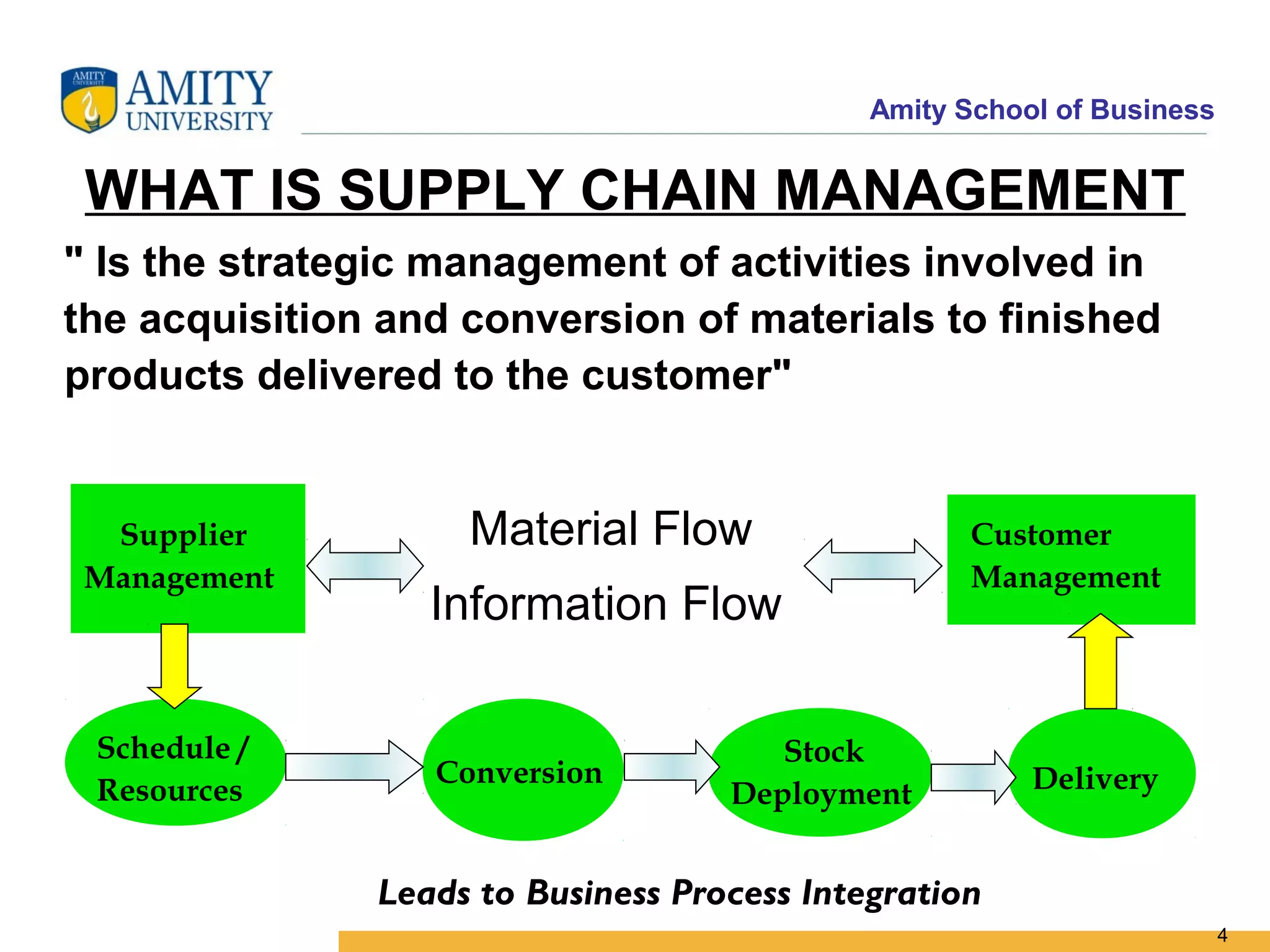
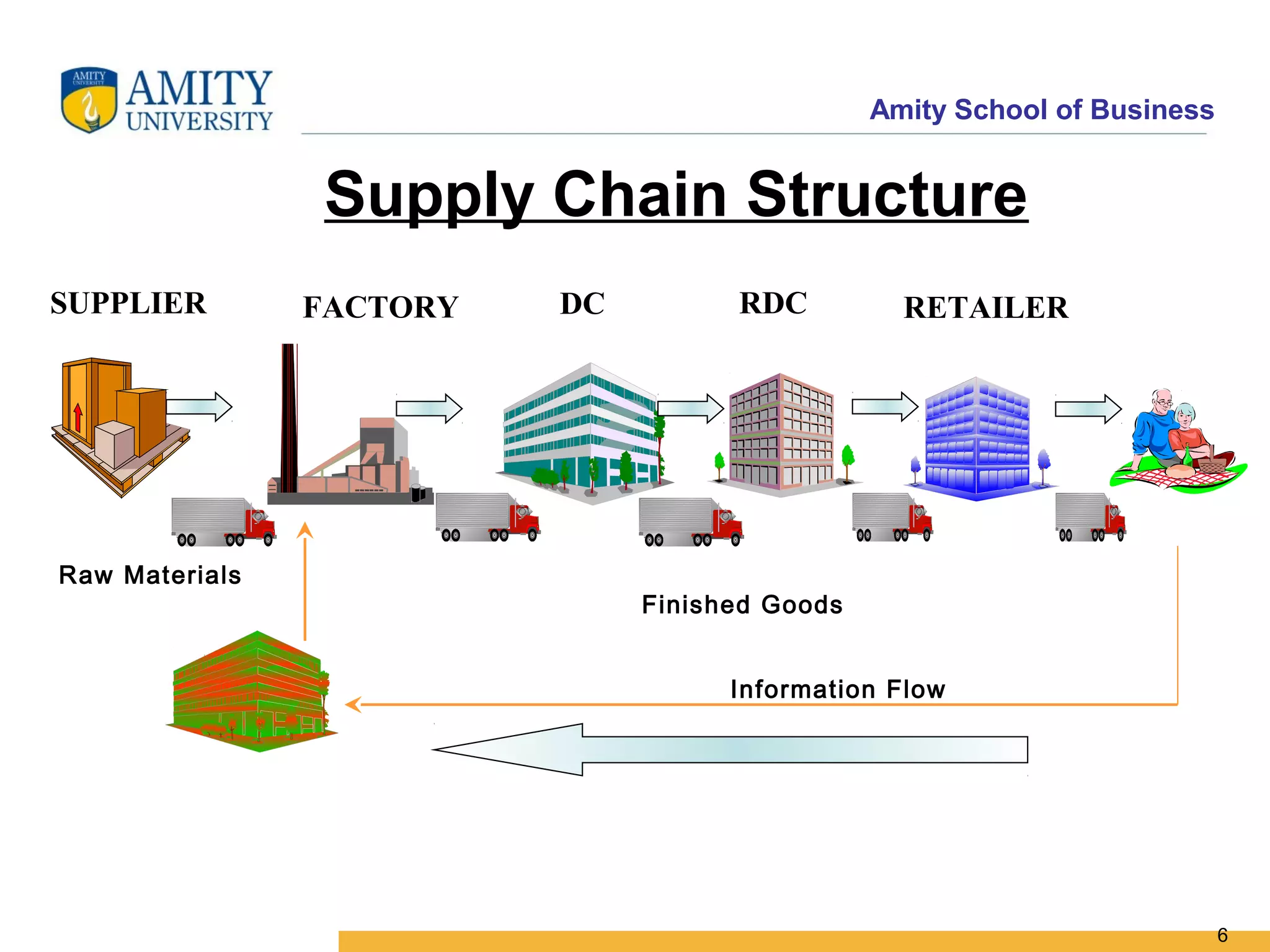
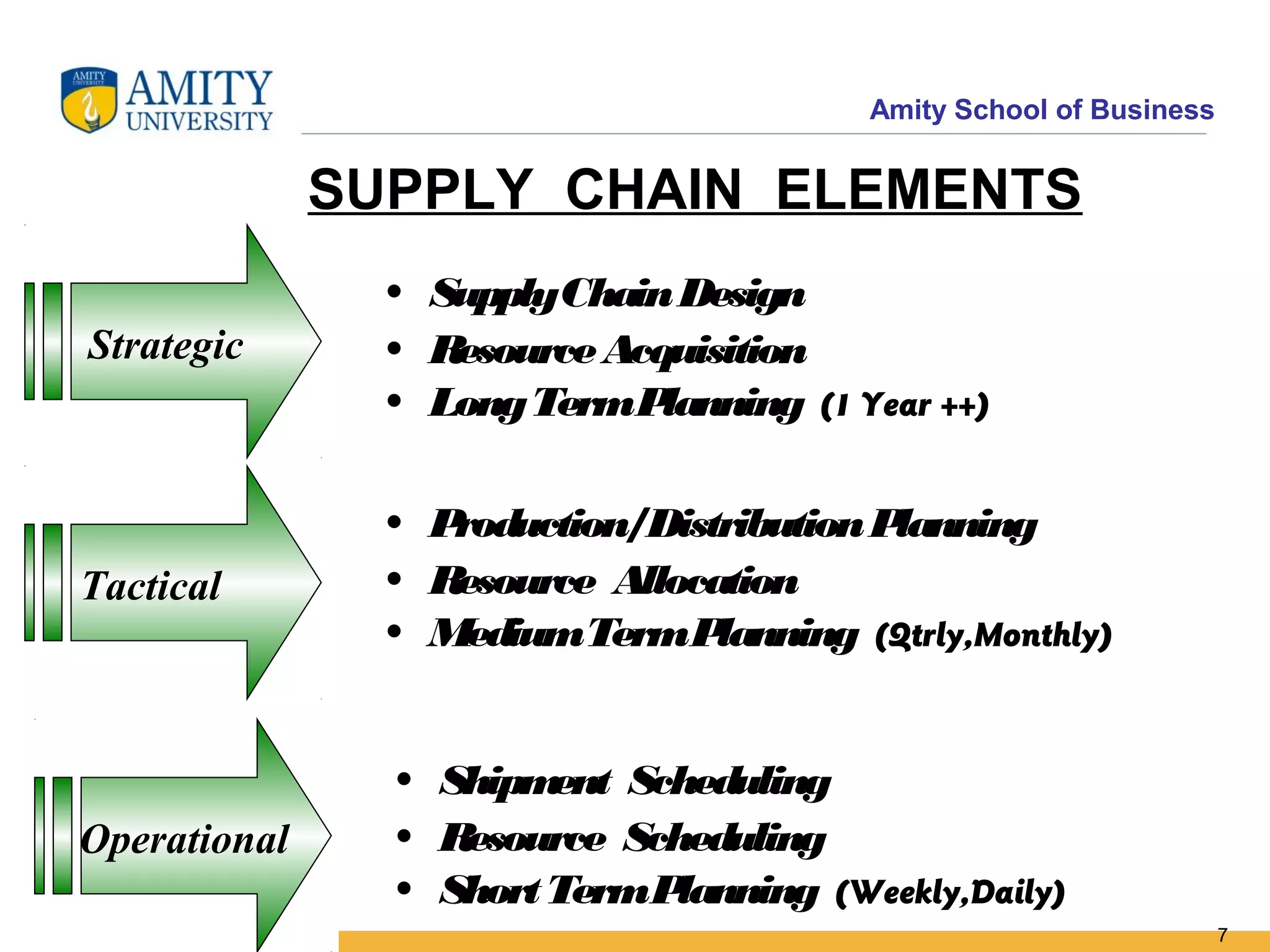
