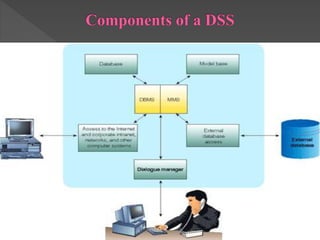
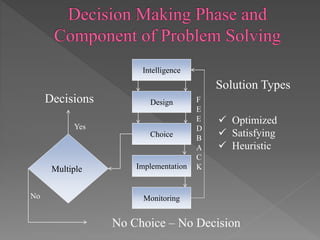
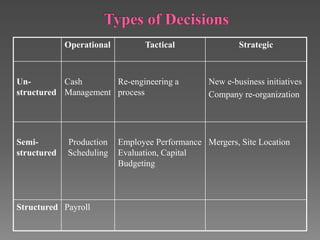
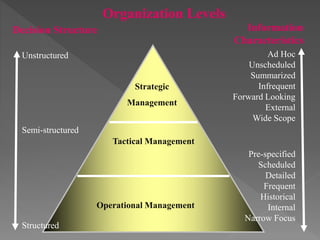
This document outlines the topics to be covered in a lesson on decision support systems (DSS). It will define DSS, describe their characteristics and components, explain different types of decisions and levels in organizations, and approaches to decision making and problem solving. Specifically, it will cover learning objectives, an overview of DSS, the difference between data-driven and model-driven DSS, and how DSS can be used to support structured and unstructured decision making at operational, tactical and strategic levels.