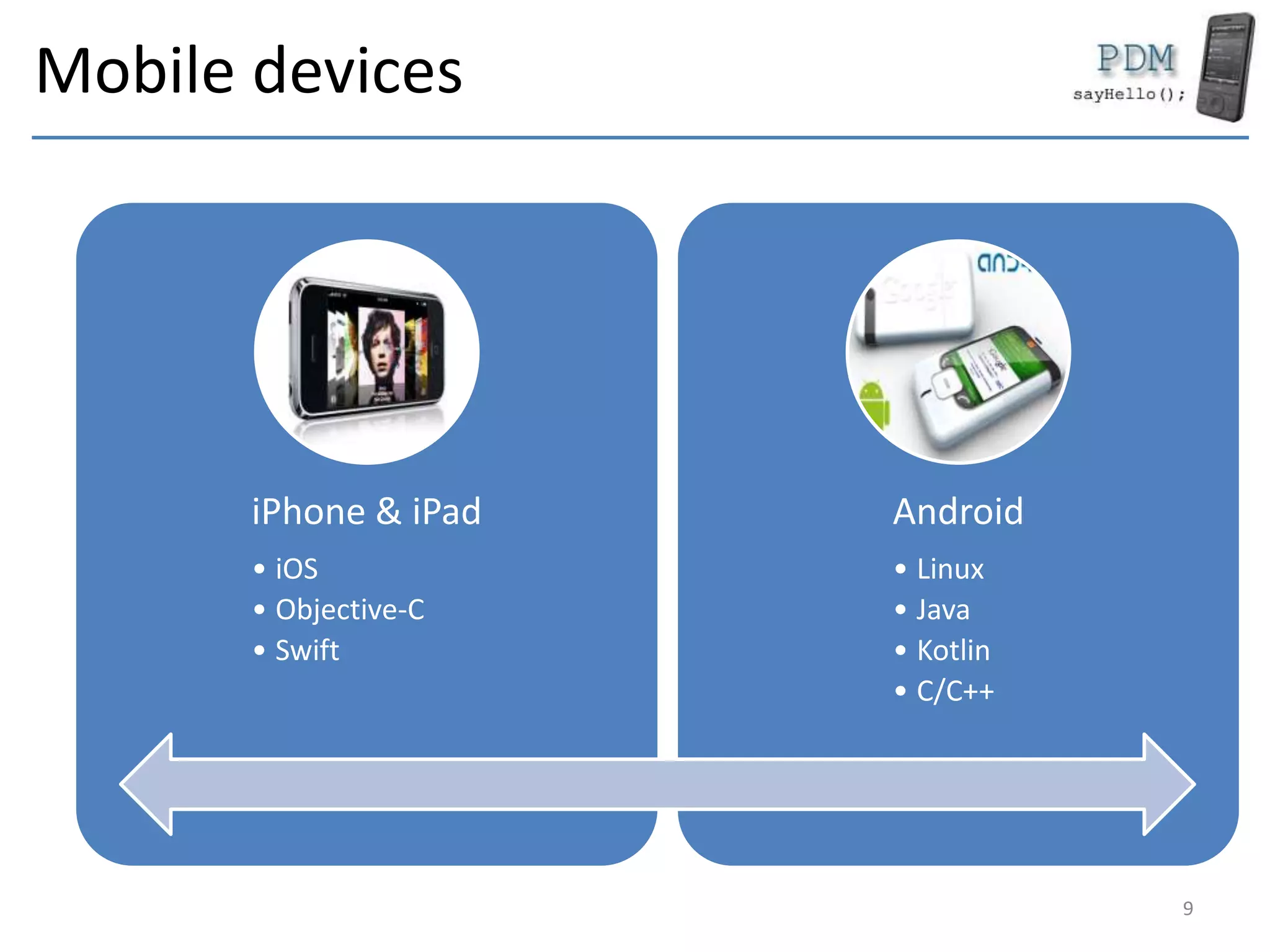
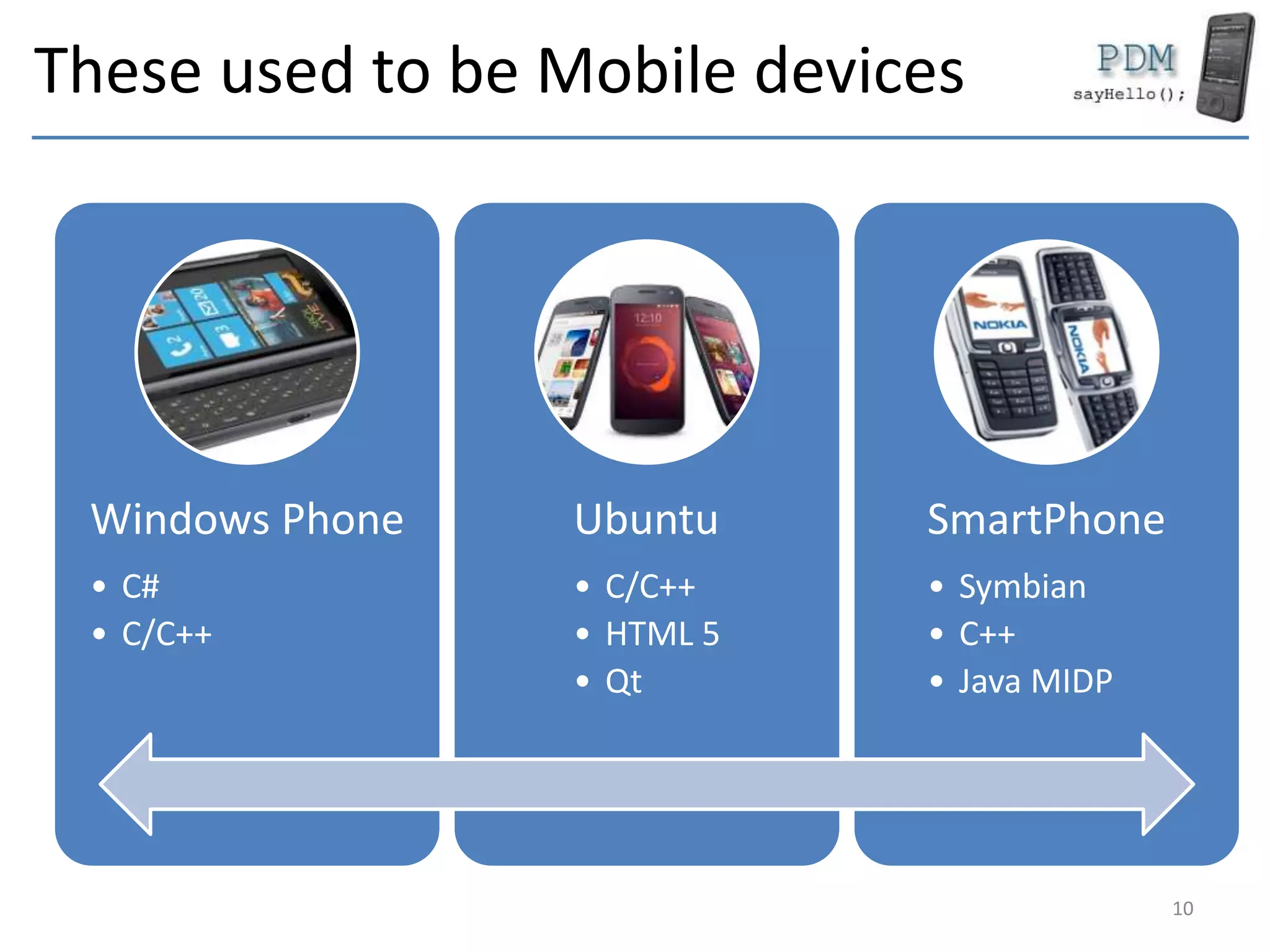
