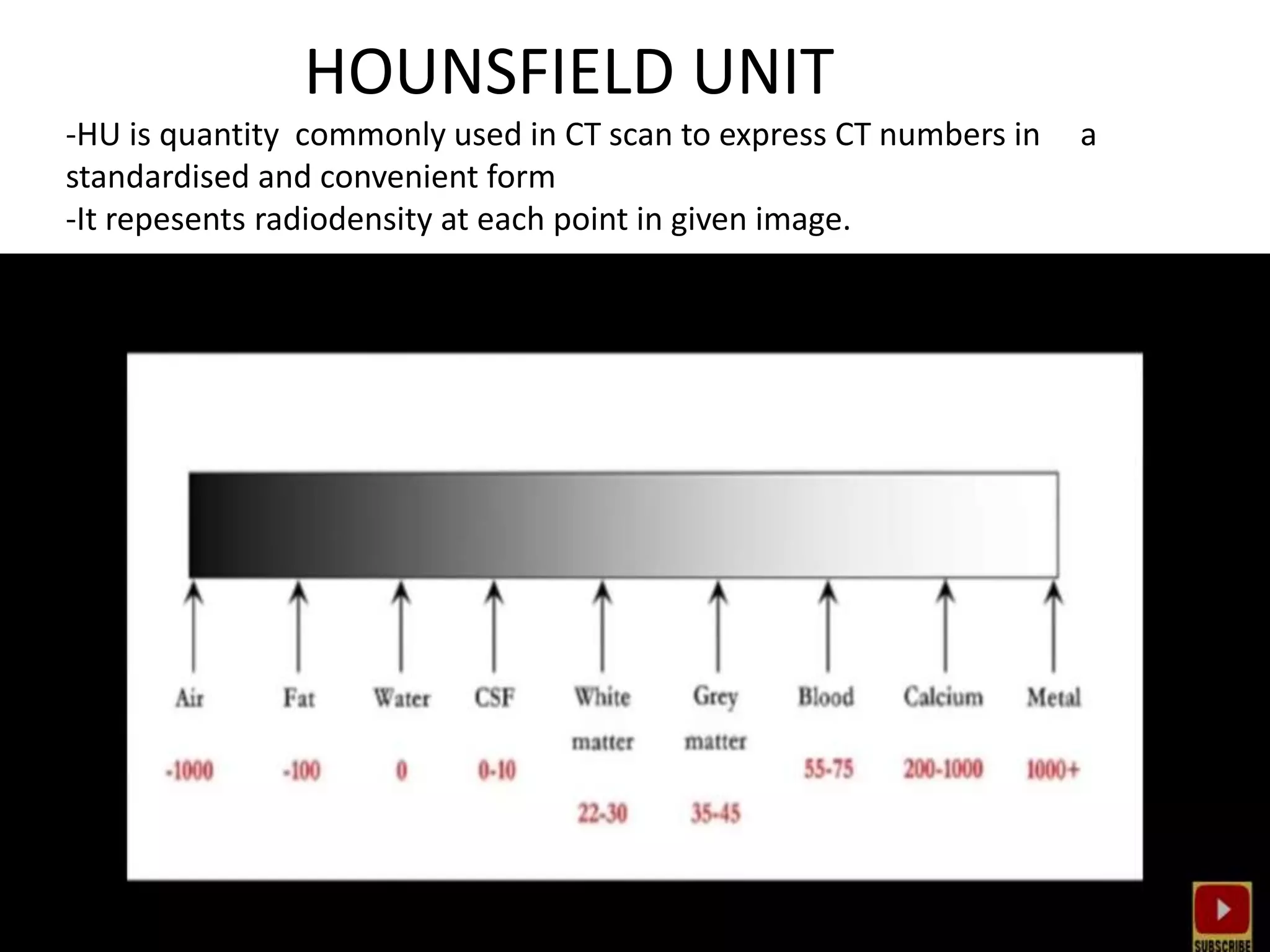
