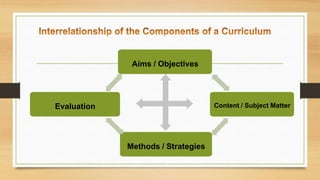
The document discusses definitions and concepts related to curriculum. It provides 10 definitions of curriculum from different education experts that focus on curriculum as the totality of a student's activities and experiences, a means to achieve educational goals, and the sum of what is taught in schools. It then lists 11 characteristics of curriculum, such as it being a totality of activities, a means to an end, reflecting educational trends, and helping achieve goals. The document explores these concepts in more depth.