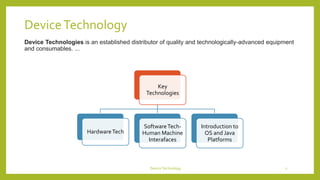
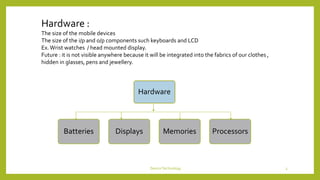
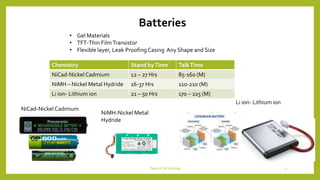
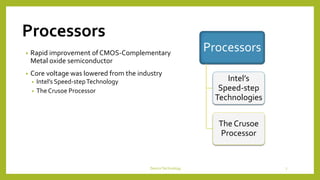
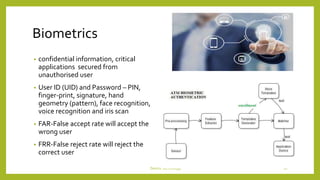
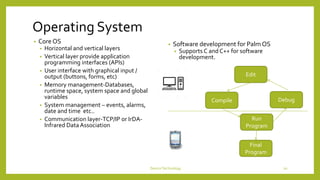
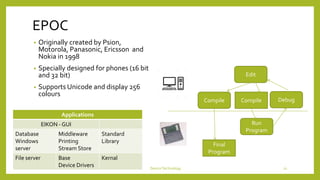
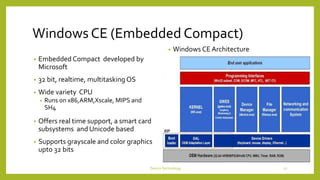
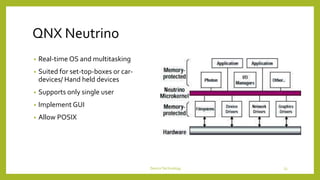
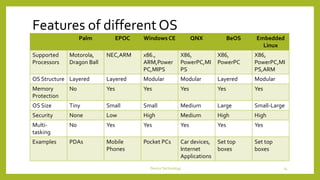
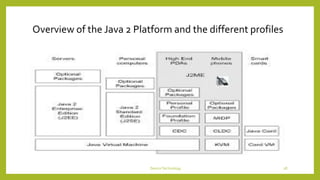
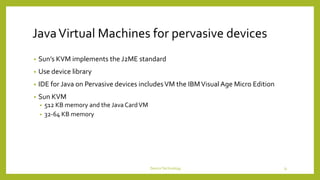
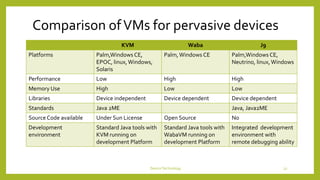
This document discusses device technologies and operating systems for mobile devices. It covers hardware components like batteries, displays and processors. It also covers software technologies like human-machine interfaces, operating systems for mobile devices like Palm OS, Windows CE, EPOC and Java platforms. It provides comparisons of different operating systems and their features for mobile and embedded systems.