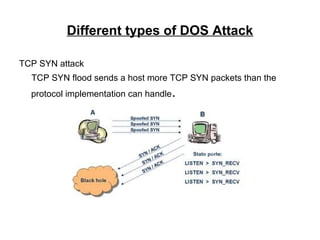
Distributed denial of service (DDOS) attacks aim to make computer or network resources unavailable. DDOS involves using bots, or infected computers controlled by an attacker, to flood a target with traffic. Common DDOS attacks include TCP SYN floods, which overwhelm a target with TCP connection requests, and Smurf attacks, which exploit IP broadcast addressing. Defenses against DDOS include rate limiting, intrusion prevention systems, blackholing traffic, and sinkholing or taking over botnets. Botnets are increasingly rented out to launch large scale DDOS attacks against targets like websites and payment processors.