The document discusses different types of computer networks:
1) Local Area Network (LAN) connects computers together within a limited area like a home, school or office using technologies like Ethernet or Wi-Fi.
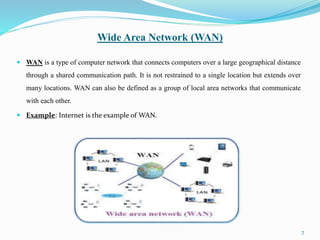
2) Wide Area Network (WAN) connects computers over a large geographical distance through shared communication paths like the Internet.
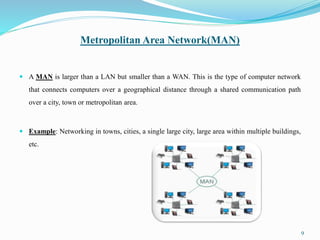
3) Metropolitan Area Network (MAN) is larger than a LAN but smaller than a WAN, connecting computers over a city or town through fiber optic cable.
4) Personal Area Network (PAN) is the most basic type of network, centered around an individual's workspace to connect devices within 10 meters like a phone, tablet and printer.