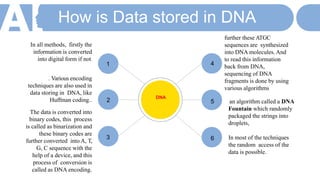
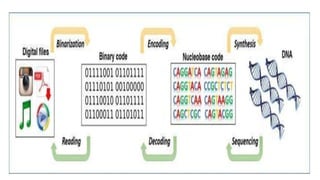
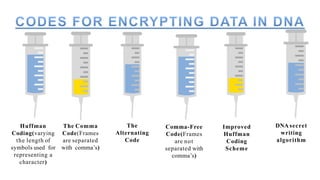
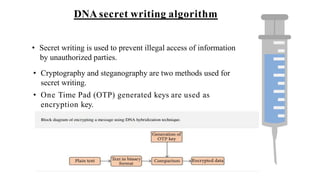
The document discusses innovative data storage using DNA, highlighting its potential to store 215 petabytes in a single gram of DNA, which could last for hundreds of thousands of years. It covers the methods of encoding digital data into DNA sequences, the advantages of this storage technology, and challenges such as high costs and slower access speeds compared to traditional storage. Overall, it emphasizes DNA's capacity for long-term, compact data storage and its implications for future data management.