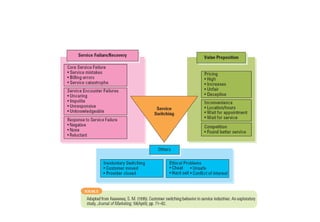
This document provides an overview of customer relationship management (CRM). It discusses the importance of customer loyalty to a firm's profitability. Loyal customers become more profitable over time through increased purchases, reduced costs, referrals, and price premiums. The document also covers assessing the lifetime value of customers, understanding the customer-firm relationship, strategies for reducing customer defections, and the objectives and key processes of CRM systems including strategy development, value creation, multi-channel integration, performance assessment, and information management.