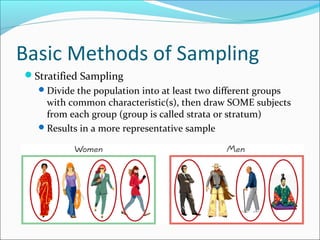
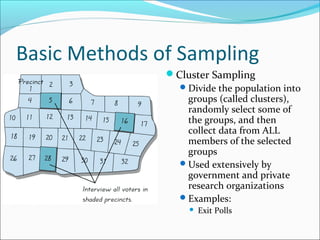
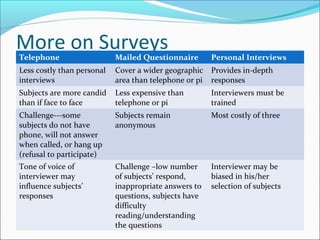
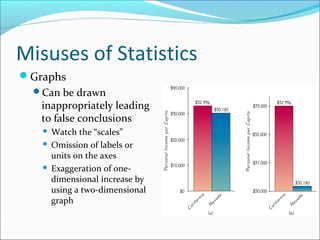
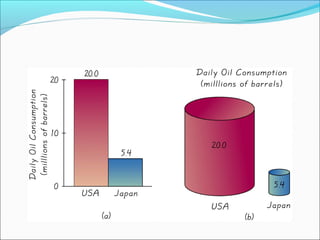
This document discusses different sampling techniques and types of studies. It identifies five basic sampling techniques: random sampling, systematic sampling, convenience sampling, stratified sampling, and cluster sampling. It also distinguishes between observational studies, where the researcher observes without interacting with subjects, and experimental studies, where the researcher manipulates variables and interacts with subjects. Finally, it outlines how statistics can be used to describe data, test hypotheses, and make estimates, but also how they can be misused through things like small or non-representative samples, biased questions, omitted data, and implying causation without evidence.