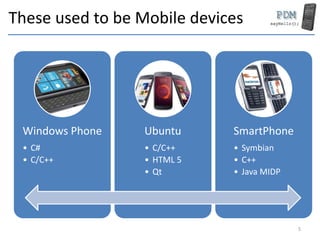
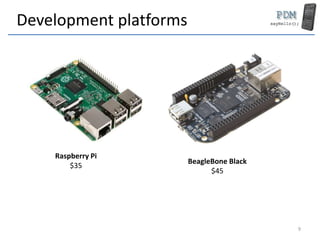
This document provides an overview of the hardware components and software platforms used in mobile devices. It discusses the main processors used (ARM, RISC), memory types (RAM, SSD), display technologies (touchscreens, resolutions), connectivity radios (WiFi, Bluetooth), operating systems (Android, iOS, Windows), and programming languages (Java, Swift, C++). It also covers other components like sensors, storage, and development boards for prototyping mobile applications.