The document discusses database concepts including:
- What a database is and its components like data, hardware, software, and users.
- Database management systems (DBMS) that enable users to define, create and maintain databases.
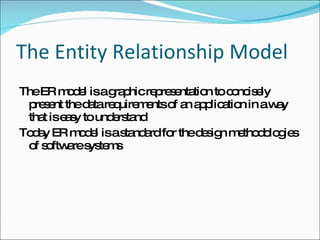
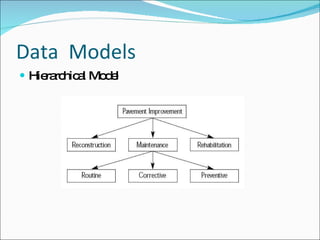
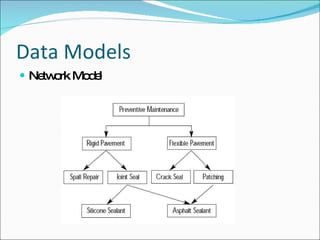
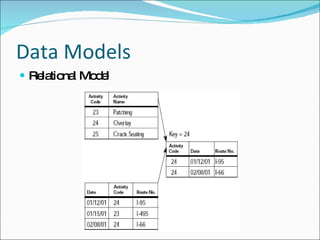
- Data models like hierarchical, network, and relational models. Relational databases using SQL are now most common.
- Database design including logical design, physical implementation, and application development.
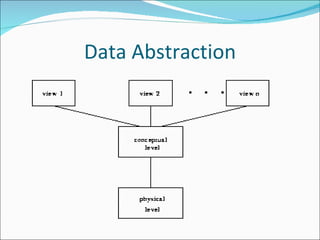
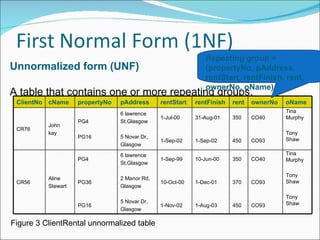
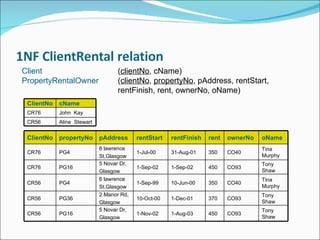
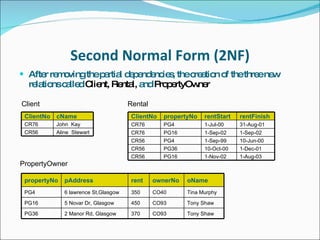
- Key concepts like data abstraction, instances and schemas, normalization, and integrity rules.



















































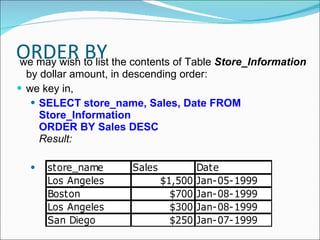
![ORDER BY We want to list the output in a particular order. This could be in ascending order, in descending order, or could be based on either numerical value or text value. In such cases, we can use the ORDER BY keyword. The syntax for an ORDER BY statement is as follows: SELECT "column_name“ FROM "table_name" [WHERE "condition"] ORDER BY "column_name" [ASC, DESC]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dbmsanimate-100317015941-phpapp01/85/D-B-M-S-Animate-66-320.jpg)