This document contains notes on physics concepts related to current and potential difference:
- Current is defined as the flow of charge per second and is measured in Amperes. An ammeter measures current in a circuit.
- Potential difference (PD) or voltage is the energy delivered per unit charge and is measured in Volts. A voltmeter measures PD across a component.
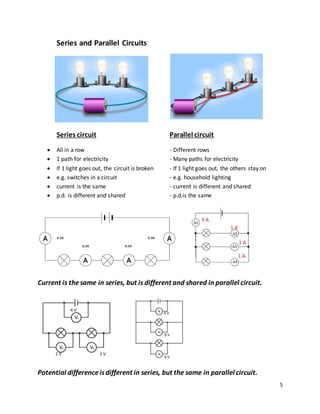
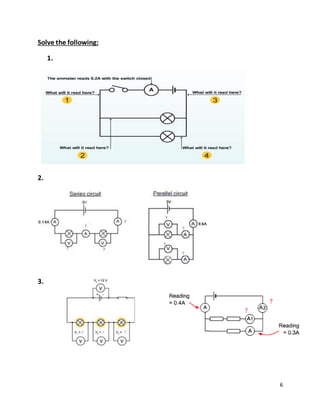
- Circuit diagrams show the connections of components in series and parallel configurations and how current and PD behave differently in each.