Embed presentation


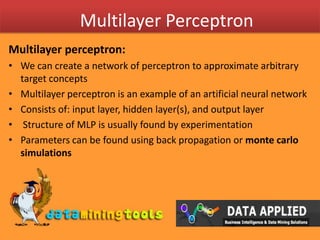
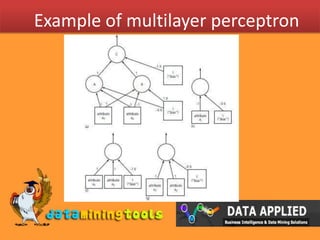





Perceptrons can perform linear classification by using hyperplanes to divide instances belonging to different classes in instance space. Multilayer perceptrons can approximate arbitrary target concepts by creating a network of perceptrons with an input, hidden, and output layer, with the structure found through experimentation. When using montecarlo simulations to determine parameters that minimize the error metric of 1/2(y-f(x))^2, random weight vectors are distributed and sampled to choose those that minimize errors, repeating until convergence to the optimal parameter values.