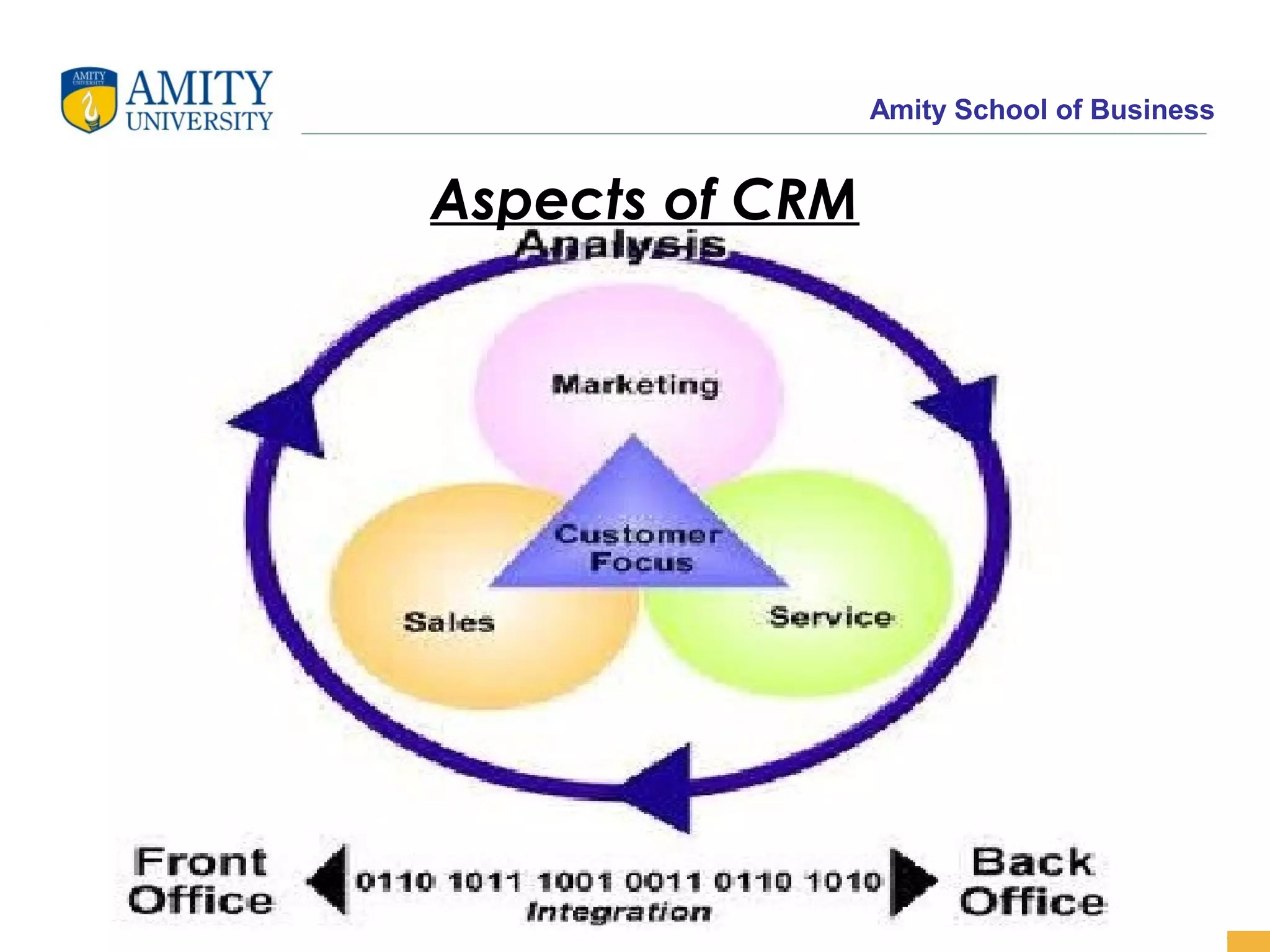
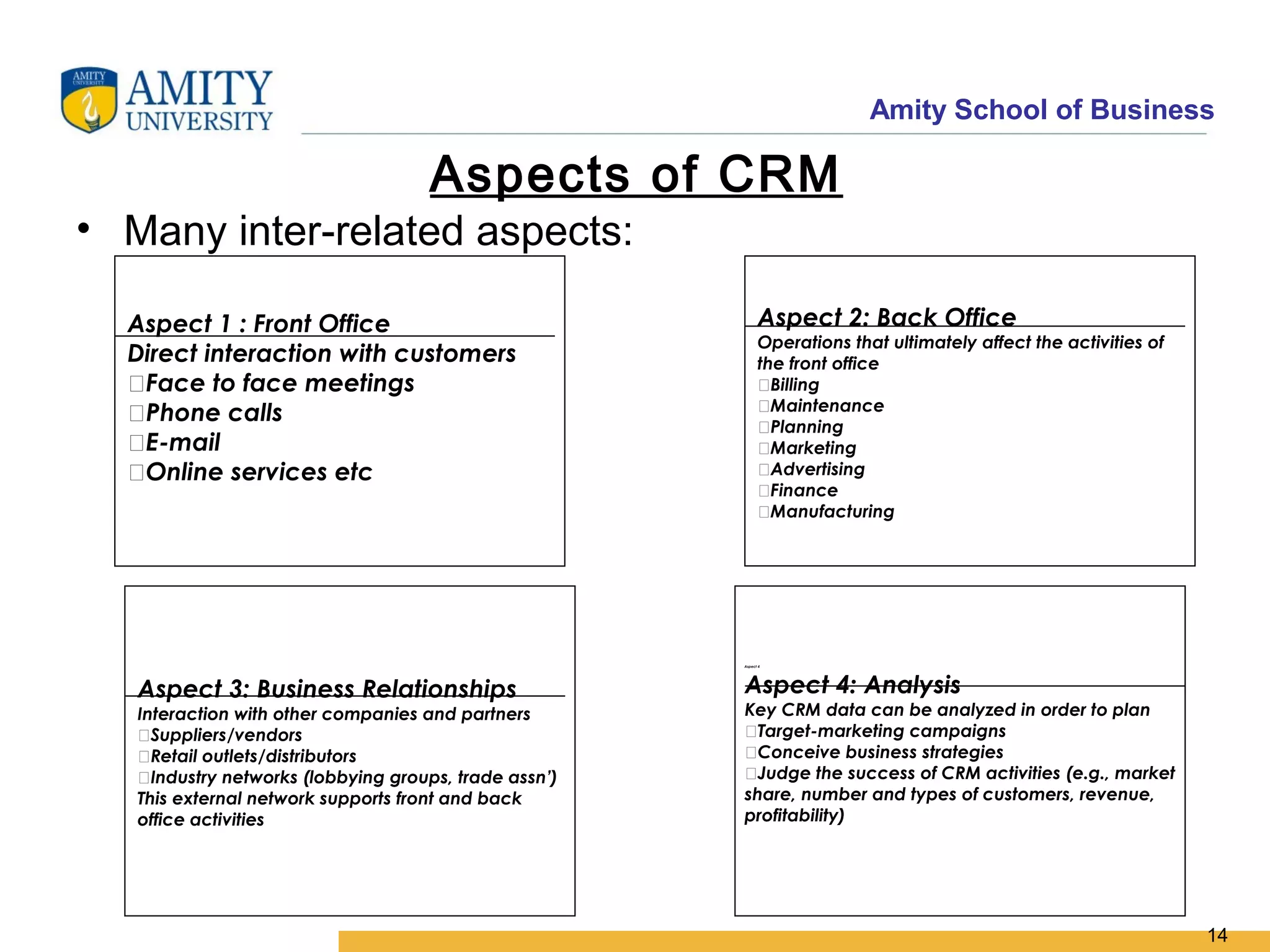
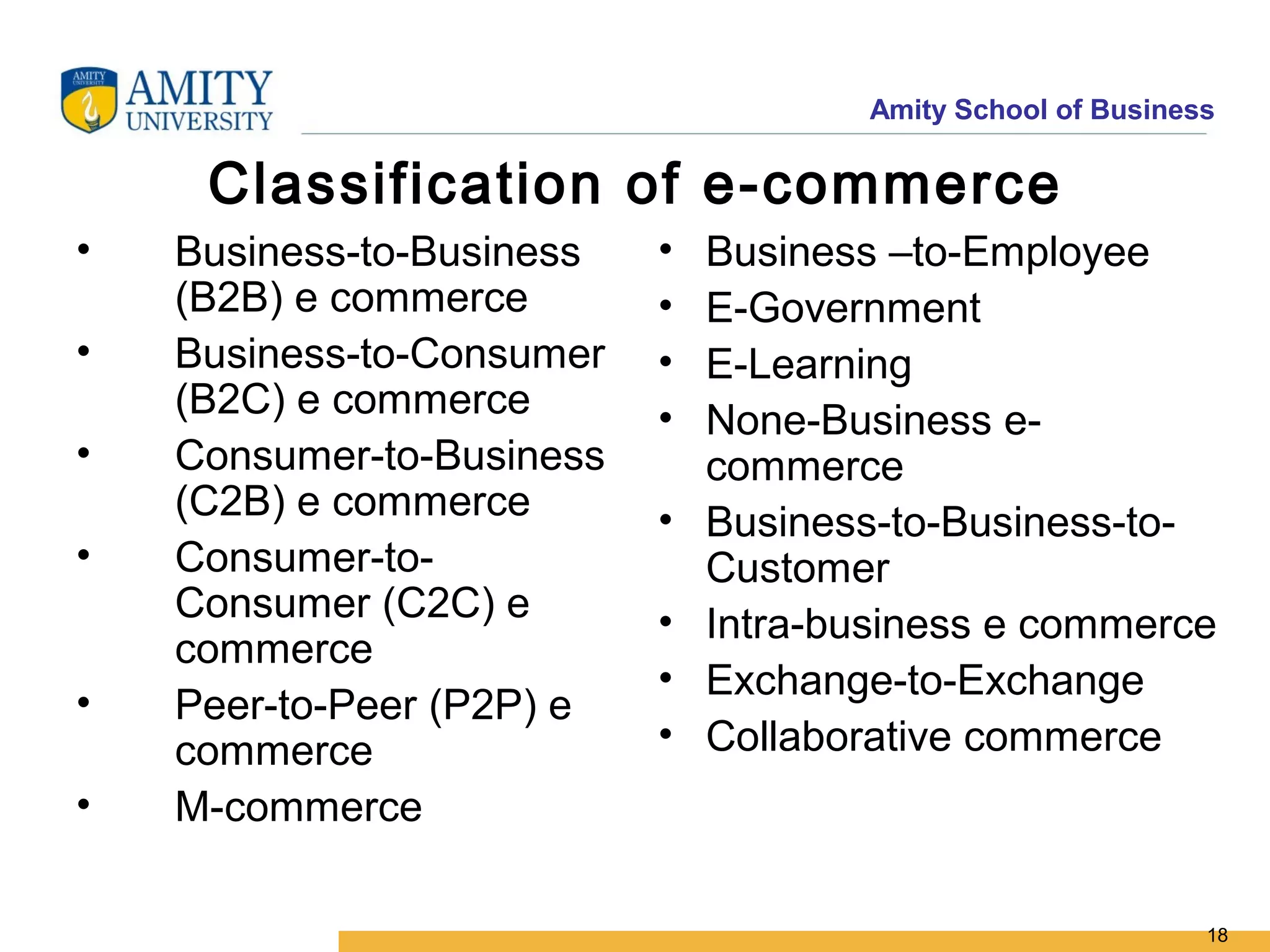
