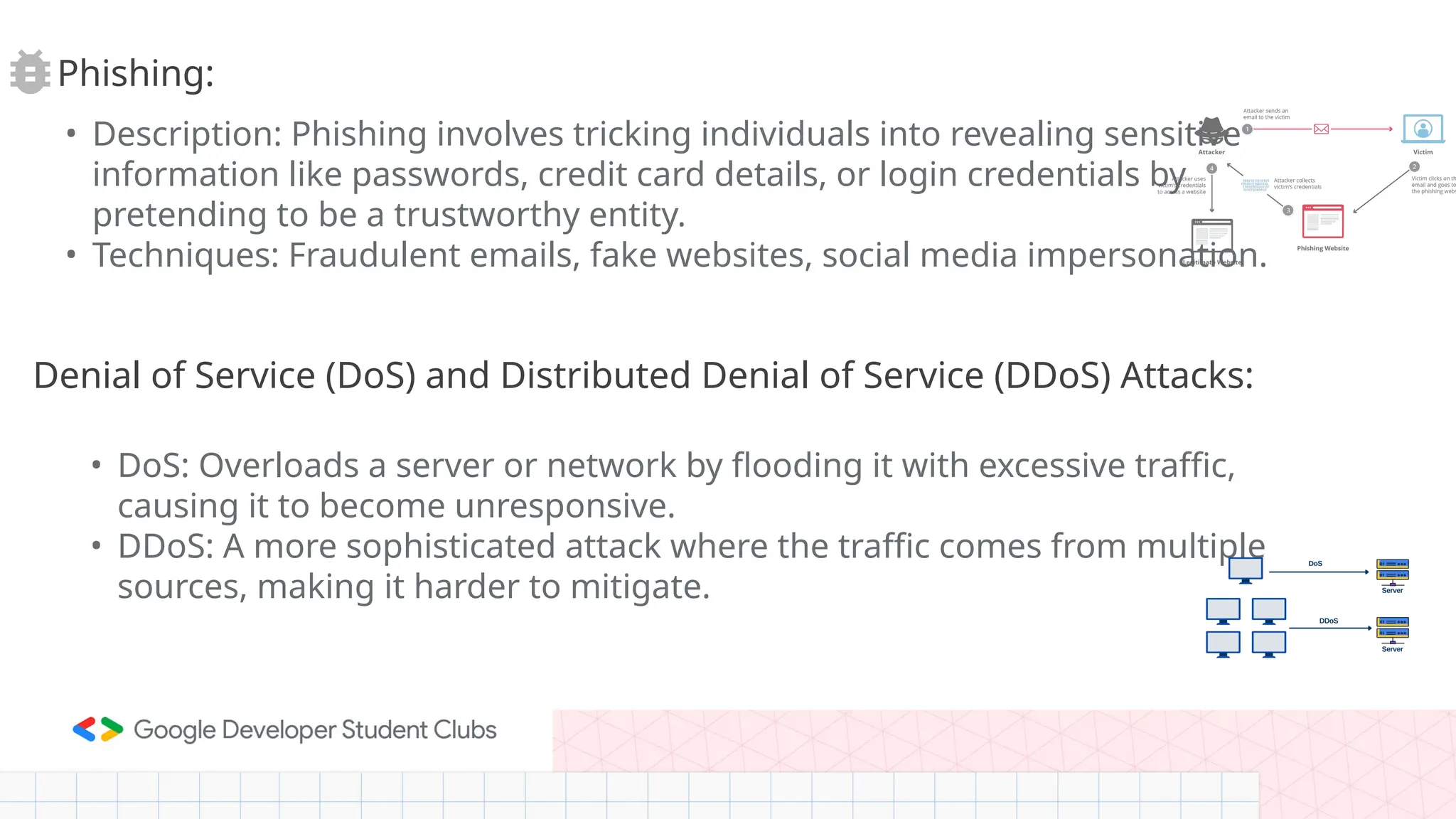
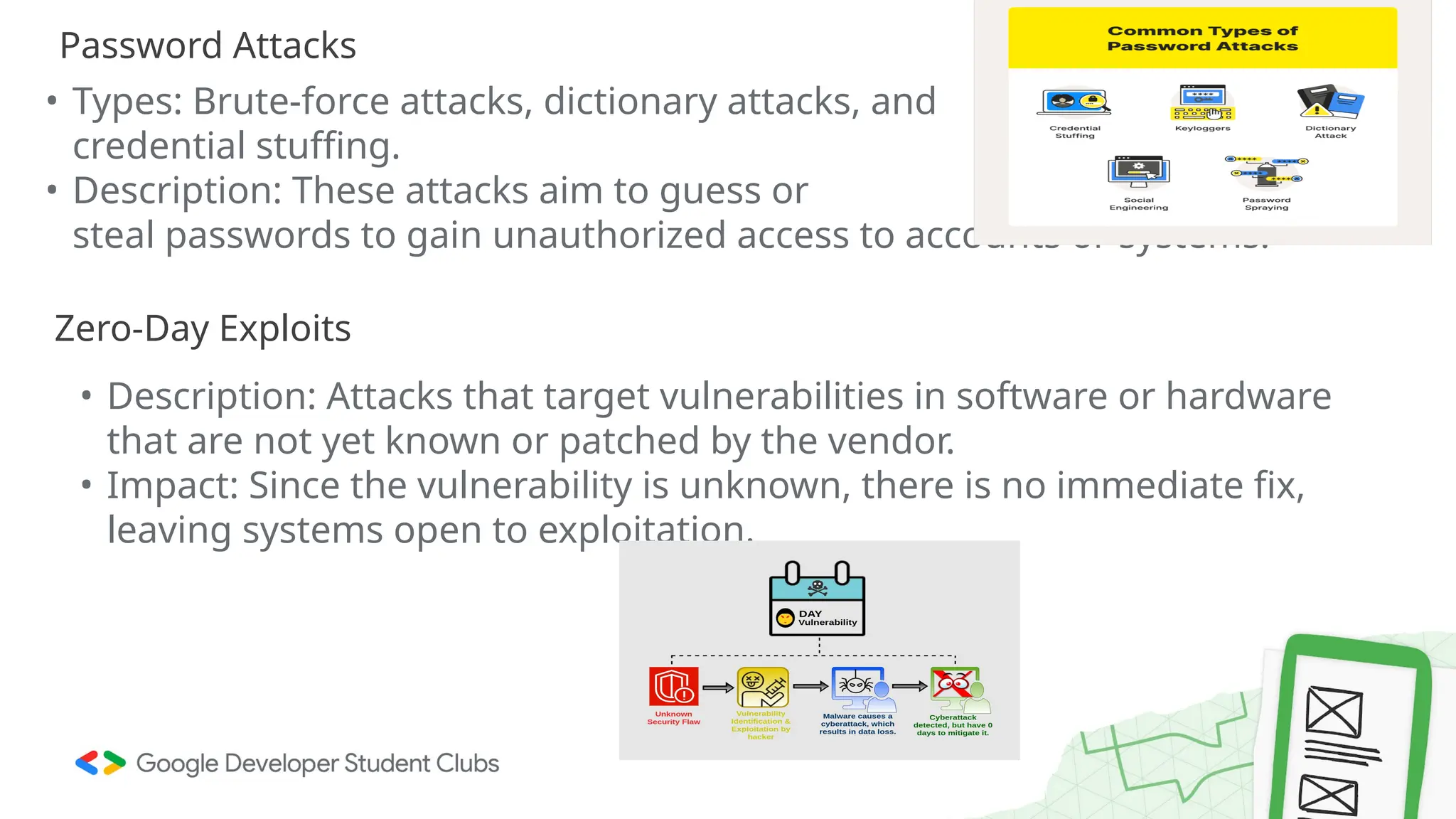
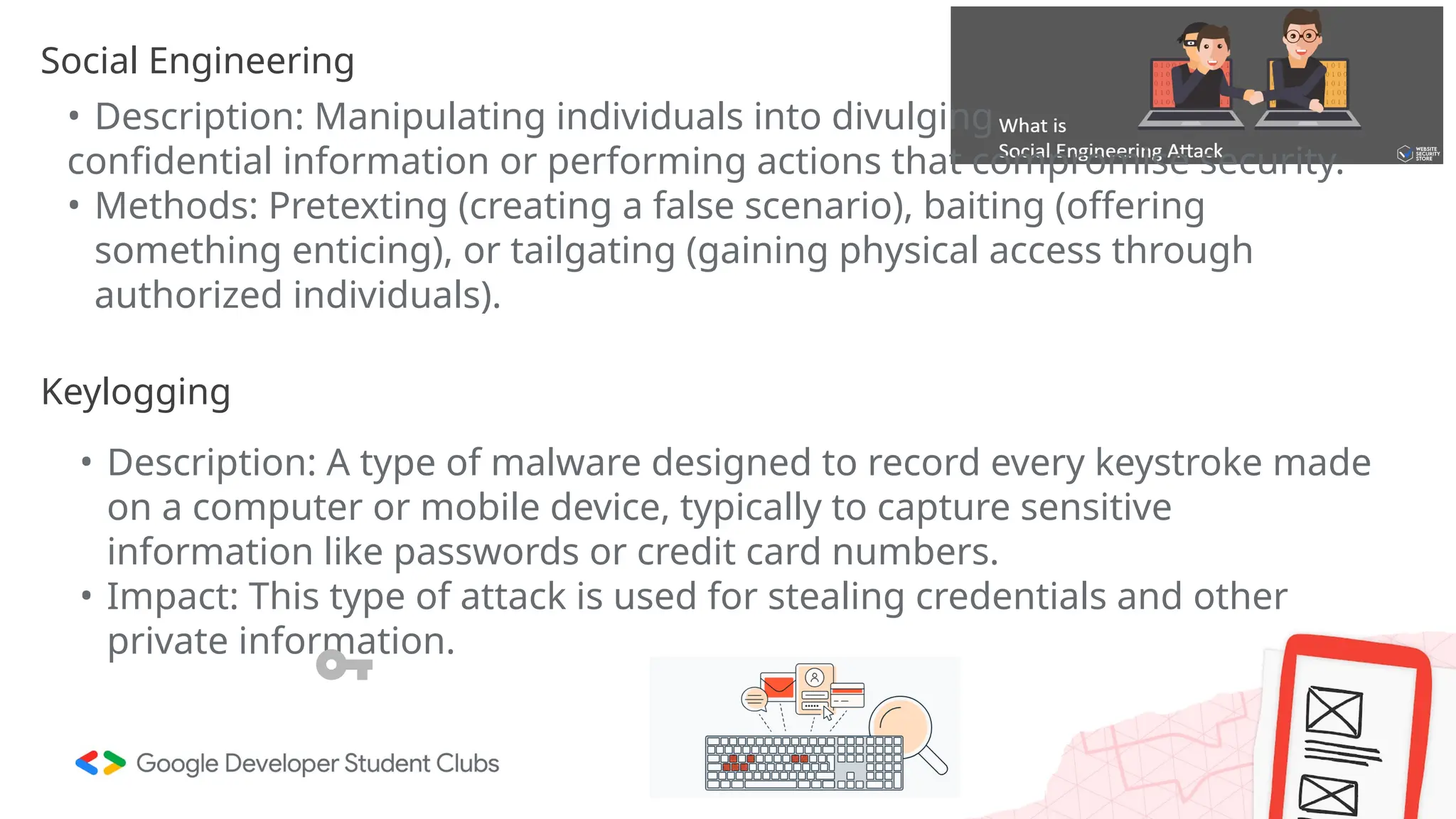
The document provides an overview of cybersecurity, defining it as the defense of computer systems and data against unauthorized access and damage. Key concepts include the CIA triad (confidentiality, integrity, availability), types of cyber threats such as phishing and ransomware, and the roles within cybersecurity, including ethical hackers and security analysts. It emphasizes the importance of awareness and best practices in preventing cyber threats and highlights various career paths in the field.