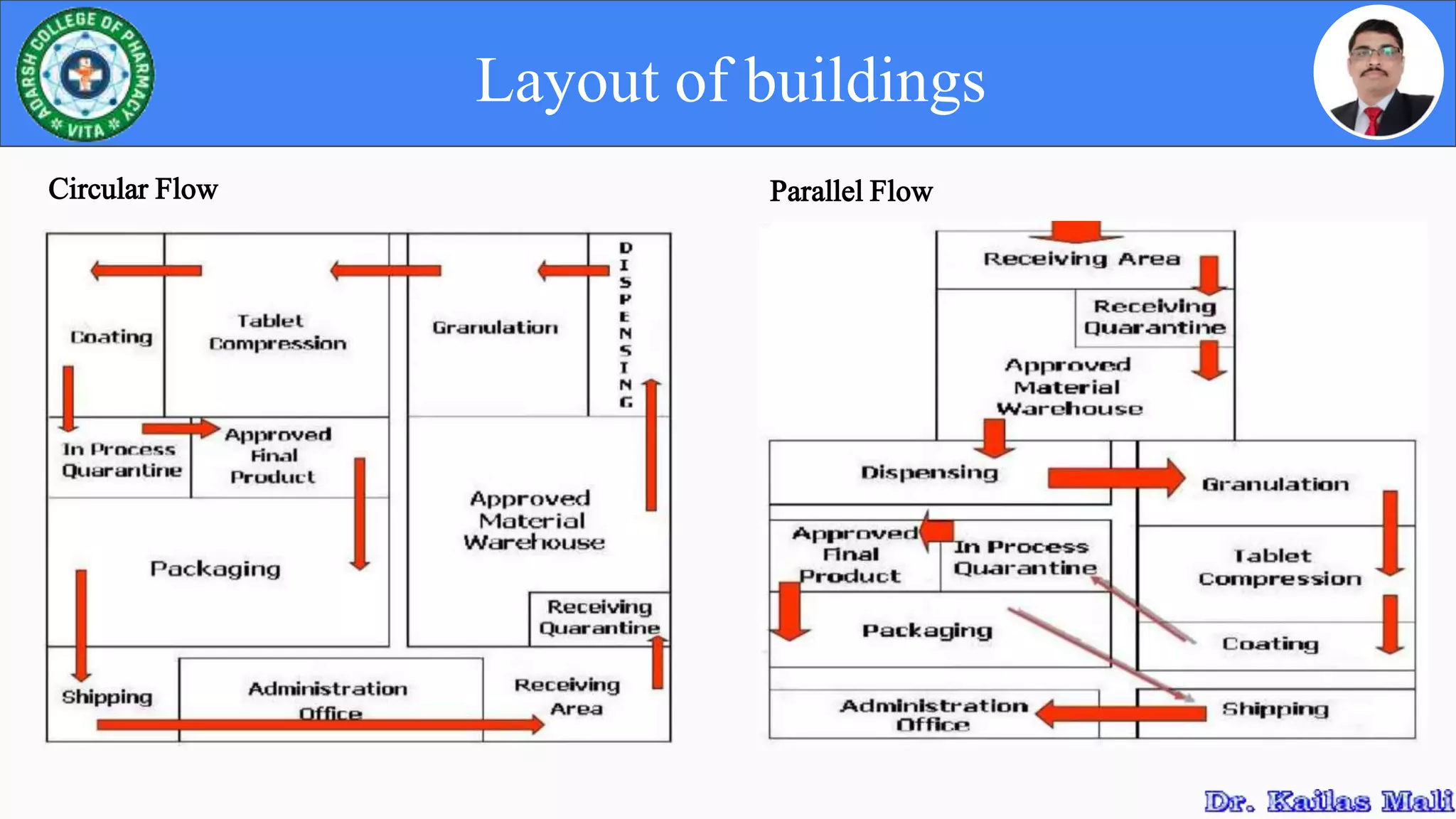
The document discusses current good manufacturing practices (cGMP) regulations for pharmaceutical manufacturing. It covers several topics:
cGMP regulations provide systems for proper design, monitoring, and control of manufacturing to ensure identity, strength, quality and purity of drug products. Facilities must have adequate design and construction to prevent contamination. Equipment must be properly qualified, installed and maintained. Sanitation procedures help prevent contamination and ensure compliance. Overall, cGMP helps assure safety and efficacy of drug products.