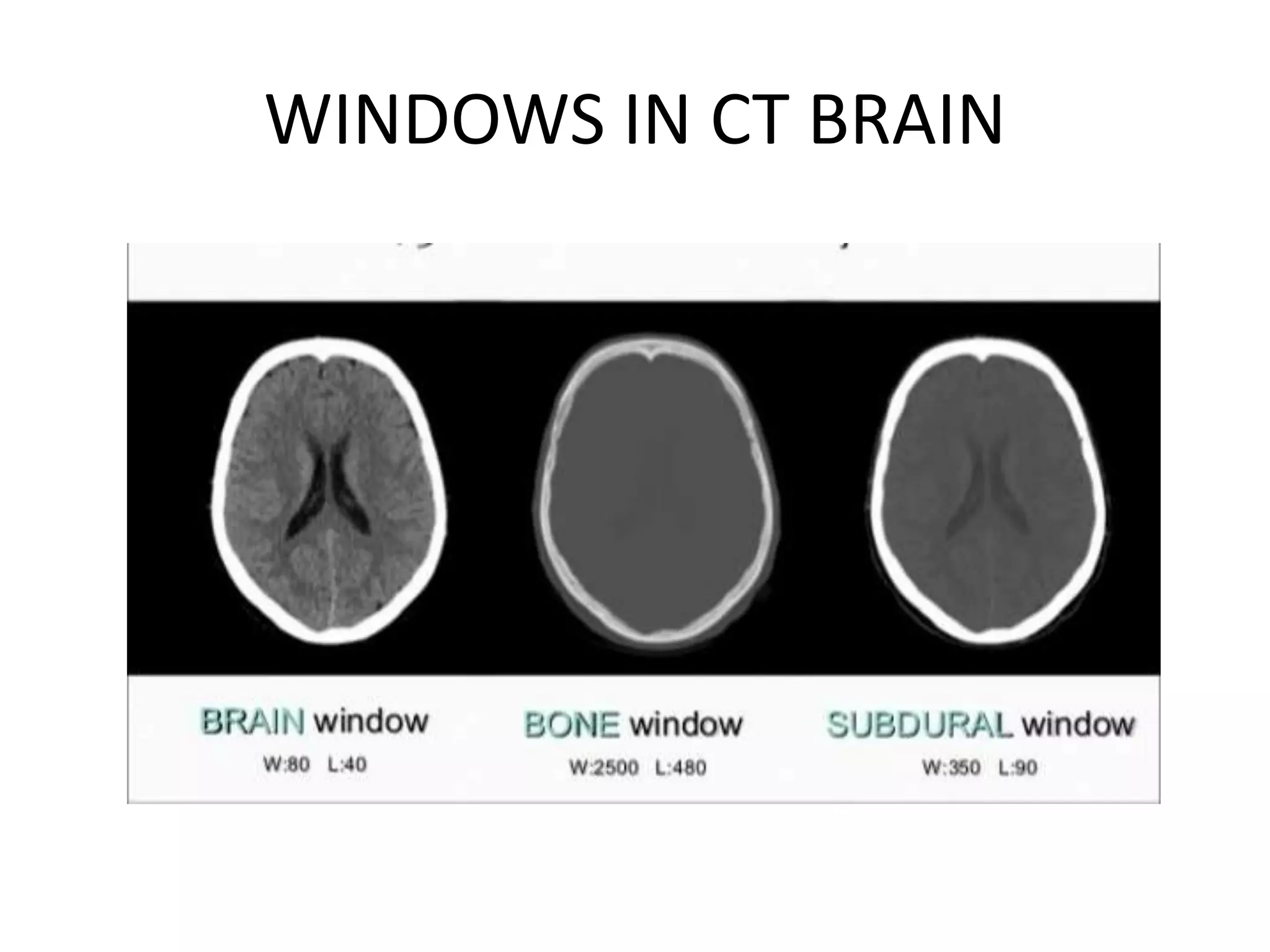