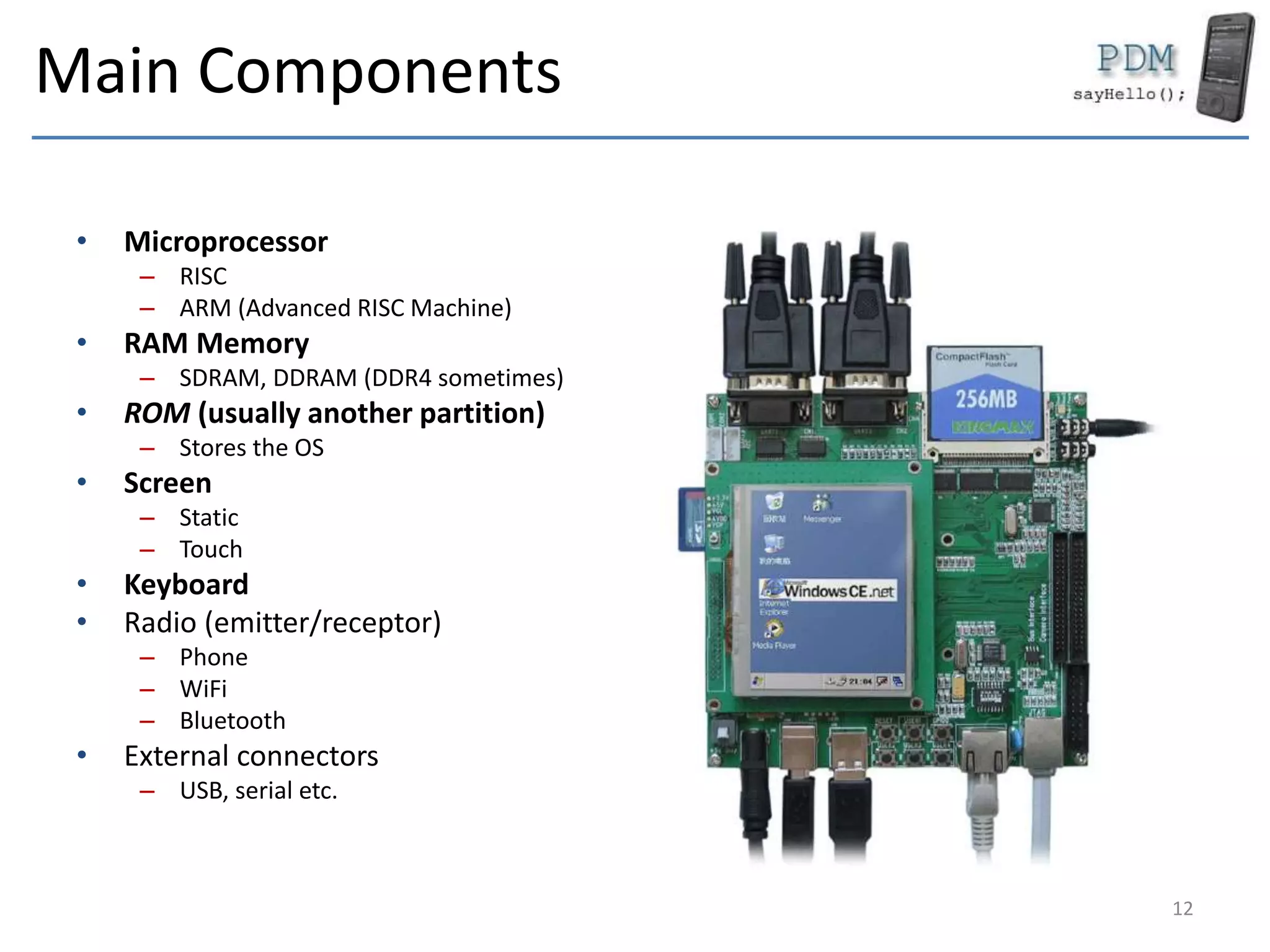
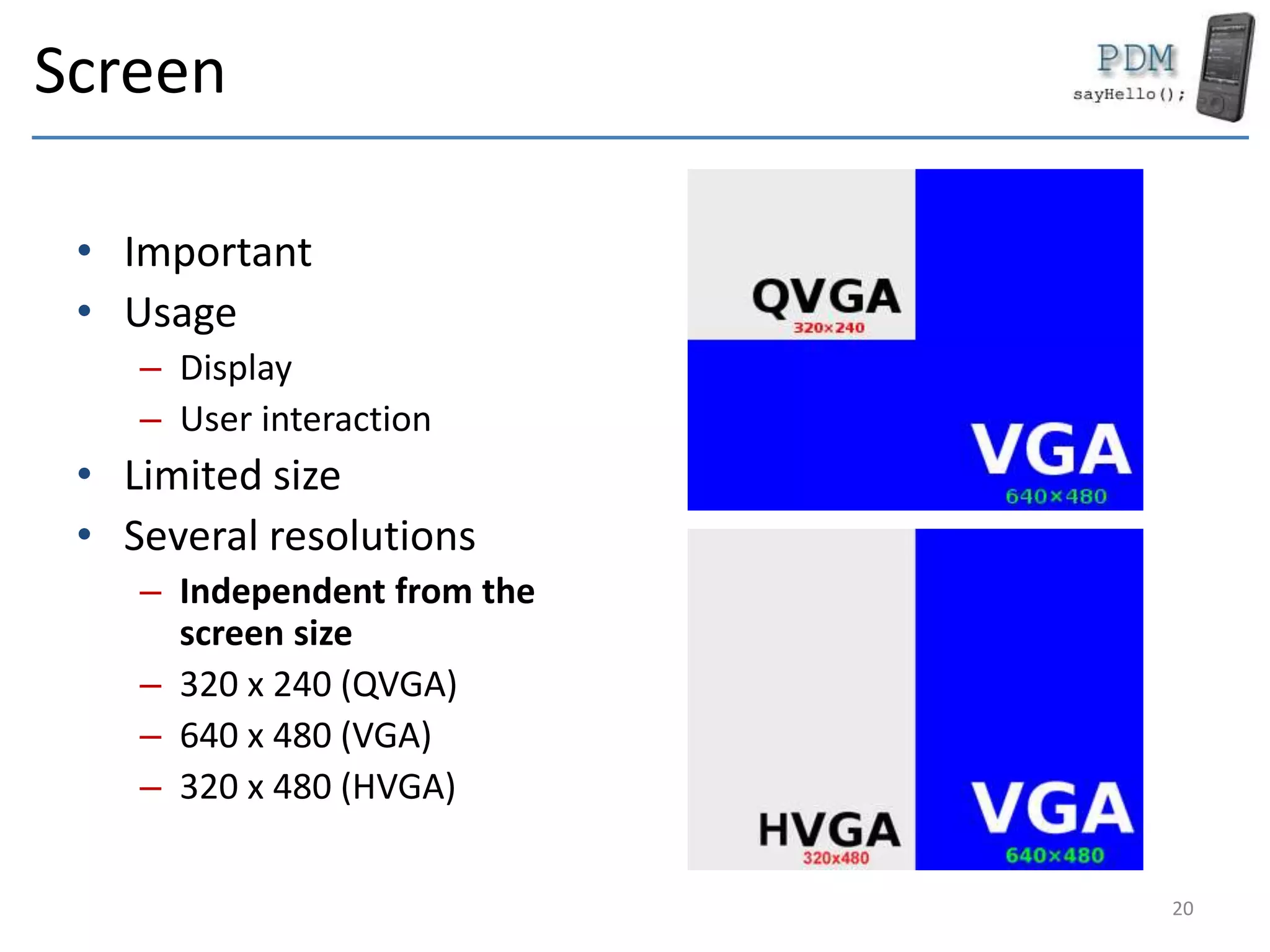
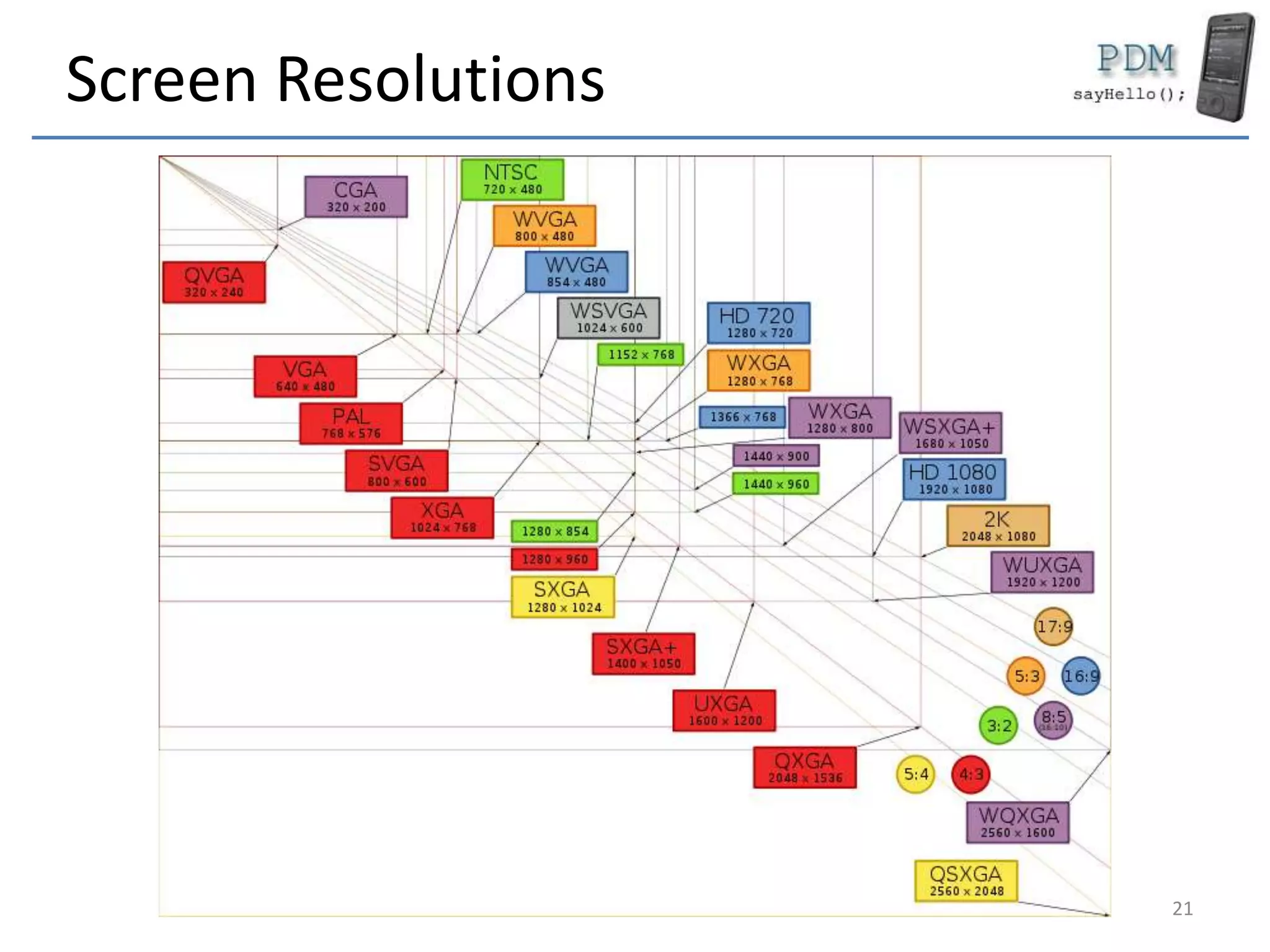
