- Prospect theory is an alternative to expected utility theory that aims to better describe how people make decisions under risk or uncertainty.
- It incorporates concepts like the certainty effect, reflection effect, and isolation effect to account for behaviors not predicted by expected utility theory.
- Prospect theory posits that people edit prospects through coding, combination, segregation, cancellation, and simplification before evaluating them.
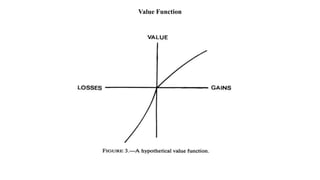
- Evaluation involves weighing the value of outcomes, where value is assessed based on gains and losses relative to a reference point and is generally concave for gains and convex for losses. Decision weights are applied to outcomes and may differ from actual probabilities.


![Violation Of Expected Utility Theory
People overweight outcomes that are considered certain, relative to outcomes which are merely
probable which we label the certainty effect
Certainty Effect
Choose between
• A: 2,500 with probability .33, B: 2,400 with certainty.
• 2,400 with probability .66,
• 0 with probability .01
N=72 [18] [82]*
A: 50% chance to
win 1,000, 50%
chance to win
nothing;
B: 450 for sure.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/prospecttheory-220918123721-c7d660c8/85/Prospect-Theory-pptx-3-320.jpg)
![Choose between
• C: 2,500 with probability .33, D: 2,400 with probability .34,
• 0 with probability .67; 0 with probability .66.
• N =72 [83]* [17]
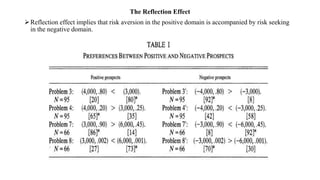
PROBLEM 1:
• A: (4,000,.80), B: (3,000).
• N = 95 [20] [80]*
PROBLEM 2:
• C: (4,000,.20), D: (3,000,.25).
• N= 95 [65]* [35]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/prospecttheory-220918123721-c7d660c8/85/Prospect-Theory-pptx-4-320.jpg)
![The certainty effect with non-monetary outcomes.
PROBLEM 3:
A: 50% chance to win a three- B: A one-week tour of
week tour of England, France and Italy England, with certainty.
N=72 [22] [78]*
C: 5% chance to win a three- D: 10% chance to win a one week
• tour of England, France, and Italy; tour of England
N=72 [67]* [33]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/prospecttheory-220918123721-c7d660c8/85/Prospect-Theory-pptx-5-320.jpg)