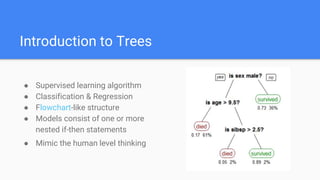
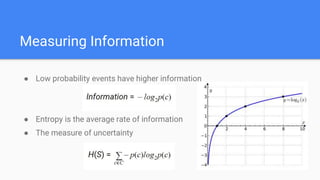
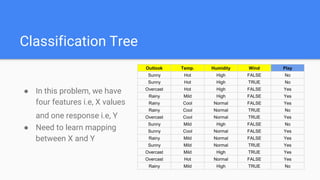
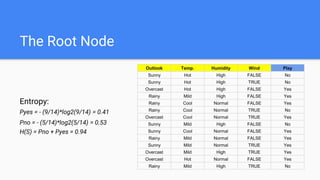
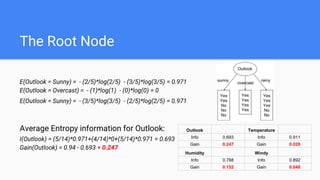
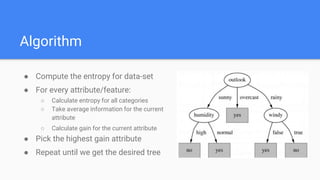
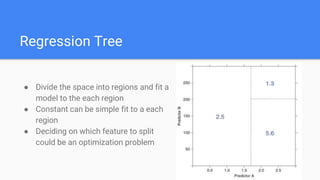
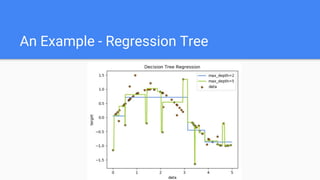
Decision trees are a supervised learning algorithm that can be used for both classification and regression problems. They work by recursively splitting the data into purer subsets based on feature values, building a tree structure. Information gain is used to determine the optimal feature to split on at each node. Trees are constructed top-down by starting at the root node and finding the best split until reaching leaf nodes. Pruning techniques like pre-pruning and post-pruning can help reduce overfitting. While simple to understand and visualize, trees can be unstable and prone to overfitting.