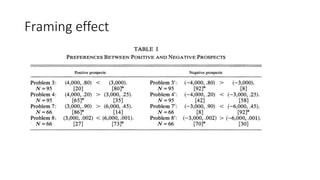
1) Prospect Theory proposes an alternative to Expected Utility Theory to explain phenomena that violate assumptions of EU Theory, such as framing effects and loss aversion.
2) According to Prospect Theory, people evaluate prospects in two phases - an editing phase where prospects are simplified, and an evaluation phase where the prospect of highest value is chosen.
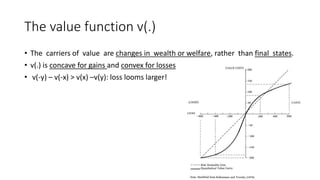
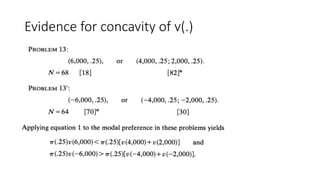
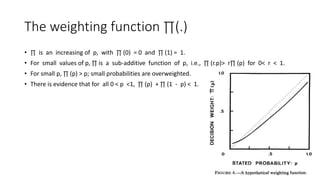
3) In the evaluation phase, Prospect Theory incorporates a value function that is concave for gains and convex for losses, reflecting loss aversion, and a weighting function that overweights small probabilities.






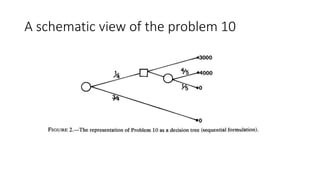




![Evaluation Phase
• Prospect theory distinguishes between evaluation of strictly positive/negative
and regular prospects.
• A regular prospect is defined as p + q < 1 or x ≥ 0 ≥ y or x ≤ 0 ≤ y; and the
corresponding evaluation is V(x, p; y, q) = ∏(p)v(x) + ∏(q)v(y).
• A strictly positive/negative prospect is defined as p + q = 1 and either x > y > 0 or
x < y < 0; and the corresponding evaluation is v(y) + ∏(p)[ v(x) - v(y) ].
• if ∏ (p) + ∏ (l - p) = 1 both evaluation are the same.
• What are the properties of v(.) and ∏(.)?](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/prospecttheory-160515154150/85/Prospect-theory-14-320.jpg)