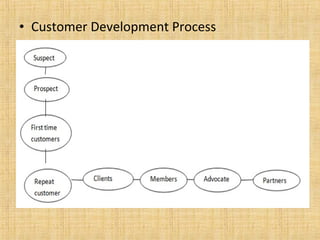
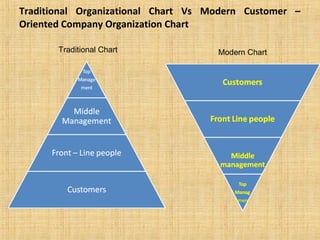
The document discusses customer relationship management (CRM). It defines CRM as establishing, developing, and sustaining long-term, beneficial relationships between organizations and their customers. CRM aims to increase customer retention through loyalty programs and databases. It reduces costs associated with acquiring new customers. CRM software helps companies provide better service and increase customer satisfaction. Properly managing customer relationships is important for customer retention, reducing costs, and growing business.