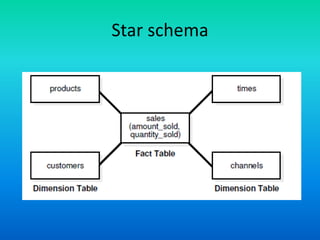
The document elaborates on the concept of a star schema, a dimensional modeling approach for organizing data in a data warehouse that separates data into facts and dimensions. It provides insights into how to derive star schemas from entity-relationship models, with a focus on sales data management, including entities such as customers, products, and sales transactions. Key features and advantages of star schemas include structural simplicity, improved query performance, and easier data retrieval despite some limitations in analysis flexibility.