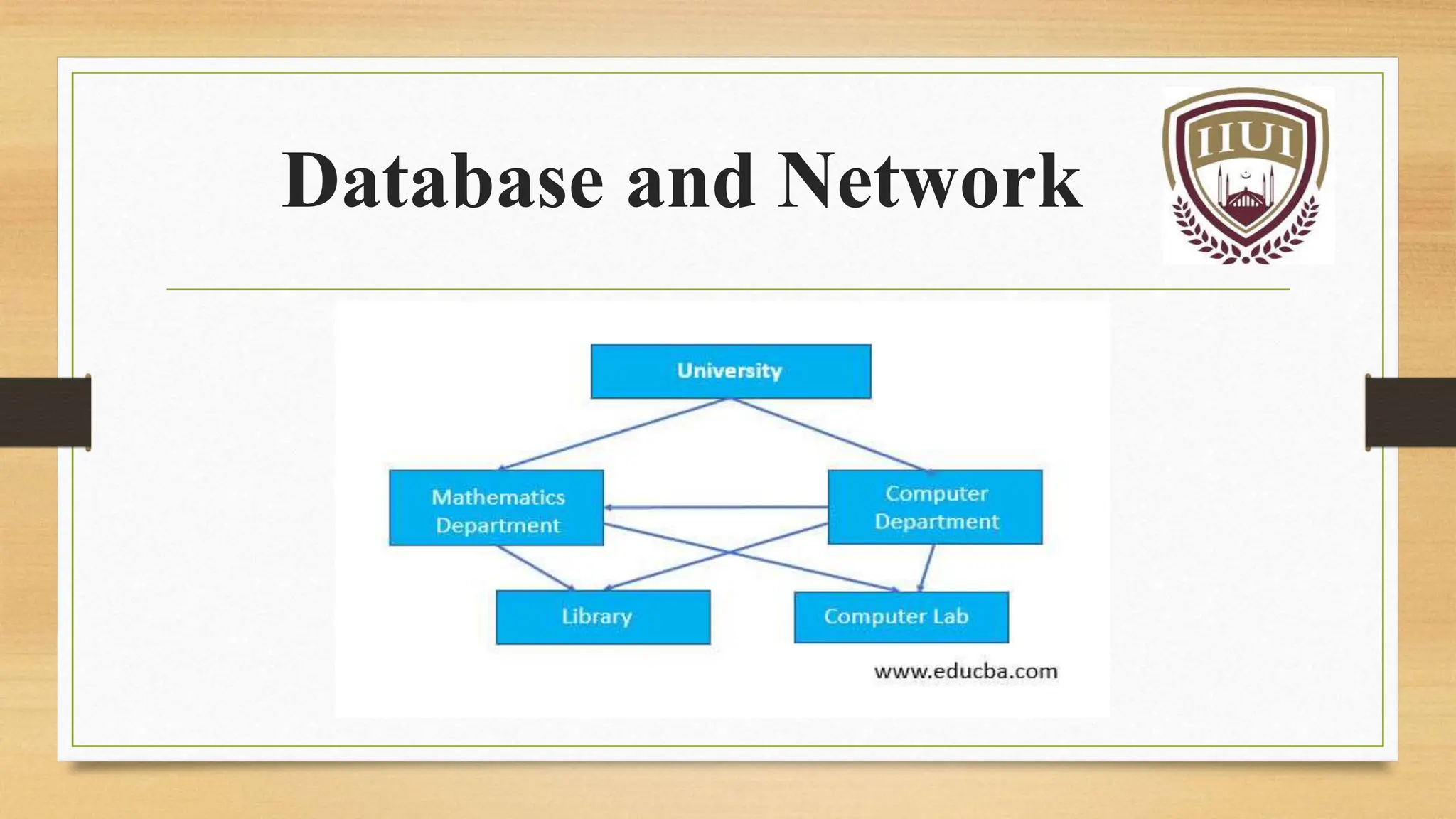
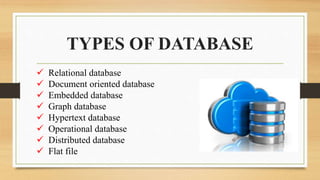
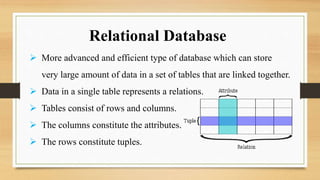
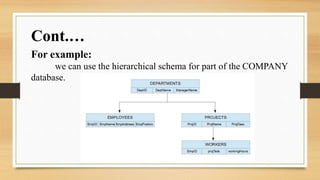
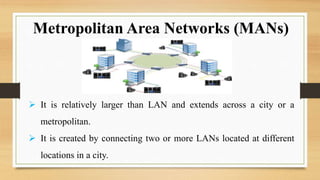
The document presents an overview of databases and computer networks, detailing their types, advantages, and disadvantages. Key database types include relational, hierarchical, and operational databases, while computer networks range from personal to wide area networks. The importance of databases and networks in managing and sharing information efficiently is emphasized.