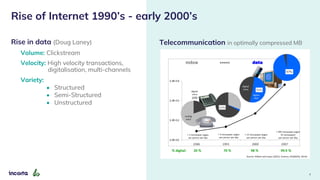
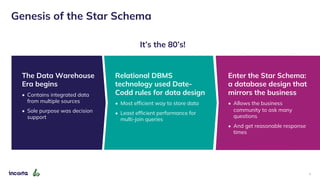
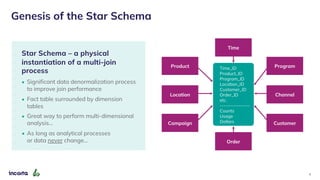
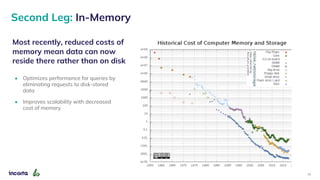
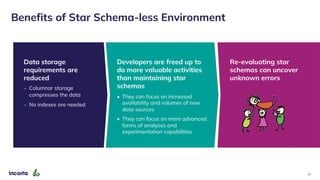
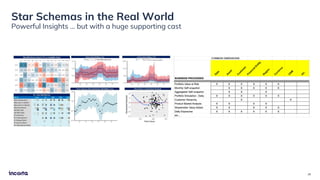
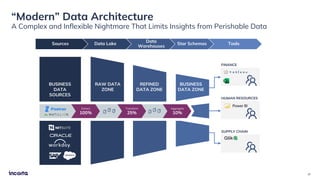
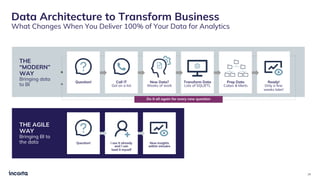
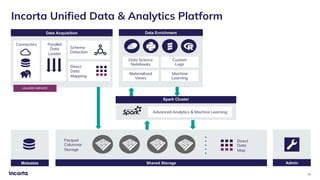
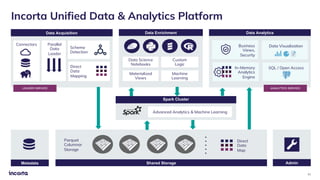
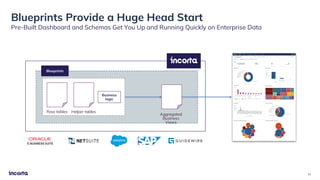
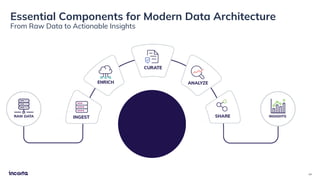
The webinar discusses the decline of the star schema in data warehousing, attributing its inefficiency to the increasingly dynamic nature of data and the emergence of new technologies. It highlights the benefits of transitioning to a star schema-less environment, which enables greater flexibility, simplifies maintenance, and enhances analytical capabilities. The session concludes with practical steps for organizations to migrate from traditional star schemas to more agile data architectures.