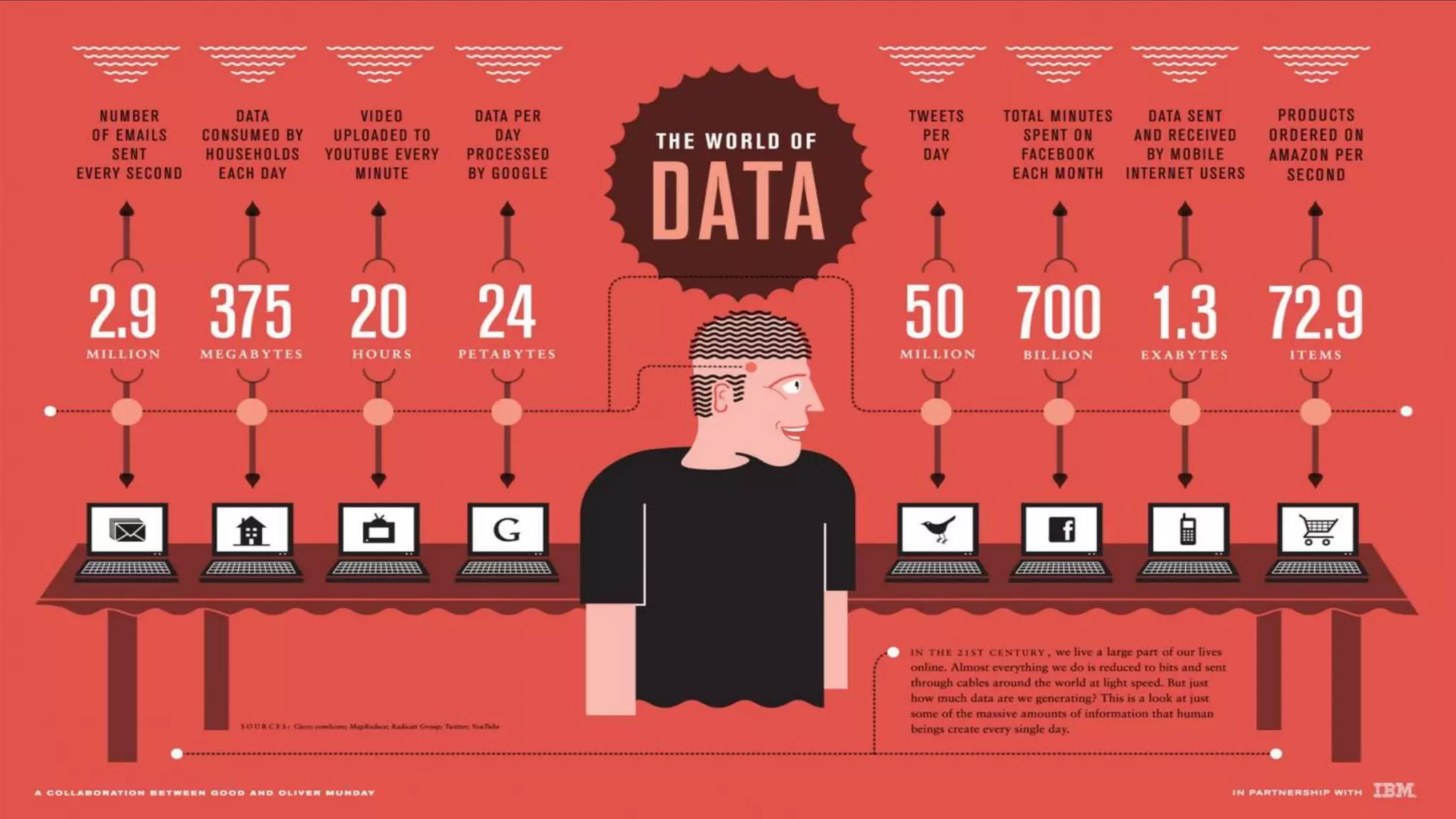
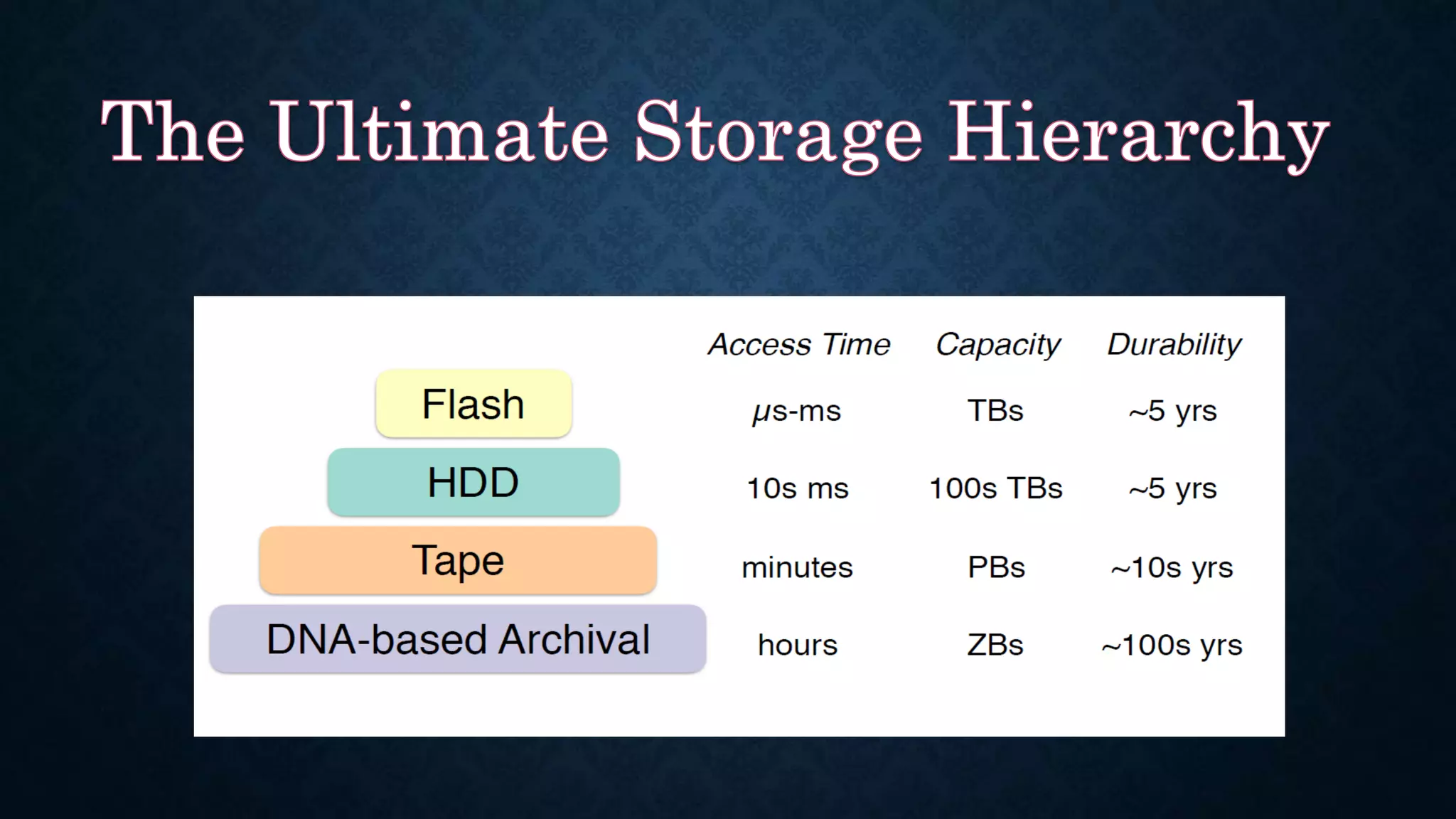
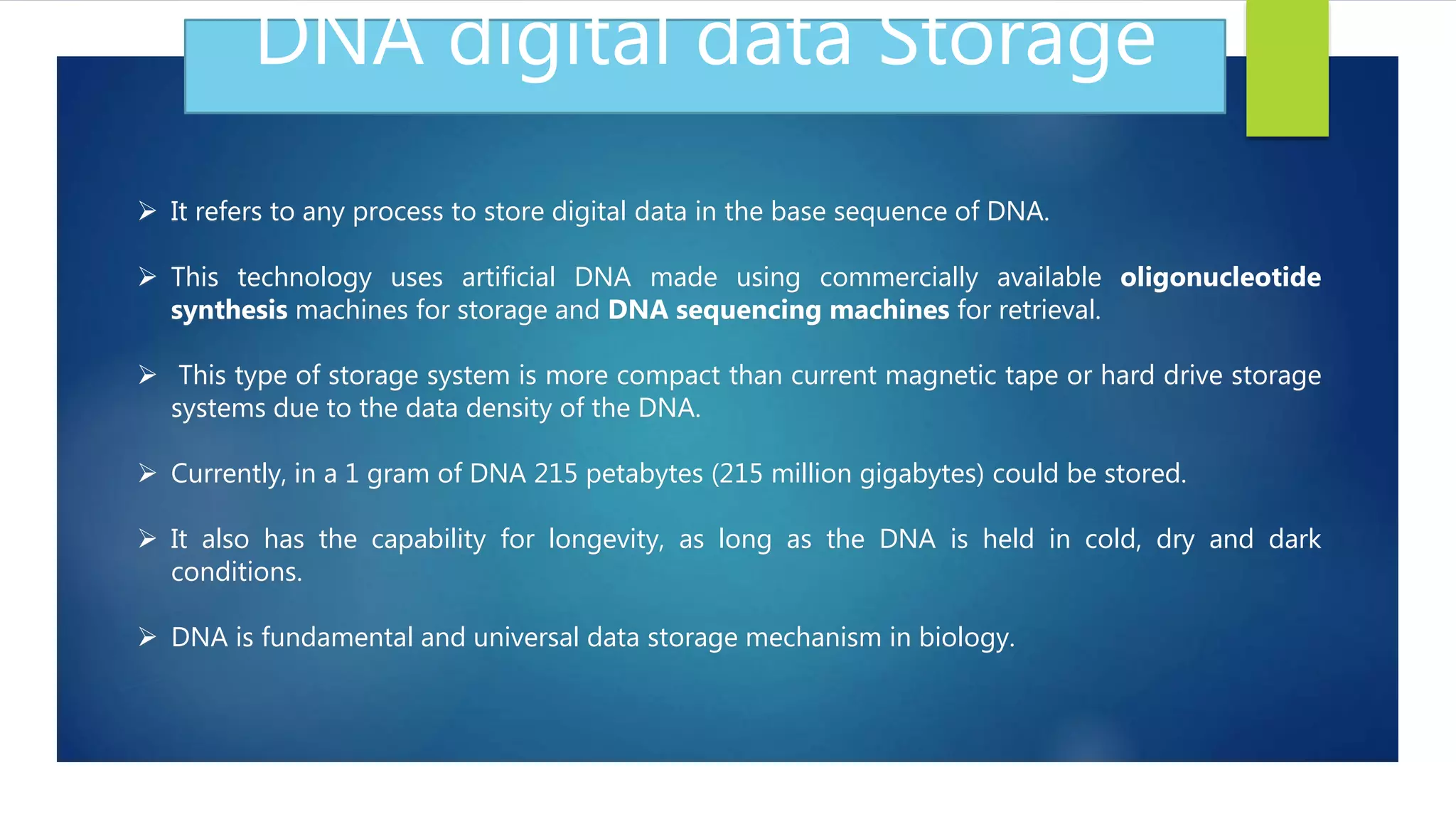
