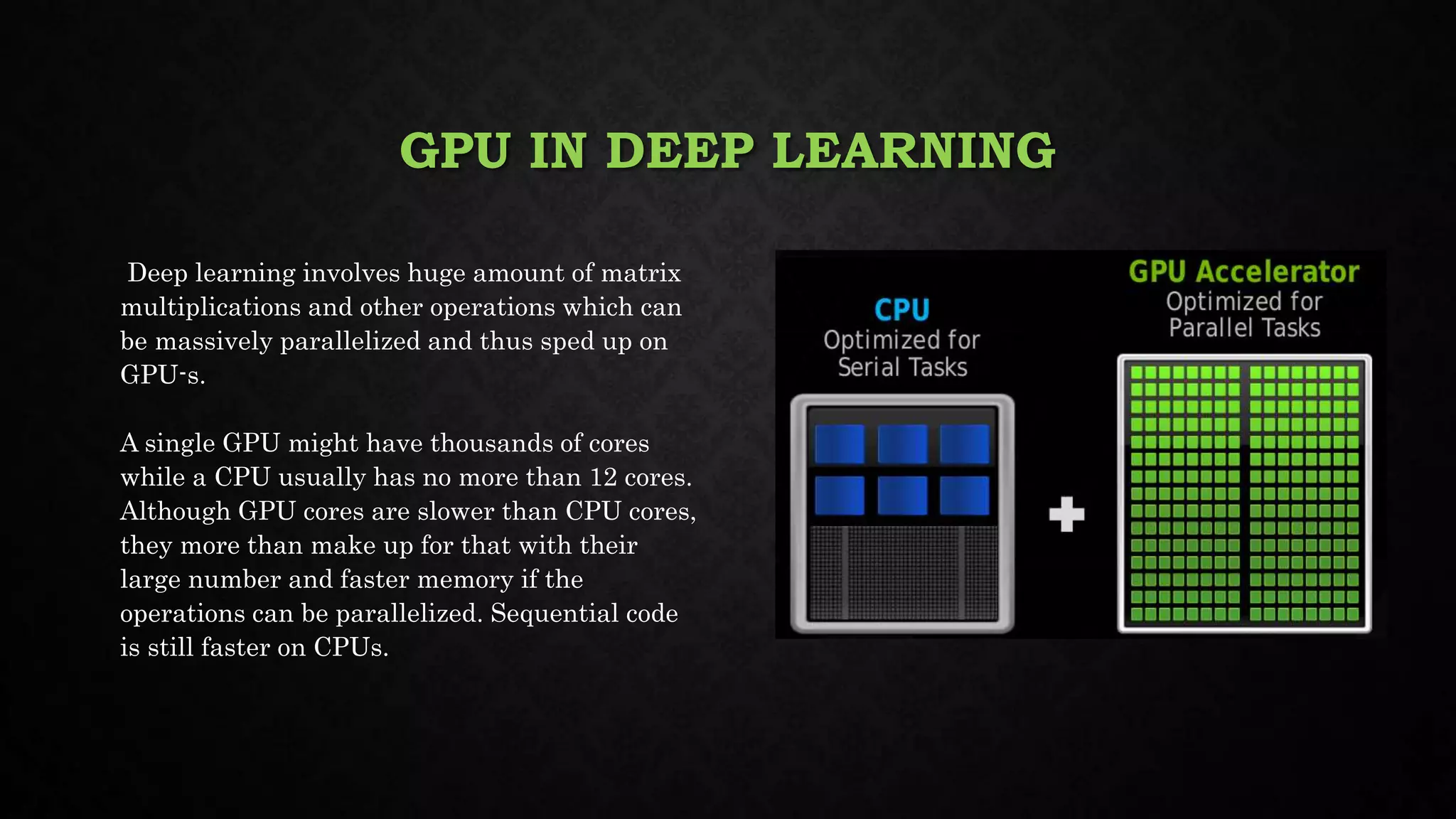
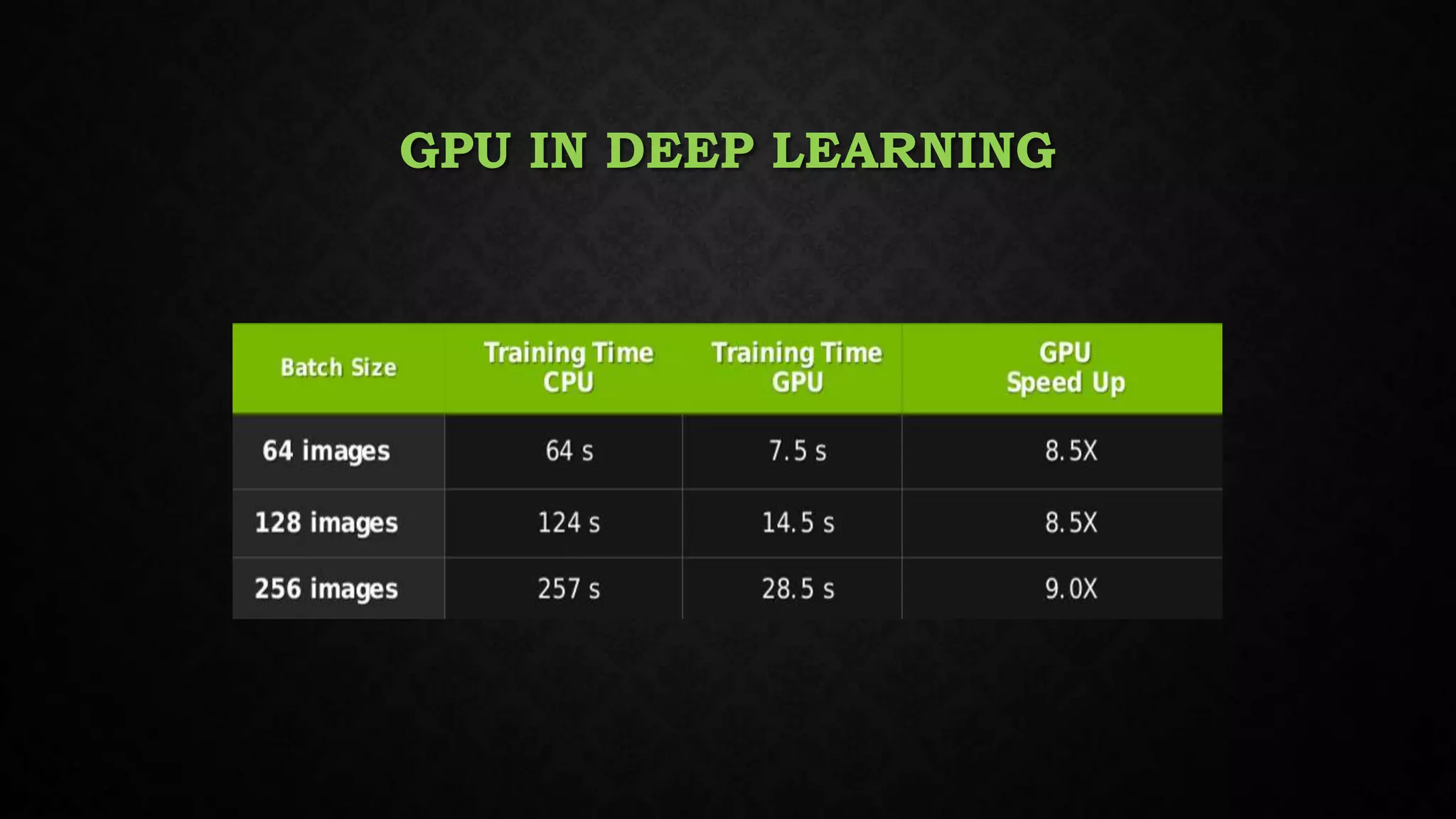
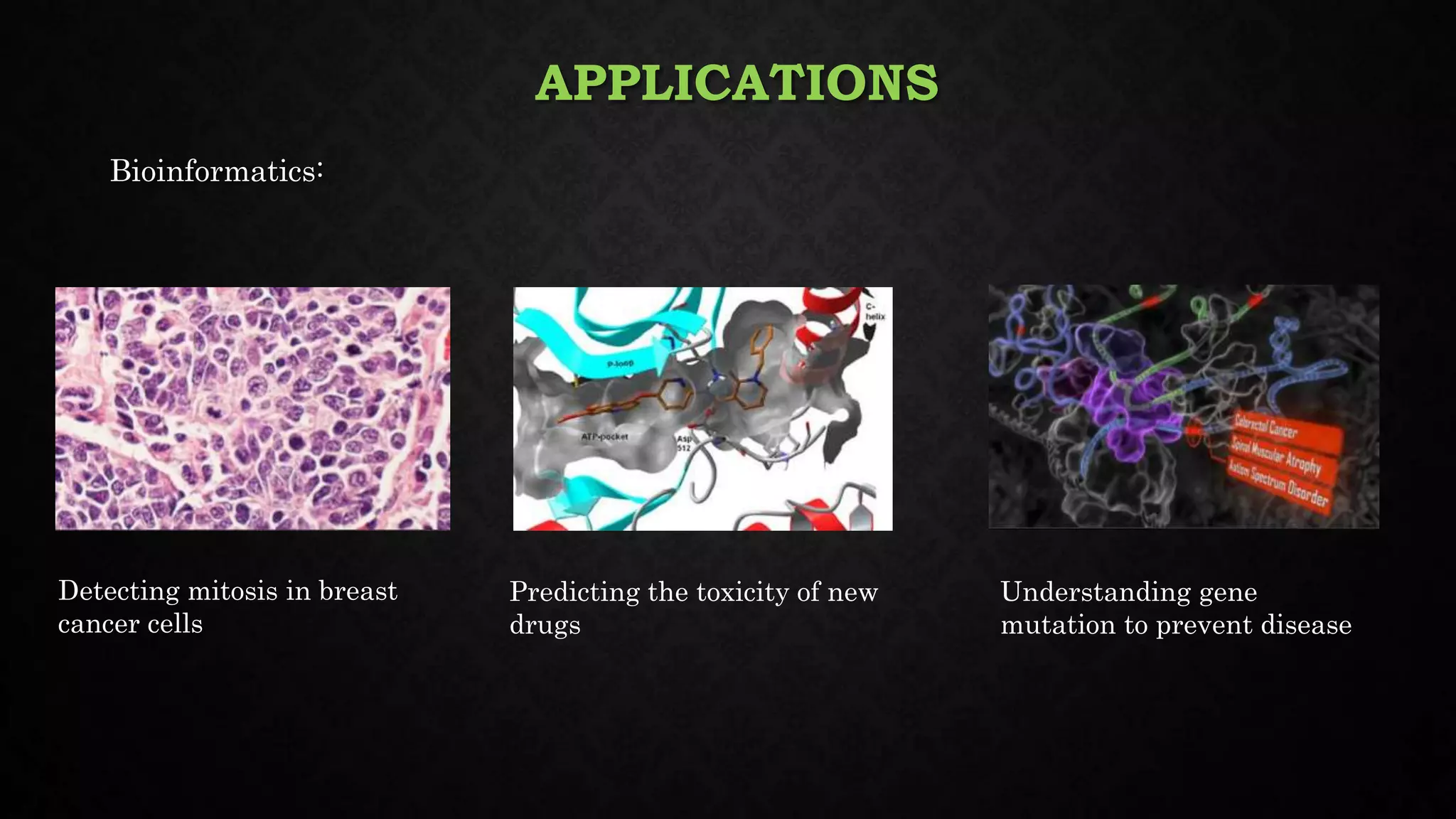
This document discusses deep learning, including its relationship to artificial intelligence and machine learning. It describes deep learning techniques like artificial neural networks and how GPUs are useful for deep learning. Applications mentioned include computer vision, speech recognition, and bioinformatics. Both benefits like robustness and weaknesses like long training times are outlined. Finally, common deep learning algorithms, libraries and tools are listed.











![ALGORITHMS, LIBRARIES AND TOOLS
Platform
● Ersatz Labs - cloud-based deep learning platform [http://www.ersatz1.com/]
● H20 – deep learning framework that comes with R and Python interfaces
[http://www.h2o.ai/verticals/algos/deep-learning/]
Framework
● Caffe - deep learning framework made with expression, speed, and modularity in mind.
Developed by the Berkeley Vision and Learning Center (BVLC)
[http://caffe.berkeleyvision.org/]
● Torch - scientific computing framework with wide support for machine learning
algorithms that puts GPUs first. Based on Lua programming language [http://torch.ch/]
Library
● Tensorflow - open source software library for numerical computation using data flow
graphs from Google [https://www.tensorflow.org/]
● Theano - a python library developed by Yoshua Bengio’s team
[http://deeplearning.net/software/theano/]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/deeplearning-170416134832/75/Deep-Learning-25-2048.jpg)