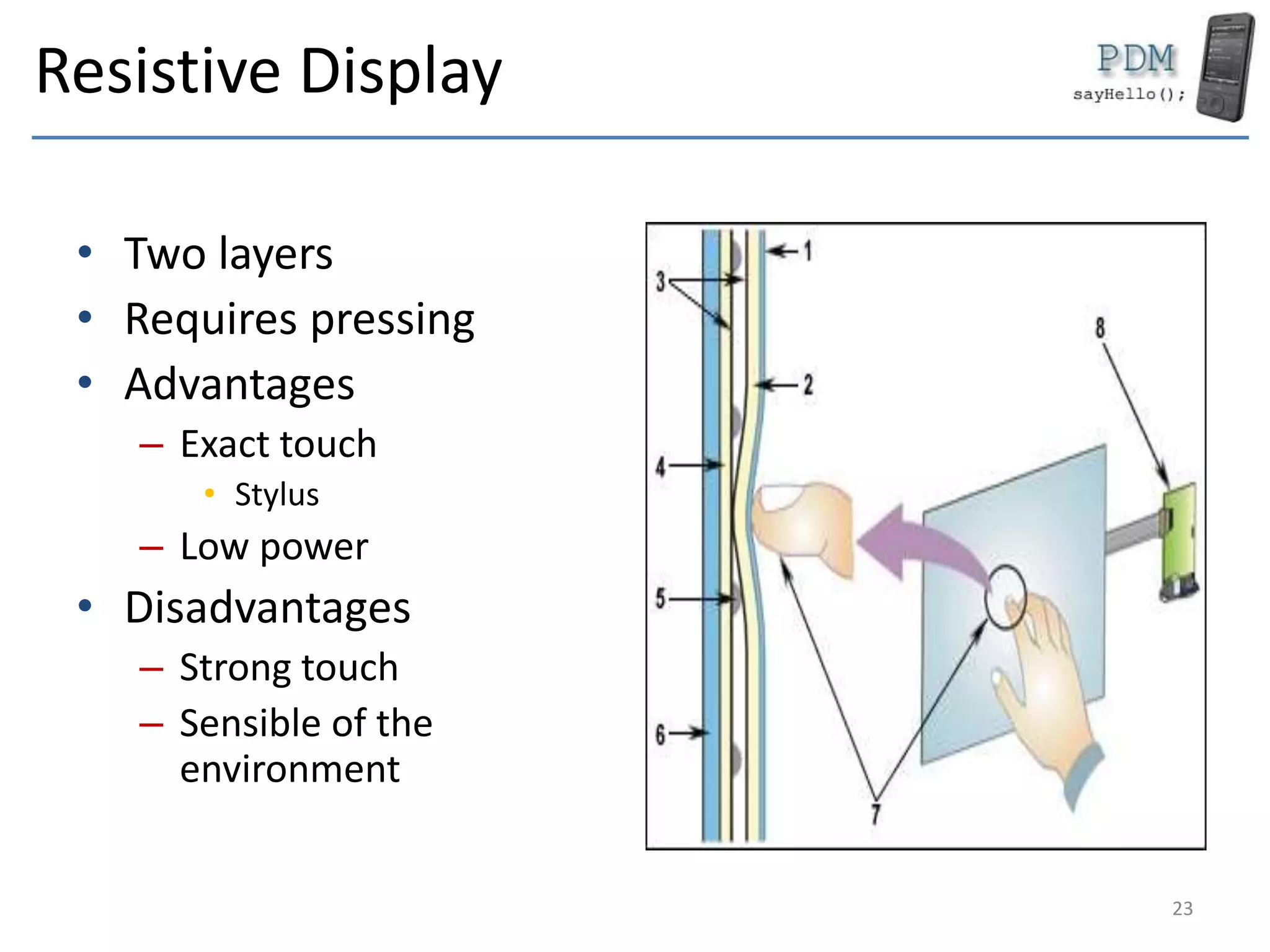
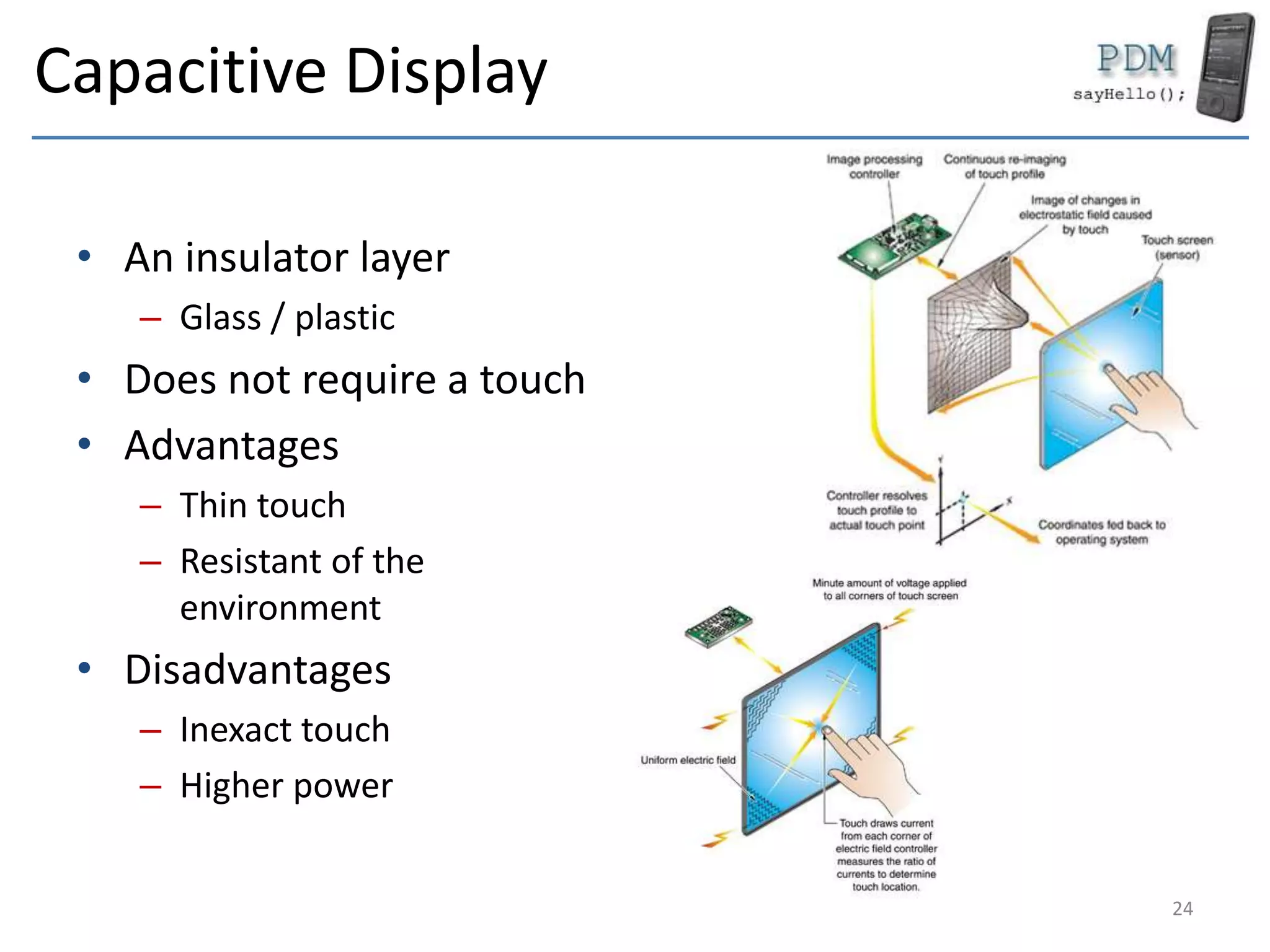
