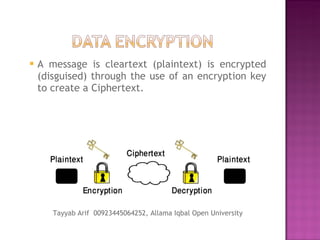
The document provides an overview of data encryption, highlighting its definition, methods, and algorithms. It explains the difference between symmetric and asymmetric encryption, details the widely used Data Encryption Standard (DES), and introduces public key cryptosystems. The text also outlines the processes of transcription and substitution in encryption, emphasizing security through the use of keys.







![Tayyab Arif Allama Iqbal Open Unviersity Pakistan Book: Telecommunication Primer BS(cs) 7 th Semster Mob: 00923445064252 [email_address] www.youtube.com/tayyab8632](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dataencryption-100603124253-phpapp01/85/Data-encryption-Description-DES-12-320.jpg)