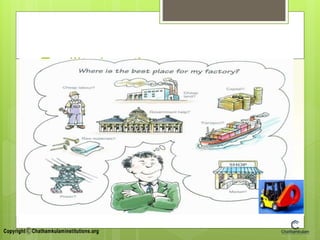
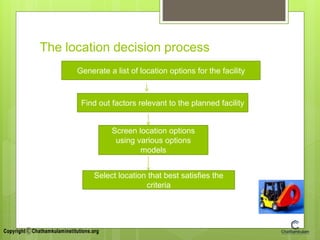
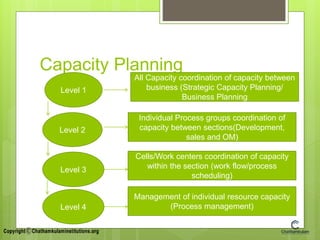
This document provides an overview of topics related to production planning and control. It discusses production planning and control, batch or job production, facility location, capacity planning models, process planning, and industrial safety. The key topics covered include the meaning and definition of production planning and control, elements of production planning like manpower and financial planning, and methods for facility location decision making. Capacity planning objectives and factors affecting capacity are also summarized.