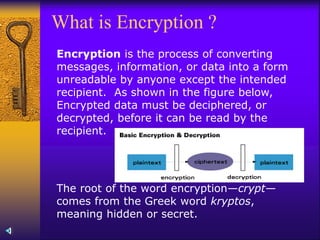
This document discusses cyber security and threats. It begins by introducing 5 cyber security experts and their names. It then discusses how cyber attacks have become a national security threat since 9/11. The document outlines what cyberspace is, how it has become a battleground for attacks, and some common cyber attack types like hacking, denial of service attacks, and virus deployment. It provides statistics on the increasing costs of cyber attacks and numbers of malicious hacking incidents. It also explains security concepts like encryption, biometrics authentication methods, and the need for information security practices.