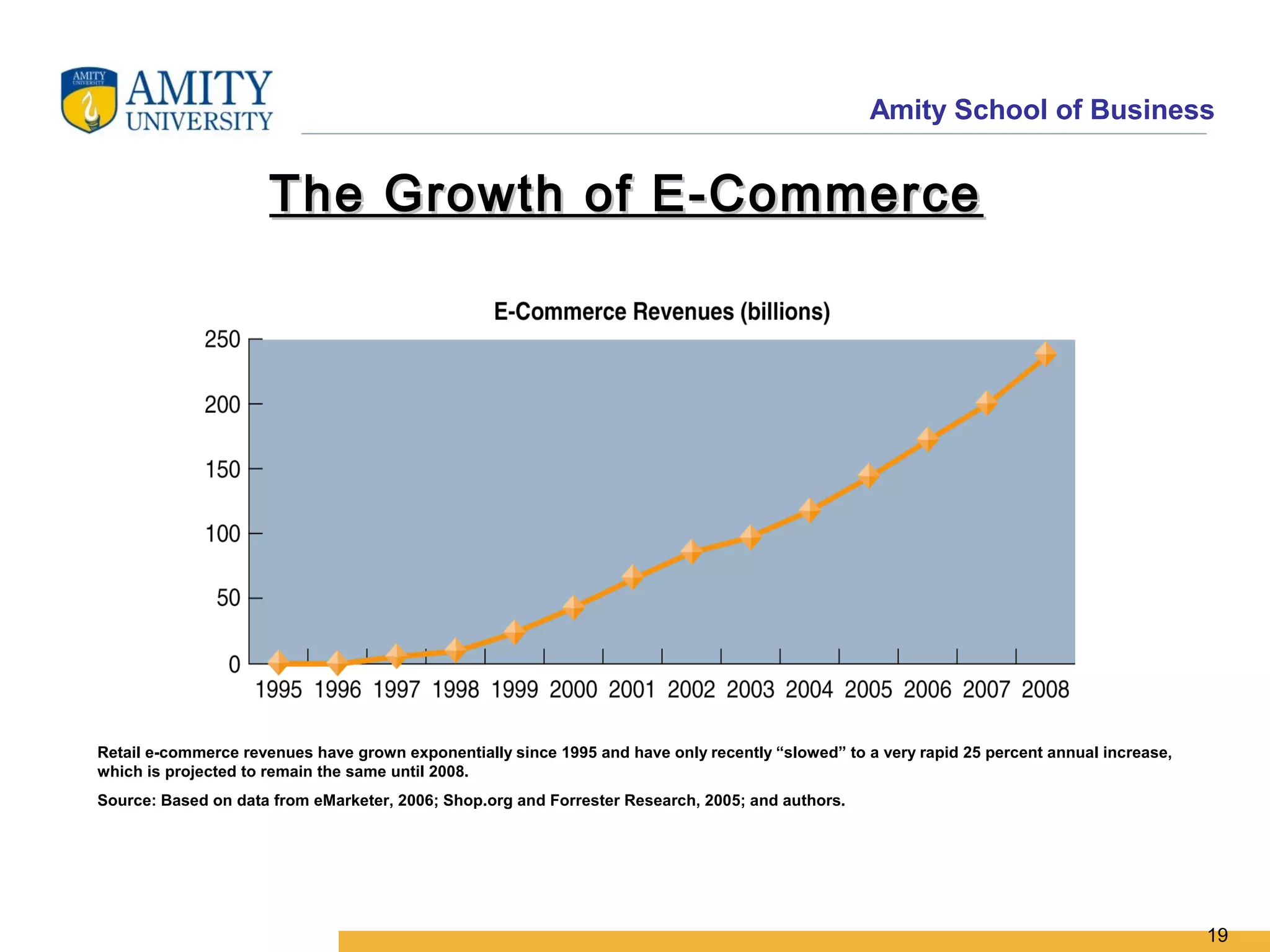
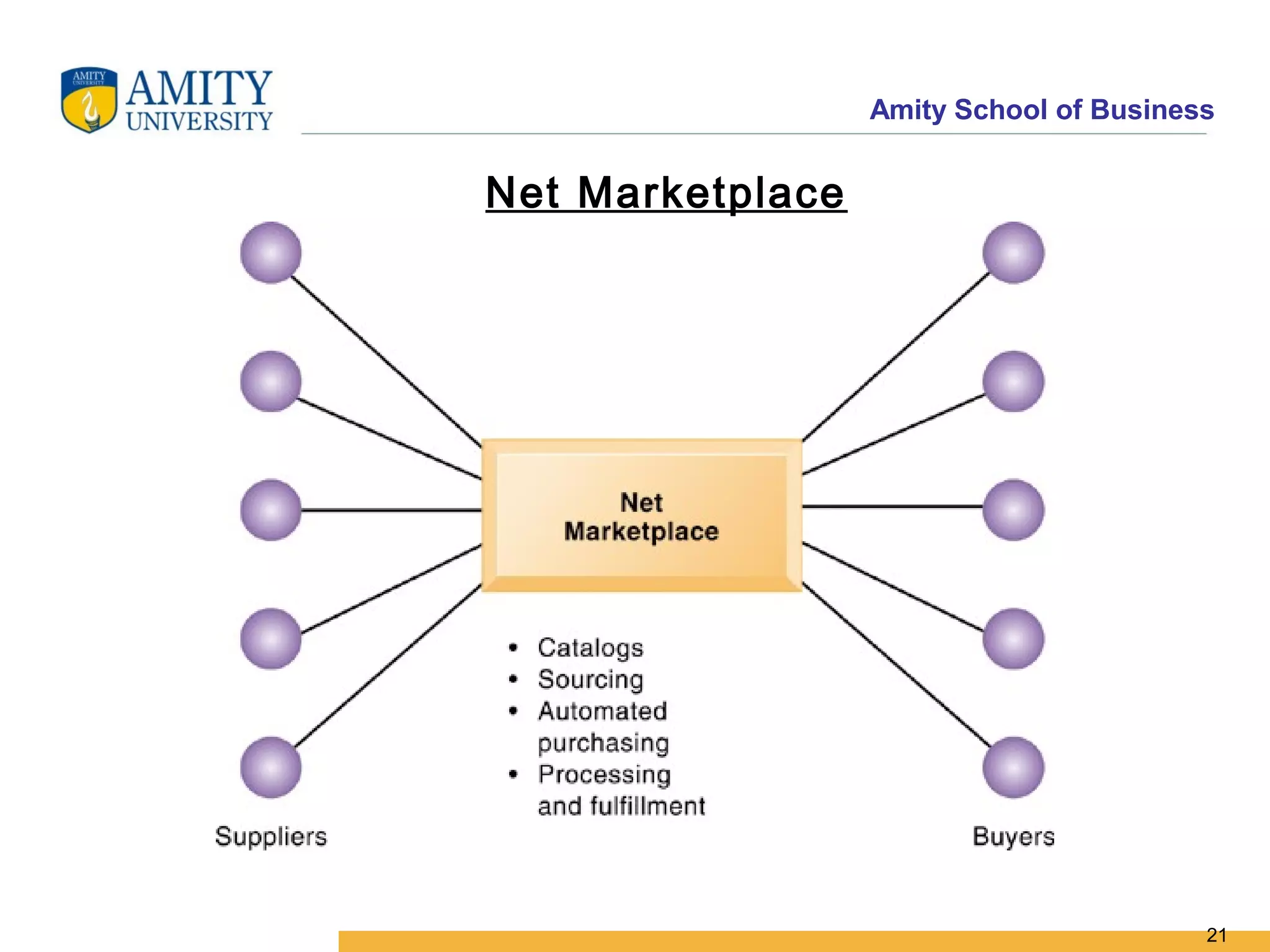
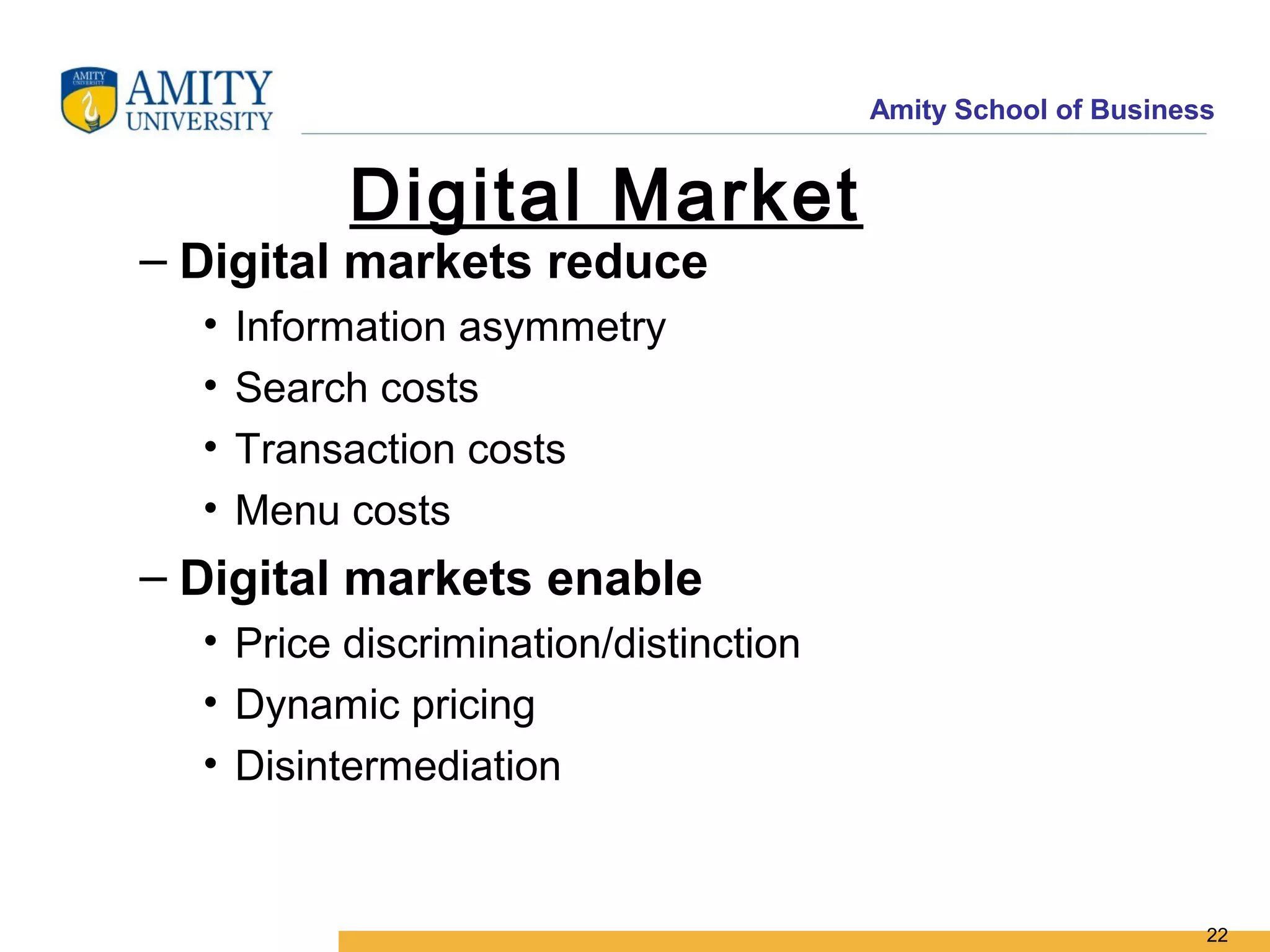
