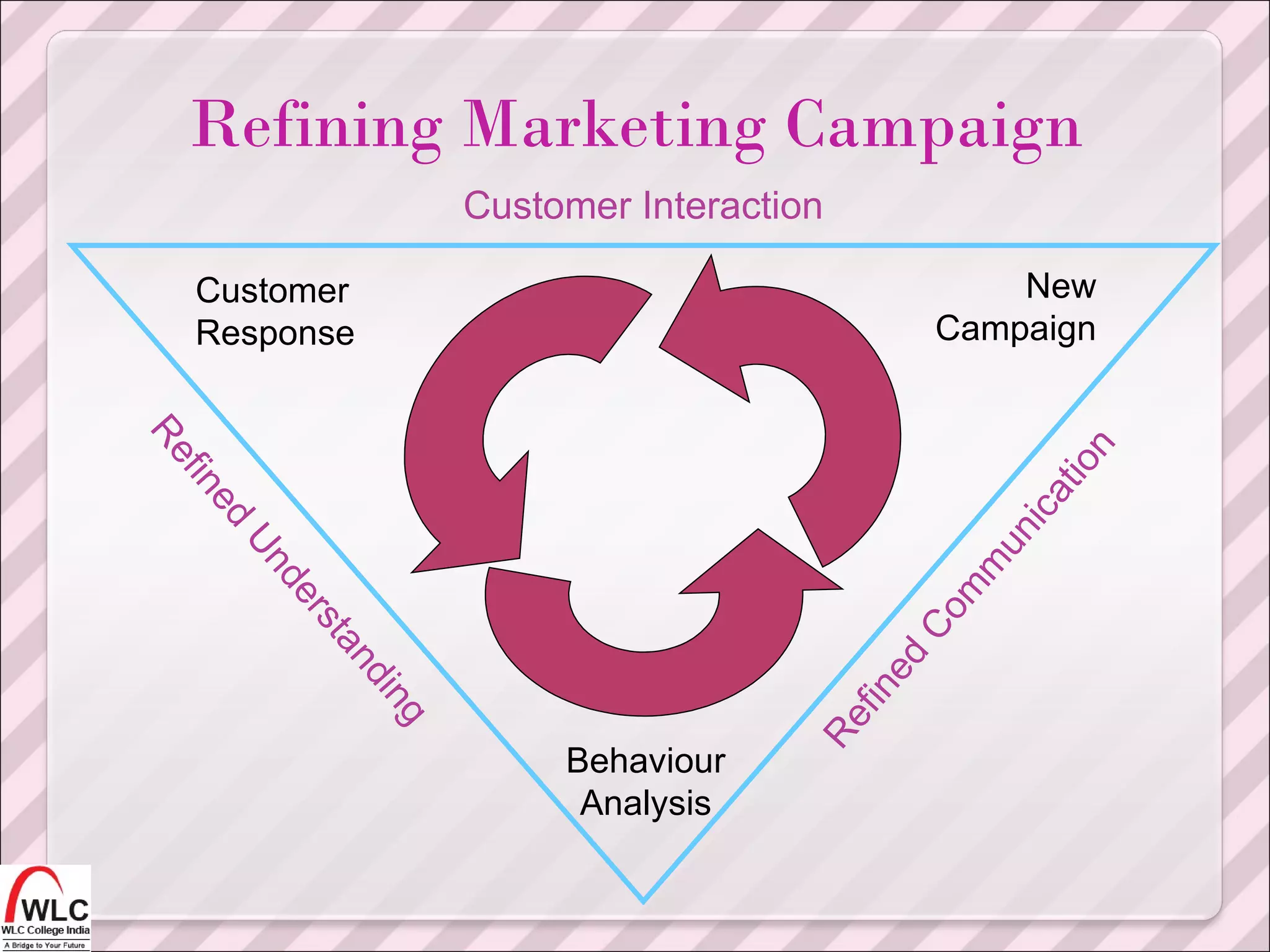
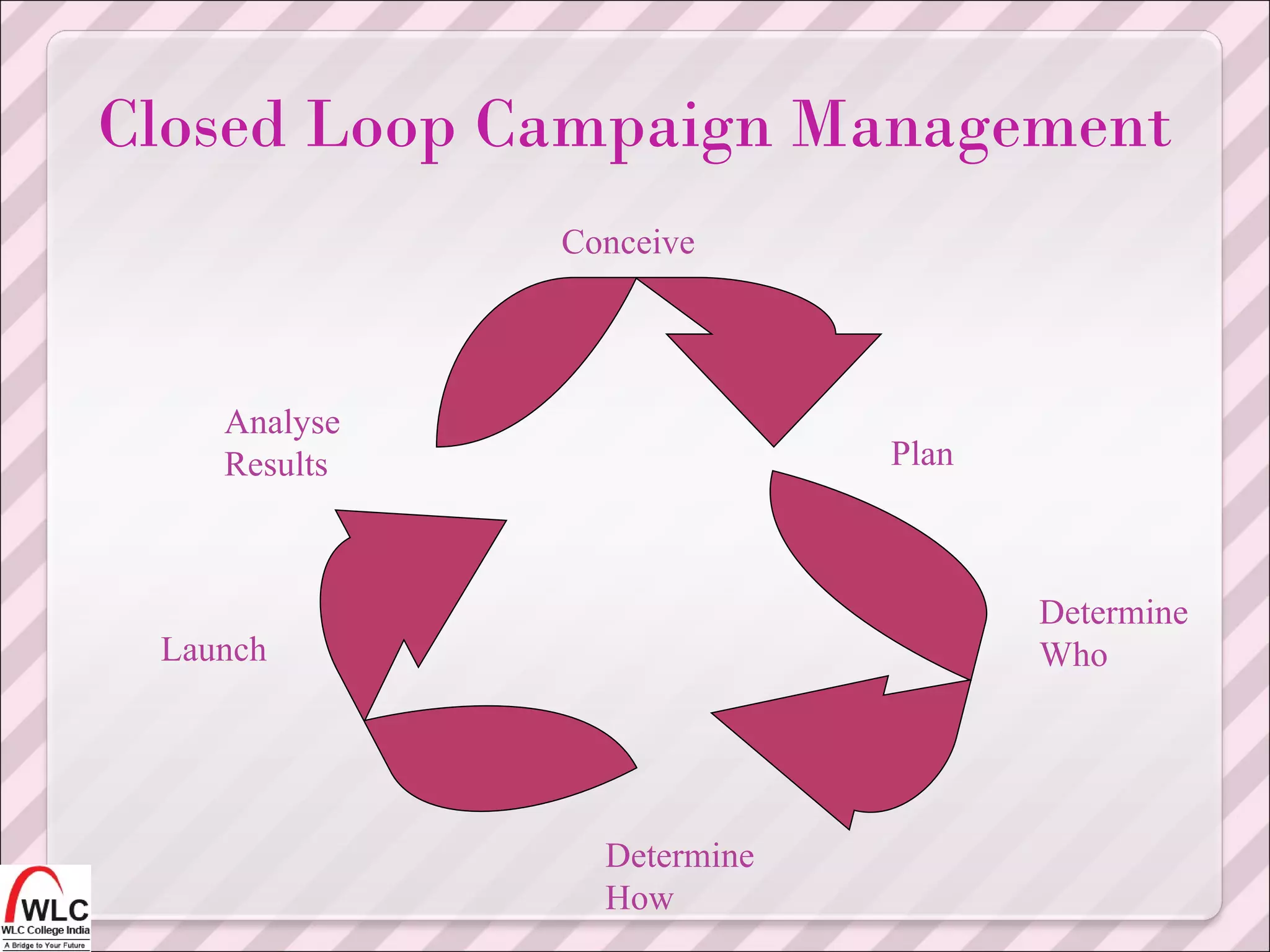
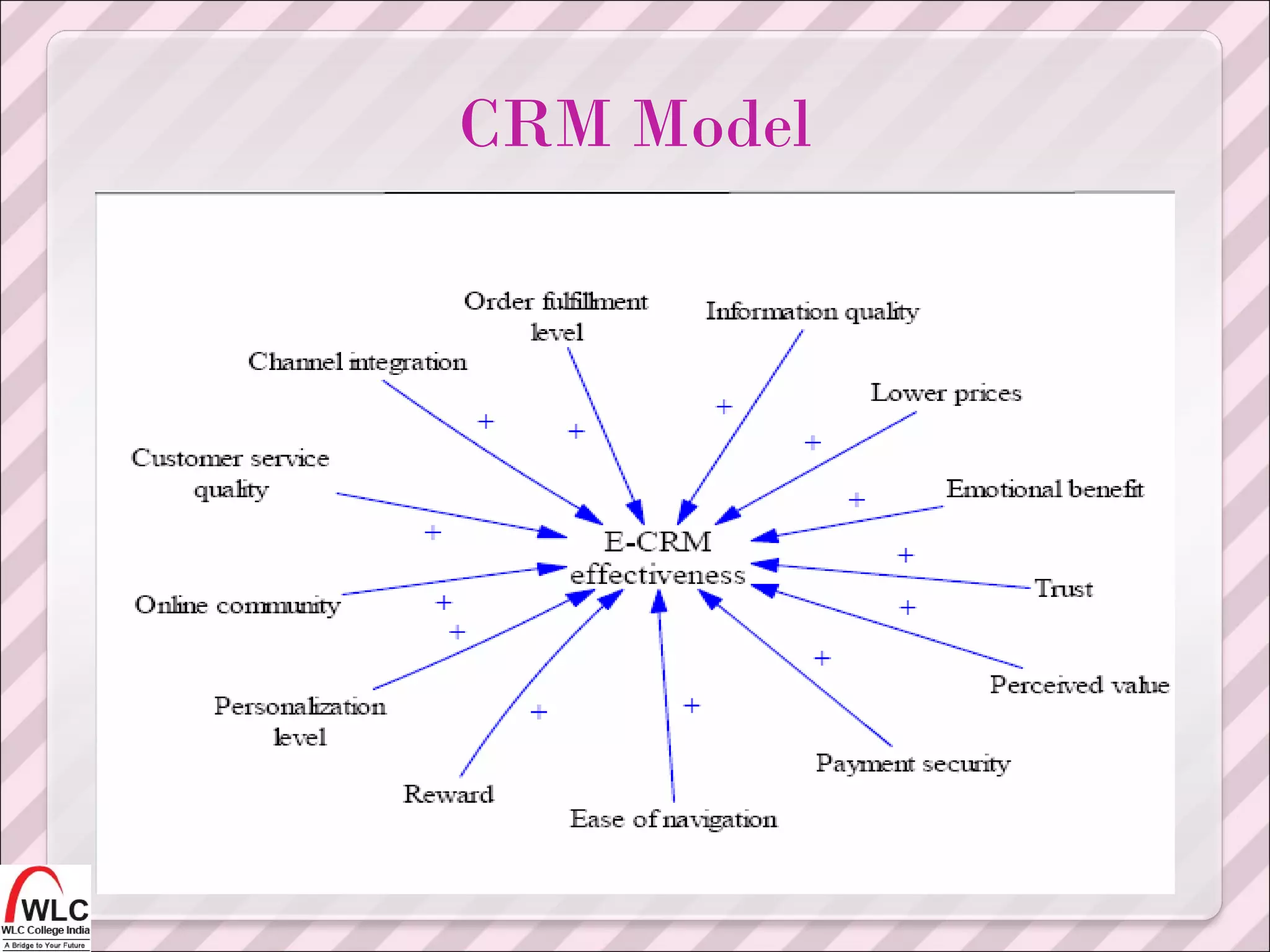
The document discusses customer relationship management (CRM) and electronic customer relationship management (eCRM). It outlines several key aspects of CRM, including acquiring and retaining customers, increasing customer satisfaction and loyalty, understanding customer needs and behaviors, and using marketing campaigns and technologies like data analysis to improve customer interactions and relationships. The document then discusses how eCRM uses electronic channels like websites and messaging to connect with customers and enhance the customer experience across different customer touchpoints. It emphasizes integrating online channels with traditional channels to implement a holistic CRM strategy.