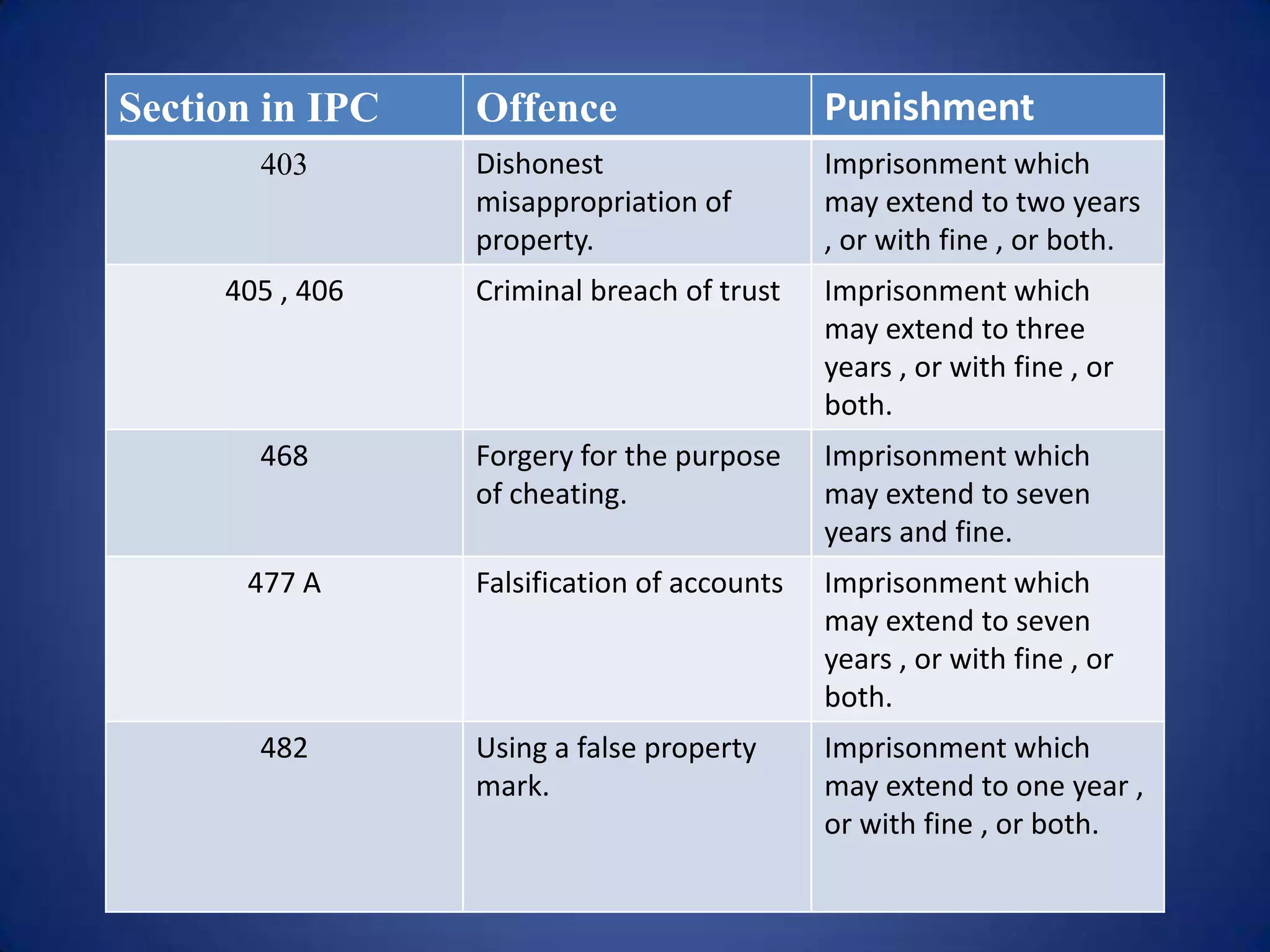
The document discusses cyber crime and the IT Act in India. It defines cyber crime narrowly as offenses outlined in the IT Act and broadly as illegal acts using the internet. Cyber crimes are classified as old crimes committed online, new internet-created crimes, and using the internet to enable old crimes. The IT Act covers hacking, cyber pornography, and cyber fraud. It discusses provisions for tampering with computer source code, cyber terrorism, and defines key cyber crimes and offenses under the act. It also provides tips for individuals and organizations to prevent cyber crimes like using strong passwords, firewalls, and keeping systems updated.