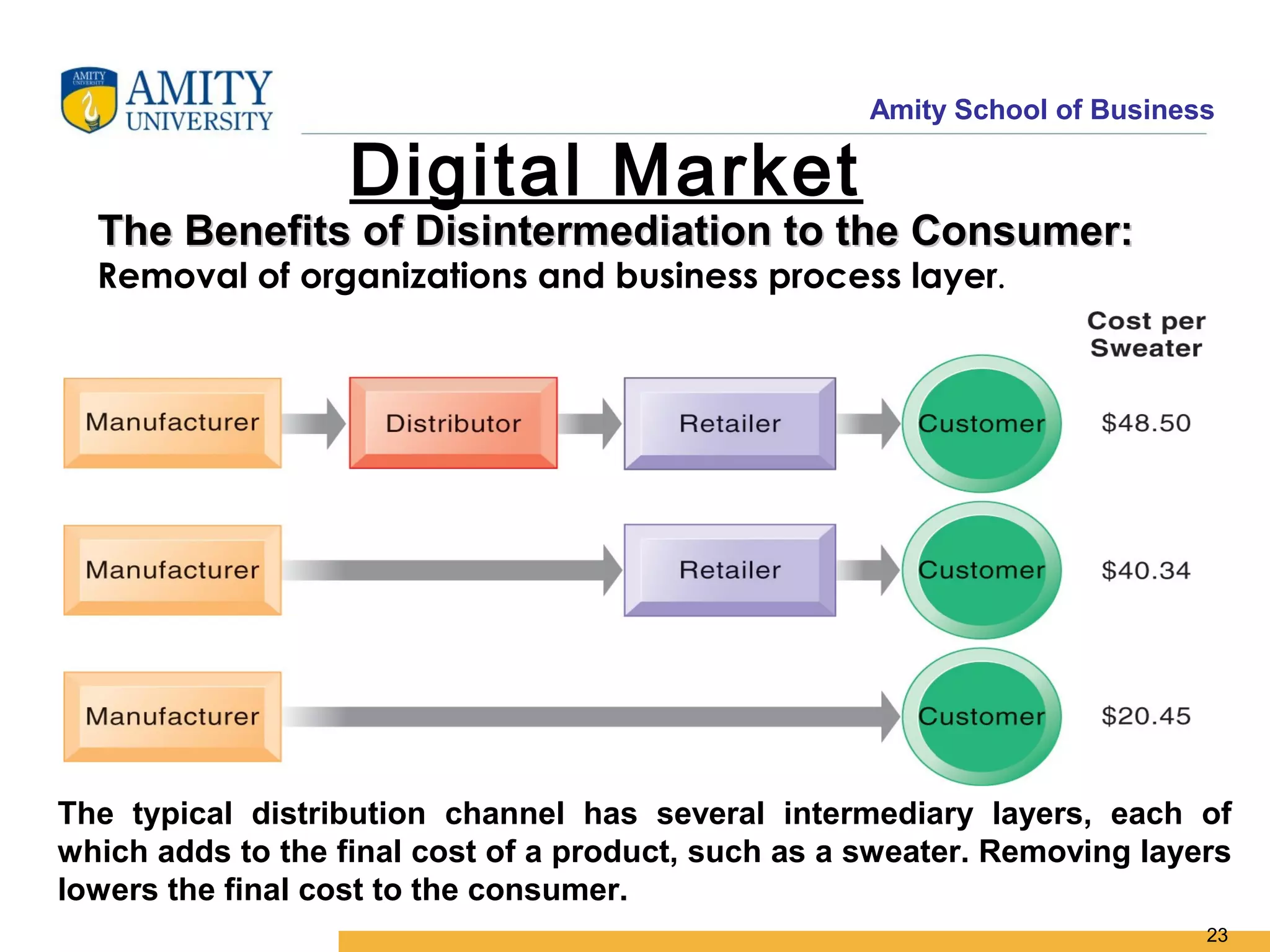
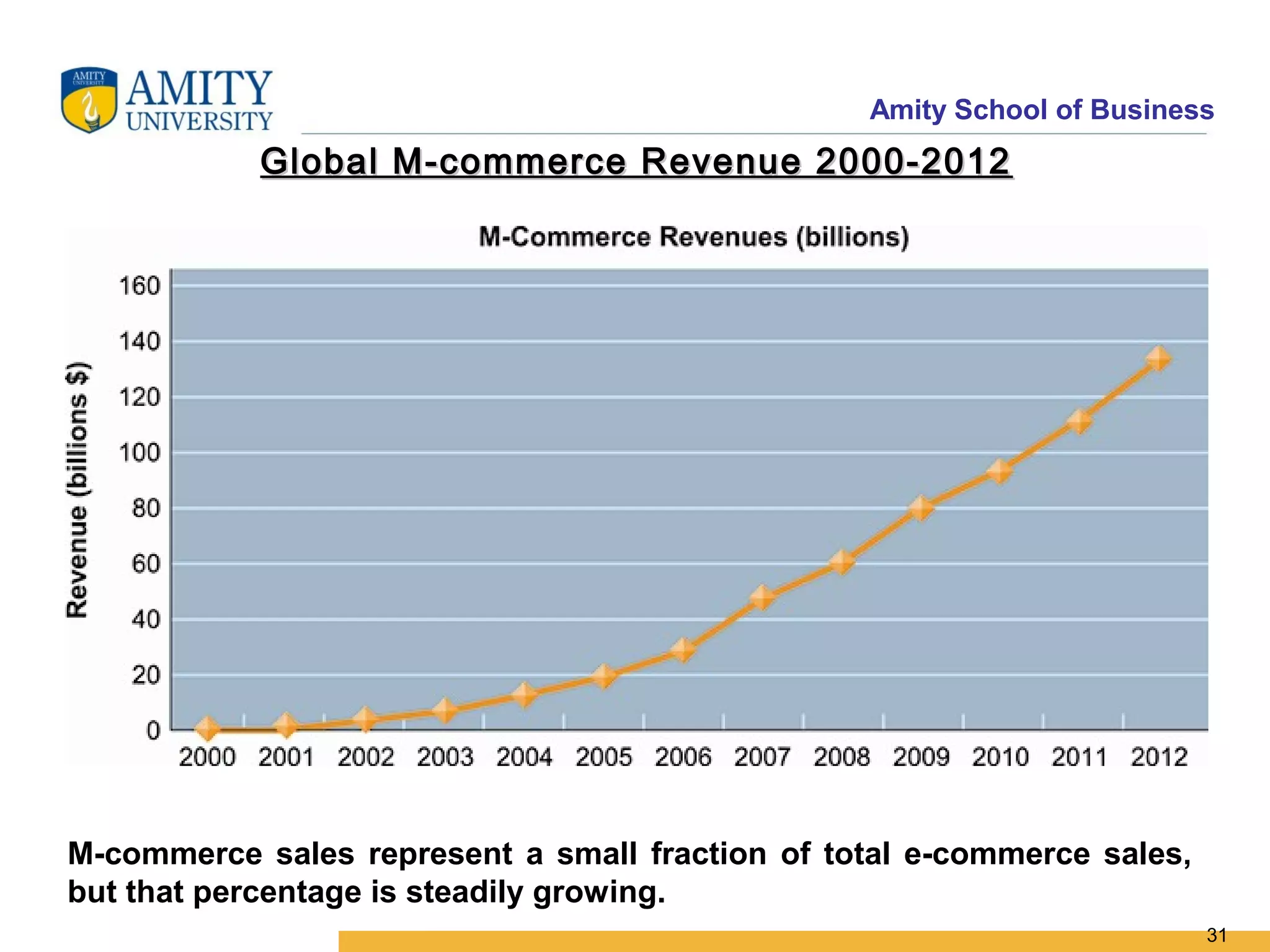
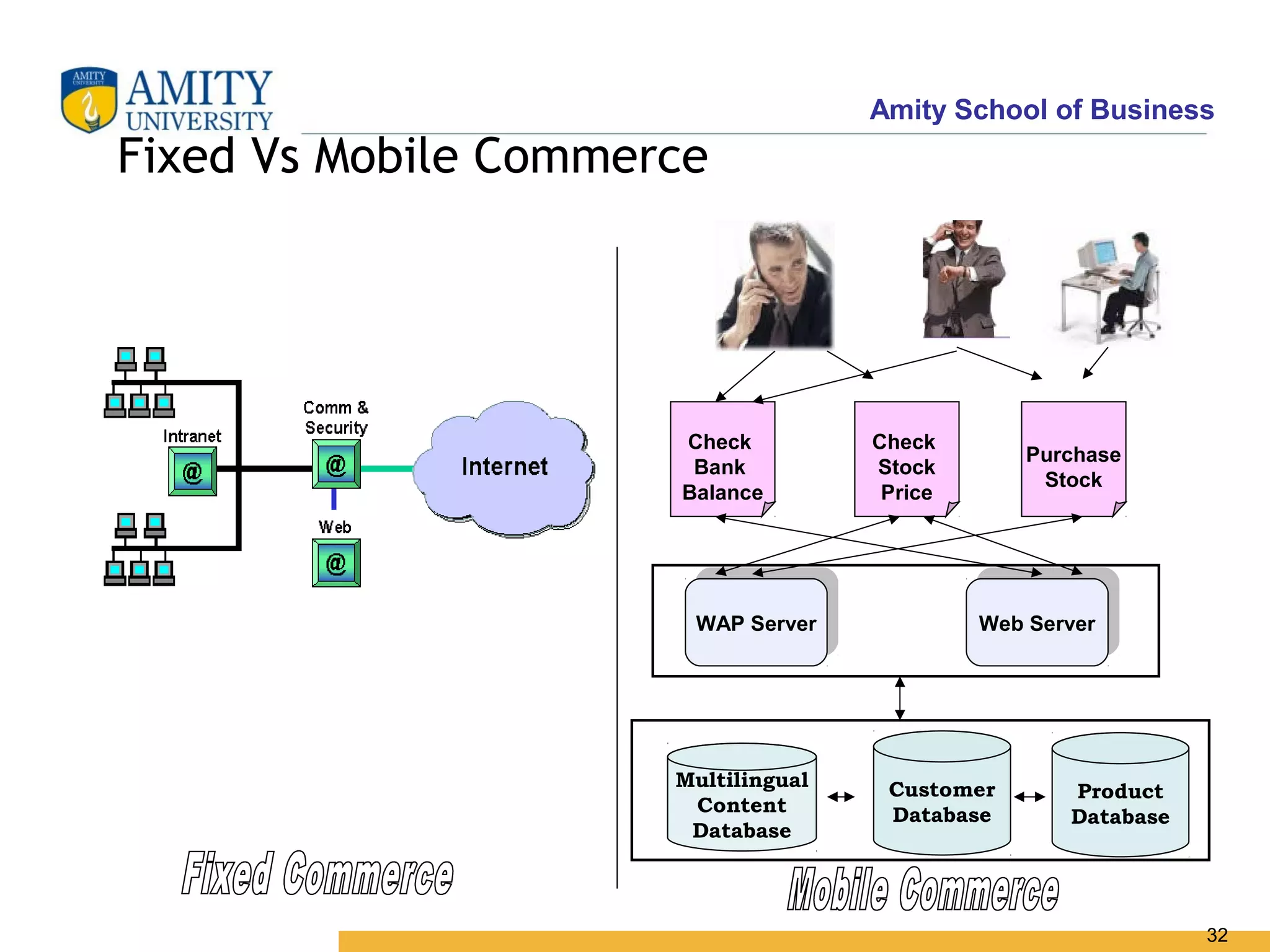
