Embed presentation
Downloaded 89 times






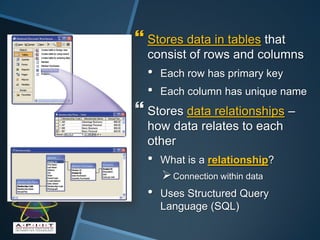










This document provides an overview of database management concepts. It discusses data security, recovery utilities, popular data models including relational, object-oriented, and multi-dimensional databases. It also discusses structured query language, data warehousing, web databases, and the roles of database analysts and administrators.
