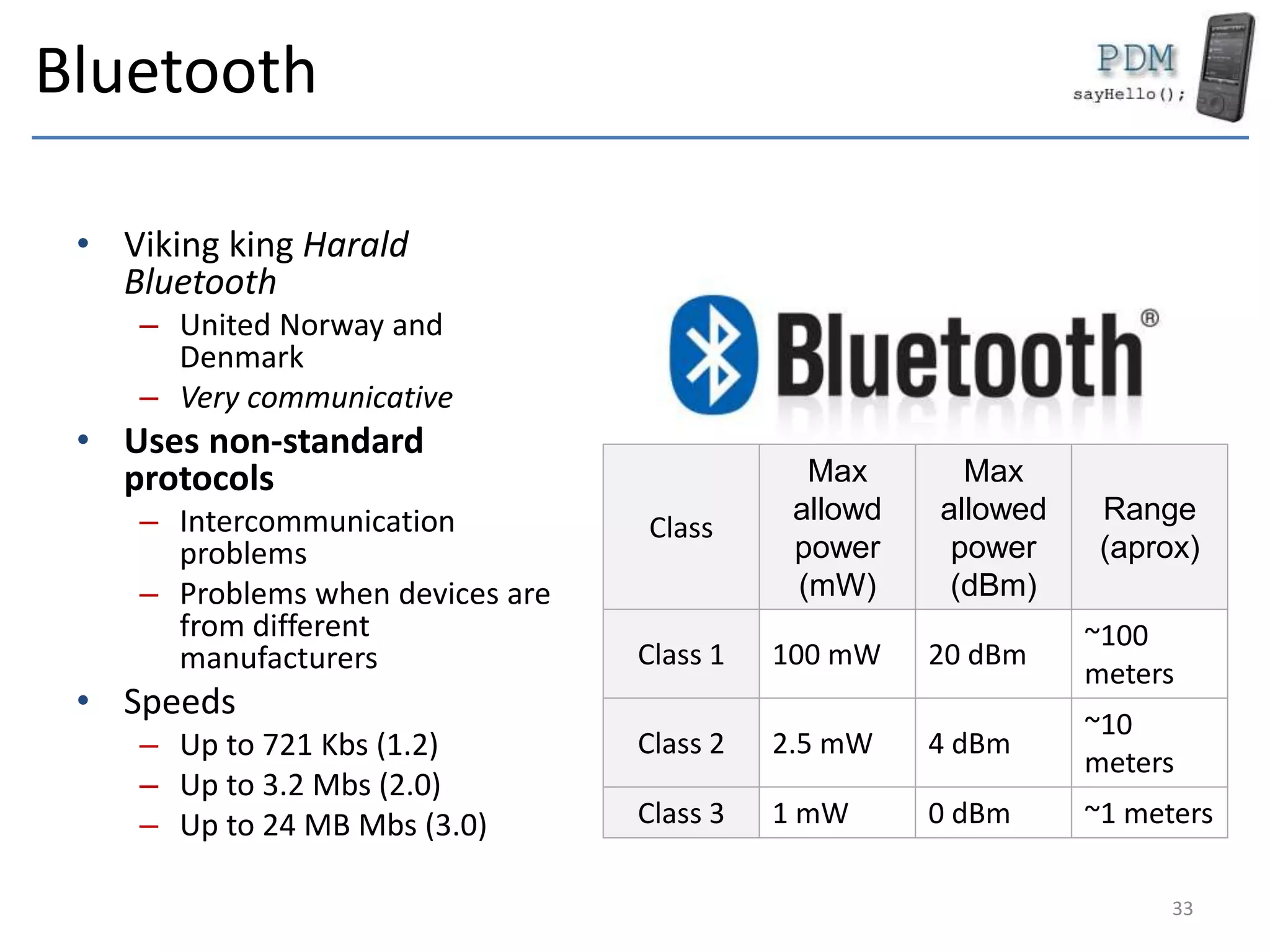
This document provides an overview of mobile devices and their components. It discusses the typical hardware in mobile devices including microprocessors, memory, storage, screens, keyboards and radios. It covers the operating systems and programming languages used in major mobile platforms like Android and iOS. The document also examines aspects like screen resolutions, touchscreen technologies, sensors and limitations of mobile devices compared to computers.