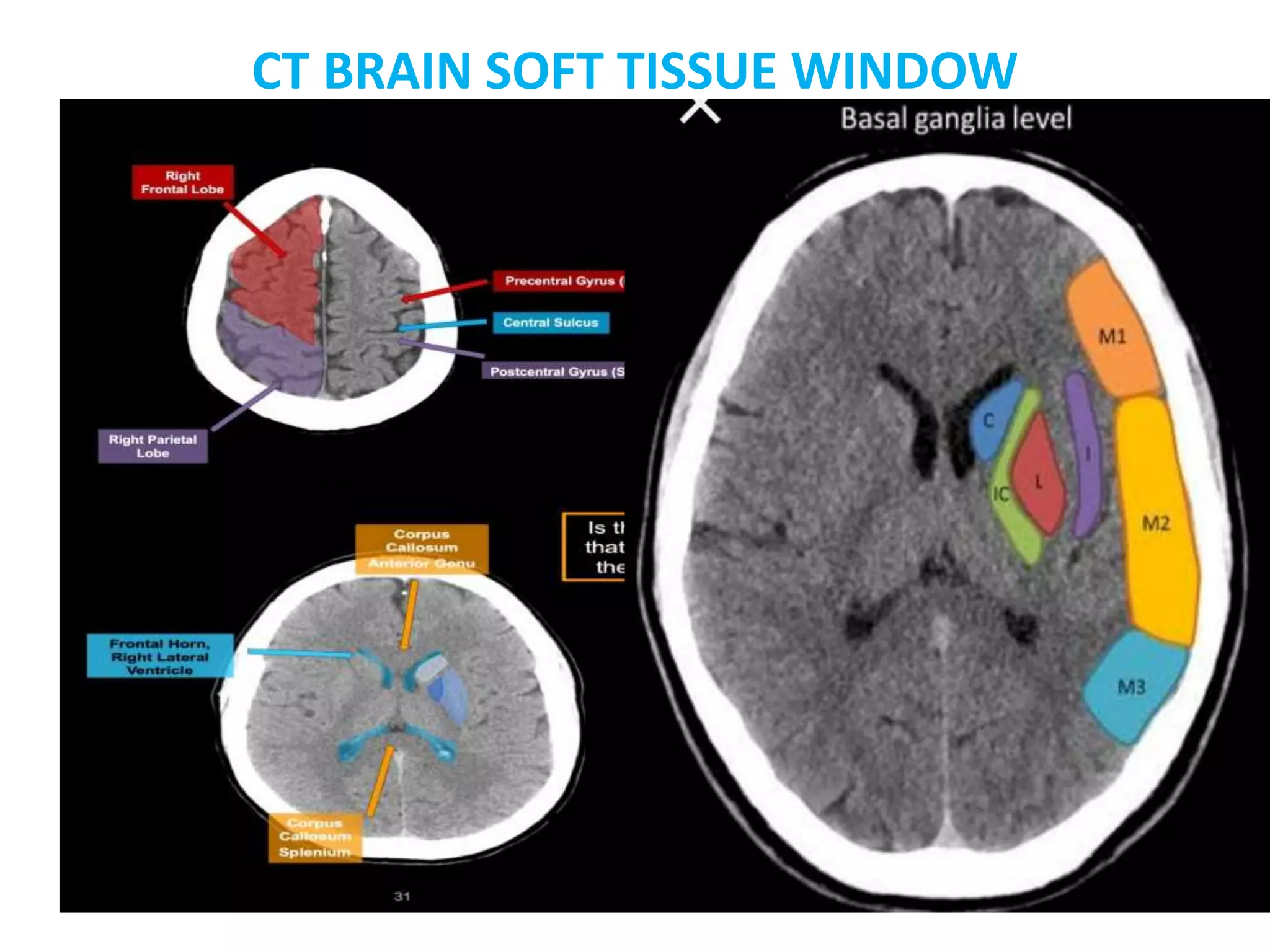
