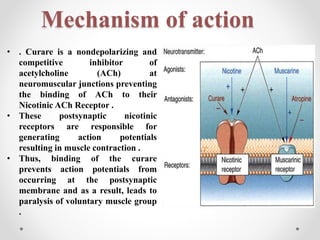
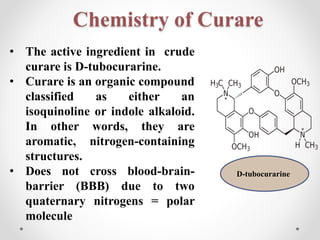
This document discusses neuromuscular blocking drugs, specifically curare alkaloids. It begins by introducing neuromuscular blockers and their uses in anesthesia and for muscle spasms. It then describes the two types - peripherally and centrally acting, listing examples of each. The main focus is on curare alkaloids, covering their types, mechanism of action by competitively blocking acetylcholine receptors, chemistry as isoquinoline or indole alkaloids, uses historically and in modern medicine, and some associated clinical features and disorders related to hypomagnesemia.