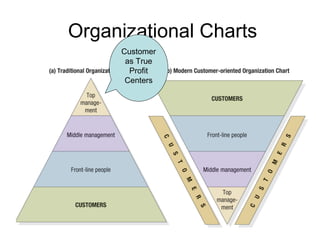
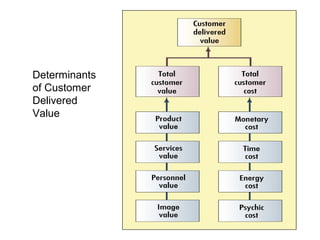
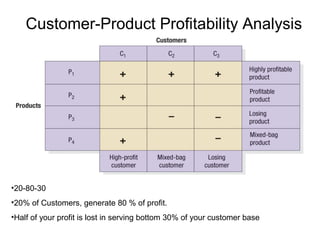
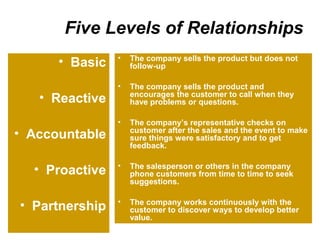
The document discusses building customer satisfaction through delivering value and high quality. It defines customer value and satisfaction, and how perceived value is determined by benefits versus costs. Specific strategies are provided, such as enhancing product attributes, improving quality, reducing prices, and focusing on customer service. Measuring satisfaction through surveys and monitoring complaints is also covered. The goal is to turn customers into loyal, long-term partners by continuously discovering ways to provide more value.