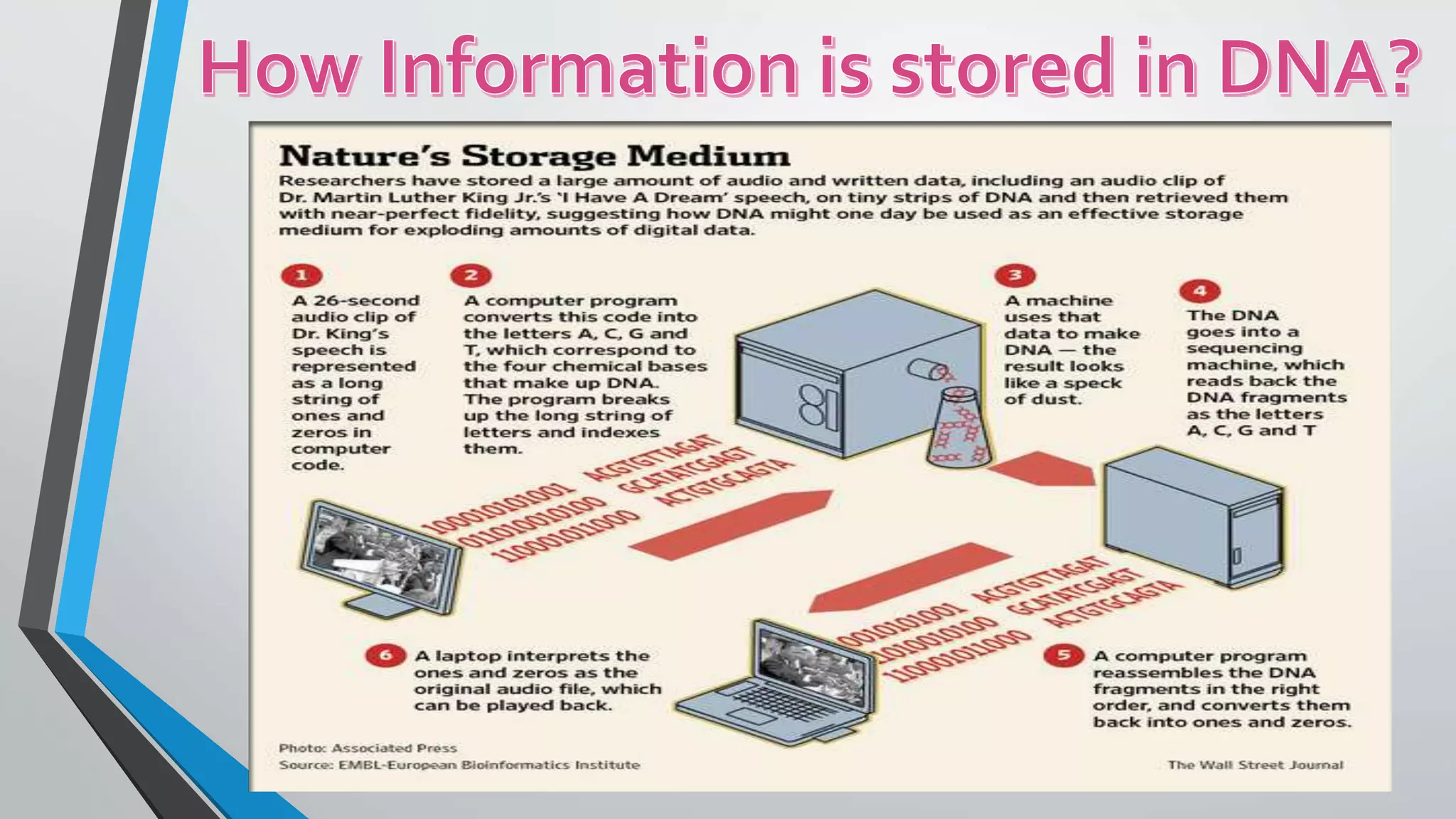
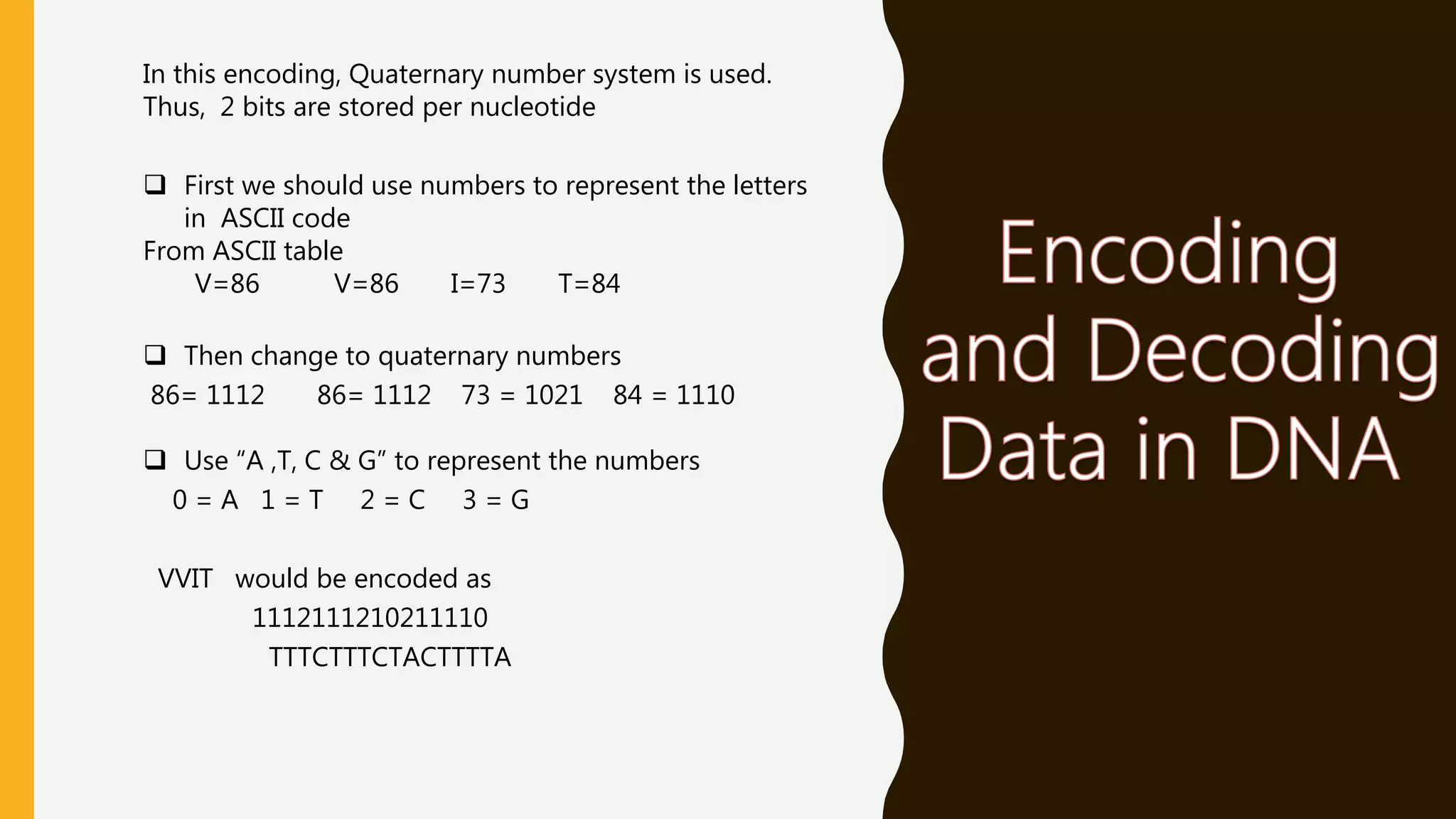
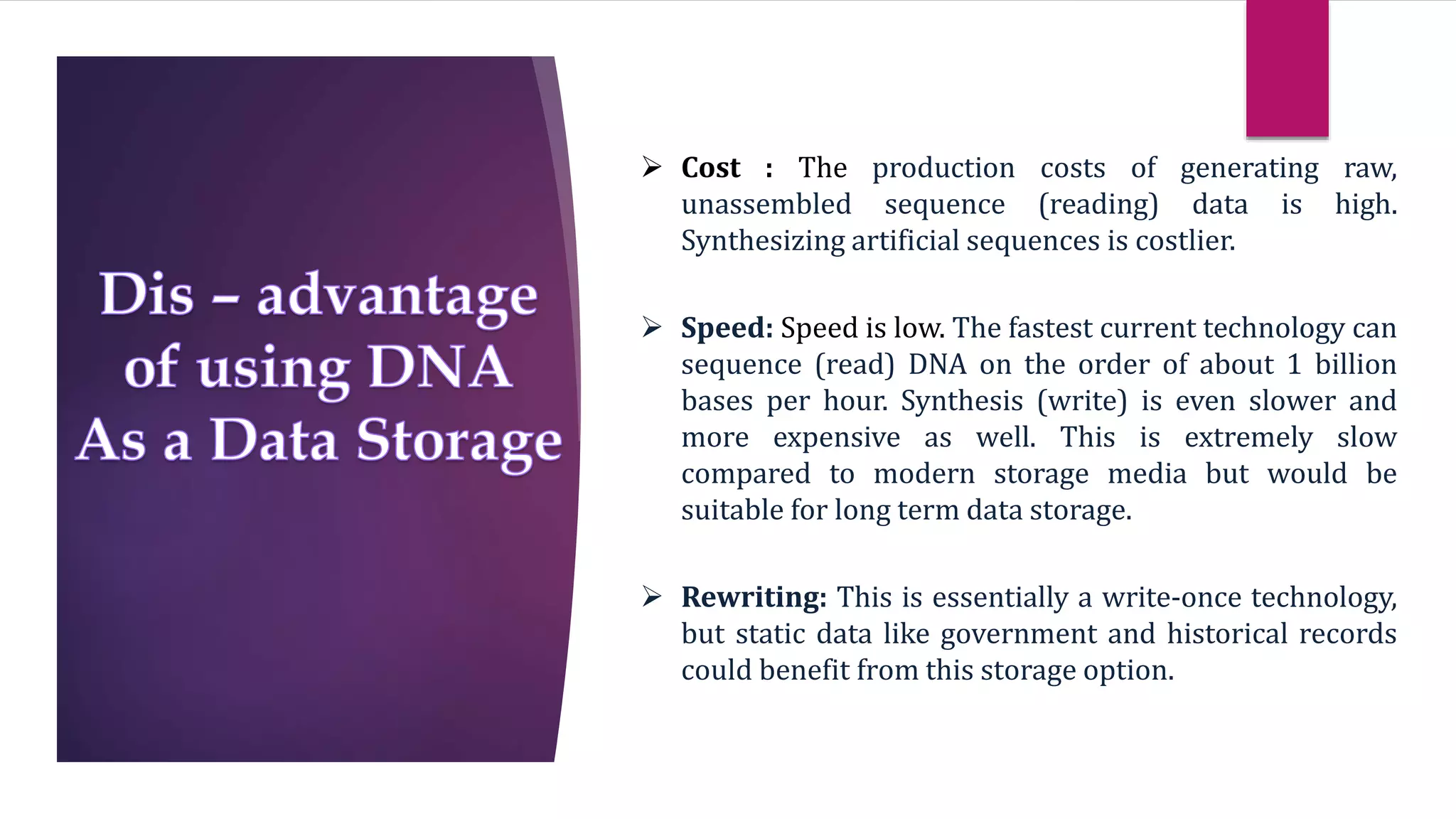
DNA is emerging as a viable alternative for digital data storage due to its high density, stability, and long shelf life, enabling the storage of vast amounts of data in compact spaces. Current conventional storage methods face limitations such as environmental pollution, data loss, and capacity constraints, making DNA's unique properties advantageous for future data archival. While the cost and speed of DNA synthesis and sequencing currently pose challenges, the potential for long-term data retention positions DNA technology as a solution for the growing demands of data storage.