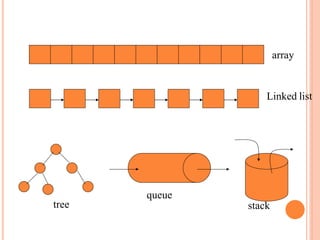
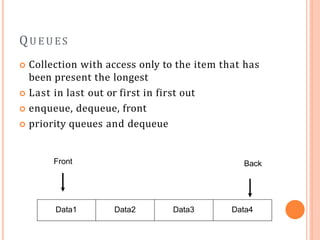
The document discusses the objectives, outcomes, and content of a course on data structures and algorithms. The main objective is to teach students how to select appropriate data structures and algorithms for solving real-world problems. Students will learn commonly used data structures like stacks, queues, linked lists, trees, and graphs. They will also learn basic algorithms and how to analyze computational complexity. The course will cover topics like recursion, sorting, searching, and hashing. Student performance will be evaluated through quizzes, assignments, projects, and exams.