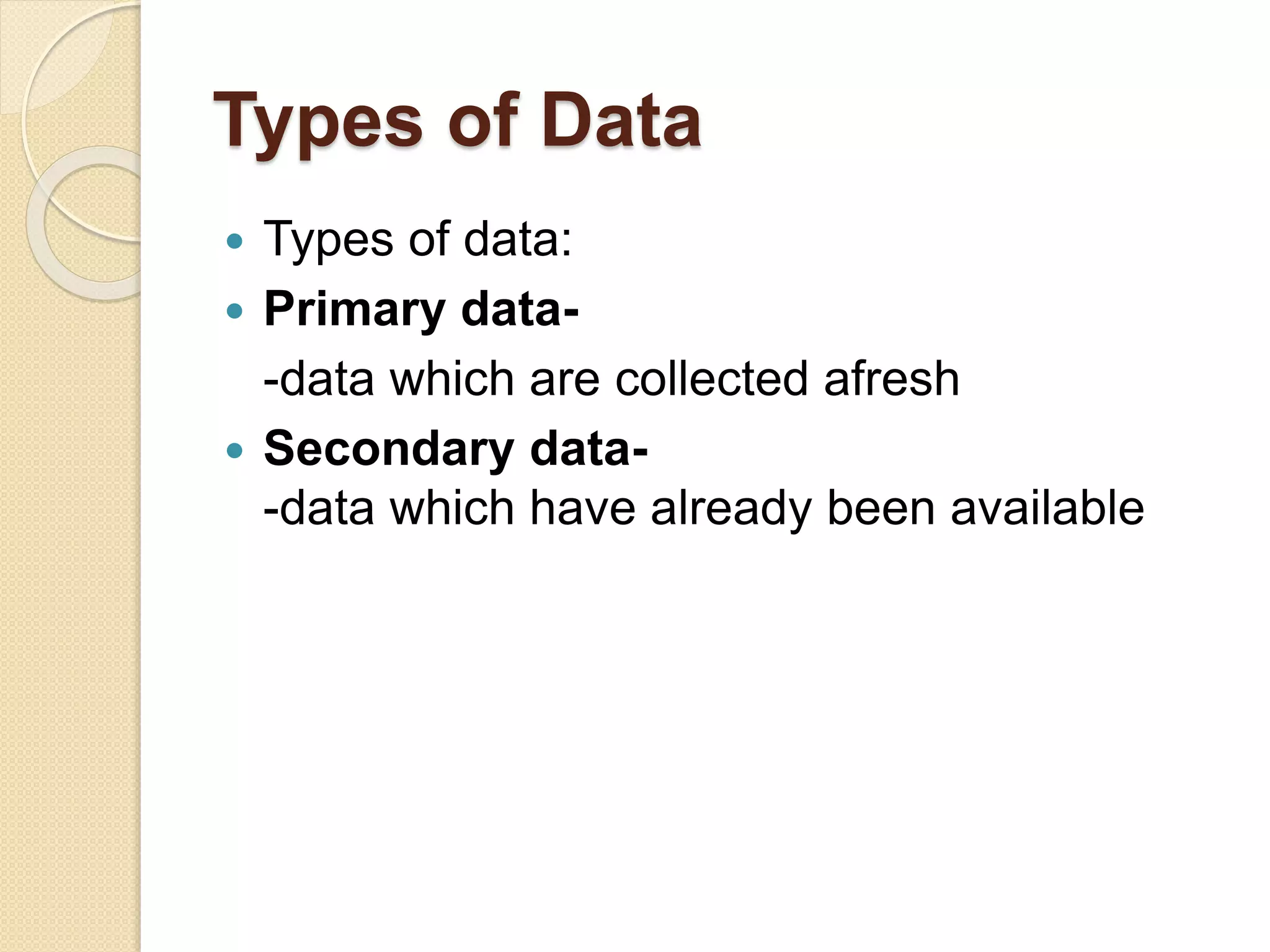
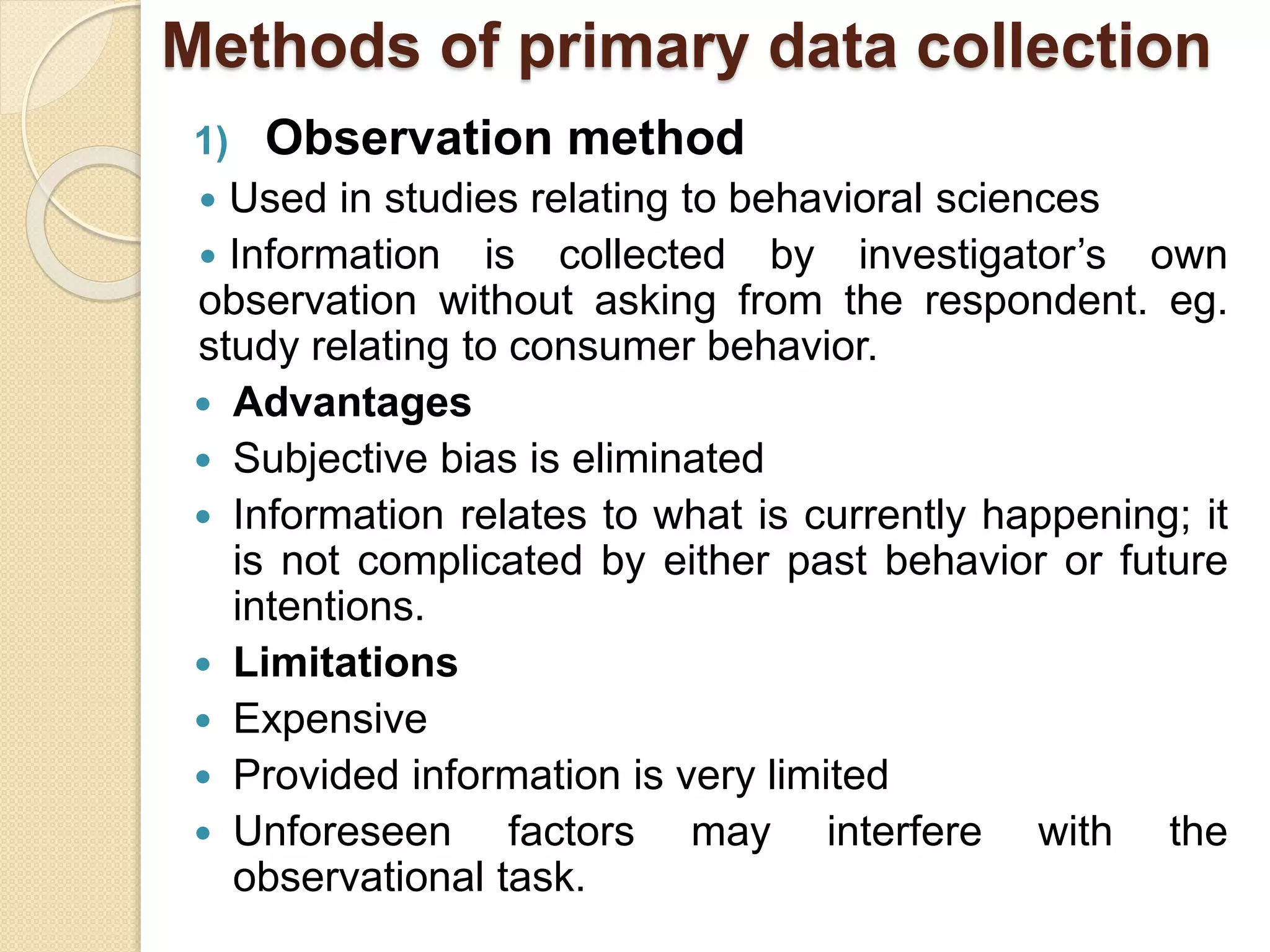
This document discusses various methods for collecting primary and secondary data. It outlines several methods for collecting primary data, including observation, interviews, questionnaires, schedules, warranty cards, audits, consumer panels, and mechanical devices. It also discusses some key advantages and disadvantages of each primary data collection method. Additionally, the document notes that secondary data can come from published sources like government publications, journals, and reports, as well as unpublished sources from individuals and organizations. Researchers must carefully evaluate whether secondary data is suitable for their specific research needs.