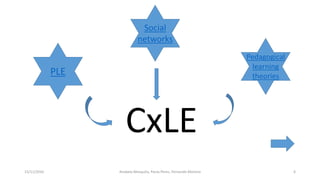
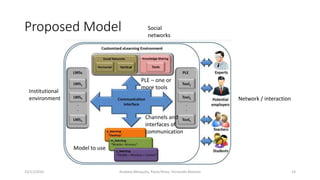
The document proposes a model for a customized learning environment (CxLE) that allows students to personalize their learning experience. It discusses shortcomings of traditional learning management systems and personal learning environments in fully empowering students. The proposed CxLE model integrates institutional learning management systems with personalized tools and social networks selected by students. It is based on constructivist and connectivist learning theories with the student at the center. Next steps include testing the CxLE concept and further integrating formal and informal learning spaces.