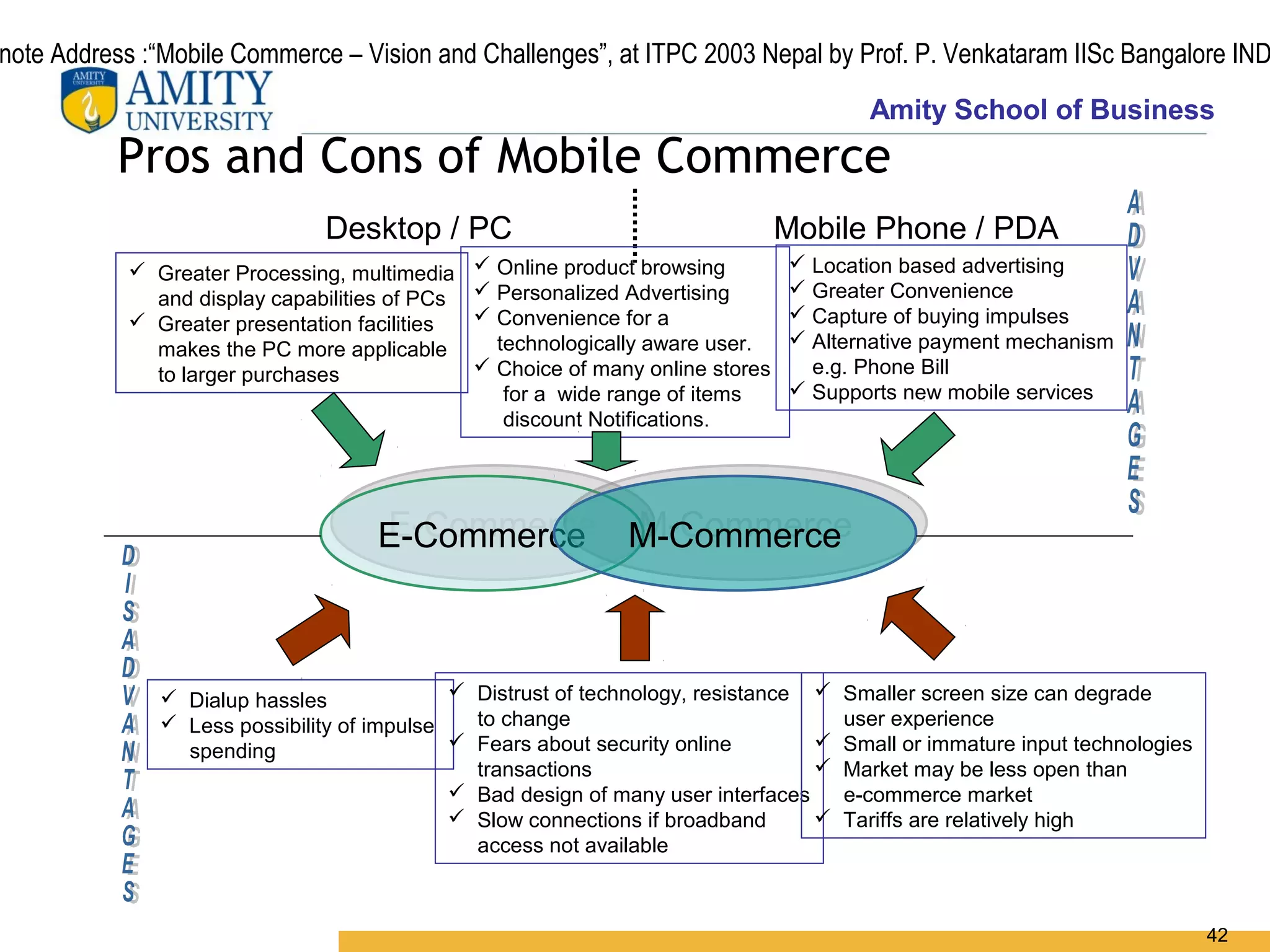
The document discusses key system applications for the digital age, including enterprise systems and e-commerce. It covers supply chain management, customer relationship management systems, digital markets, digital goods, and m-commerce services and applications. Specifically, it describes supply chain elements and structures, the purpose and applications of CRM, classifications of e-commerce, and the growth of retail e-commerce revenues since 1995.