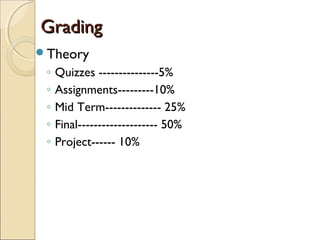
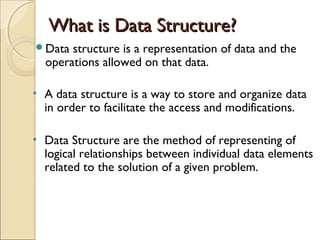
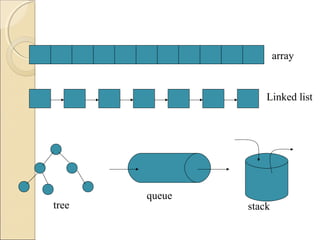
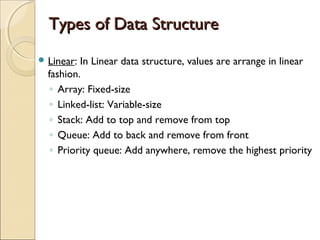
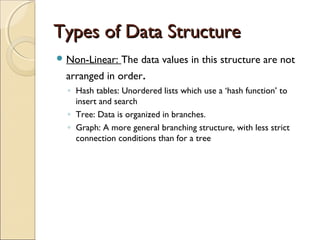
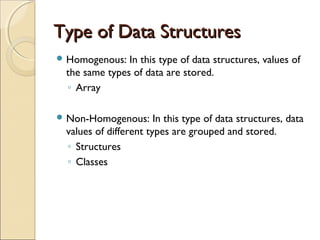
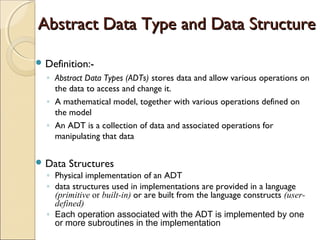
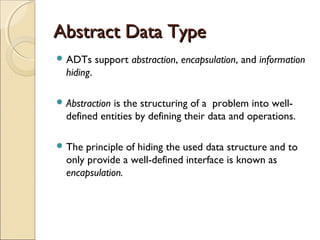
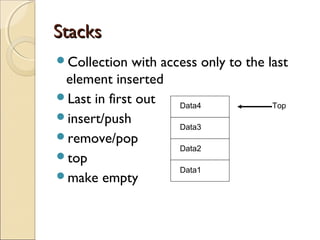
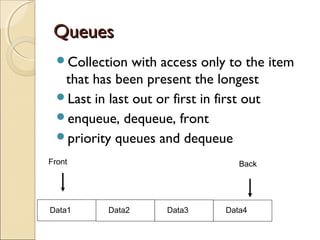
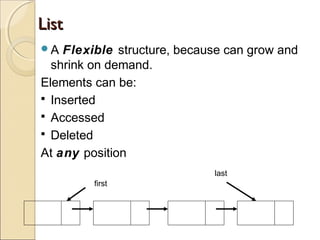
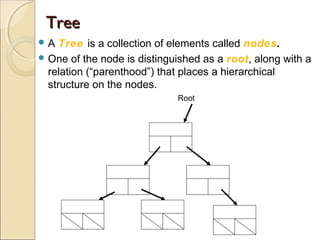
The document provides information about the Data Structures CS-203 course, including textbooks, topics covered like recursion, stacks, queues, lists, trees, sorting, searching and graphs. It will be graded based on quizzes, assignments, mid-term, final and project. An introduction to data structures and abstract data types is given, defining them and describing common linear and non-linear structures like arrays, linked lists, trees, queues and stacks. The relationship between abstract data types and data structures is also explained.