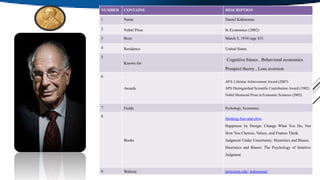
Daniel Kahneman is an Israeli-American psychologist and economist noted for his work on cognitive biases and behavioral economics. He received the Nobel Memorial Prize in Economic Sciences in 2002 for integrating insights from psychological research into economic science, especially regarding human judgment and decision-making under uncertainty. Kahneman is known for developing prospect theory and for his work on loss aversion, cognitive biases, and heuristics. Some of his influential books include Thinking, Fast and Slow and Judgment Under Uncertainty.