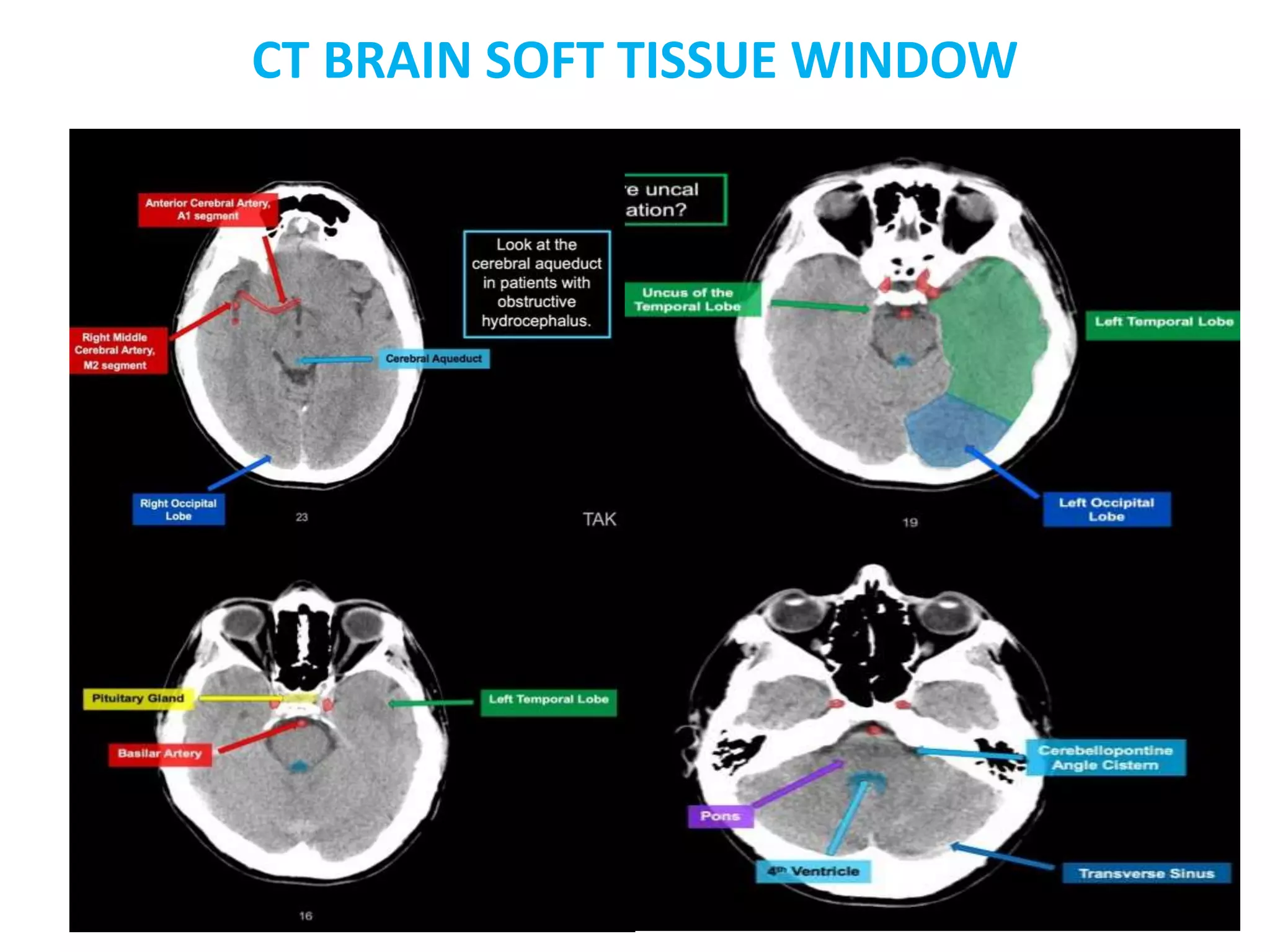
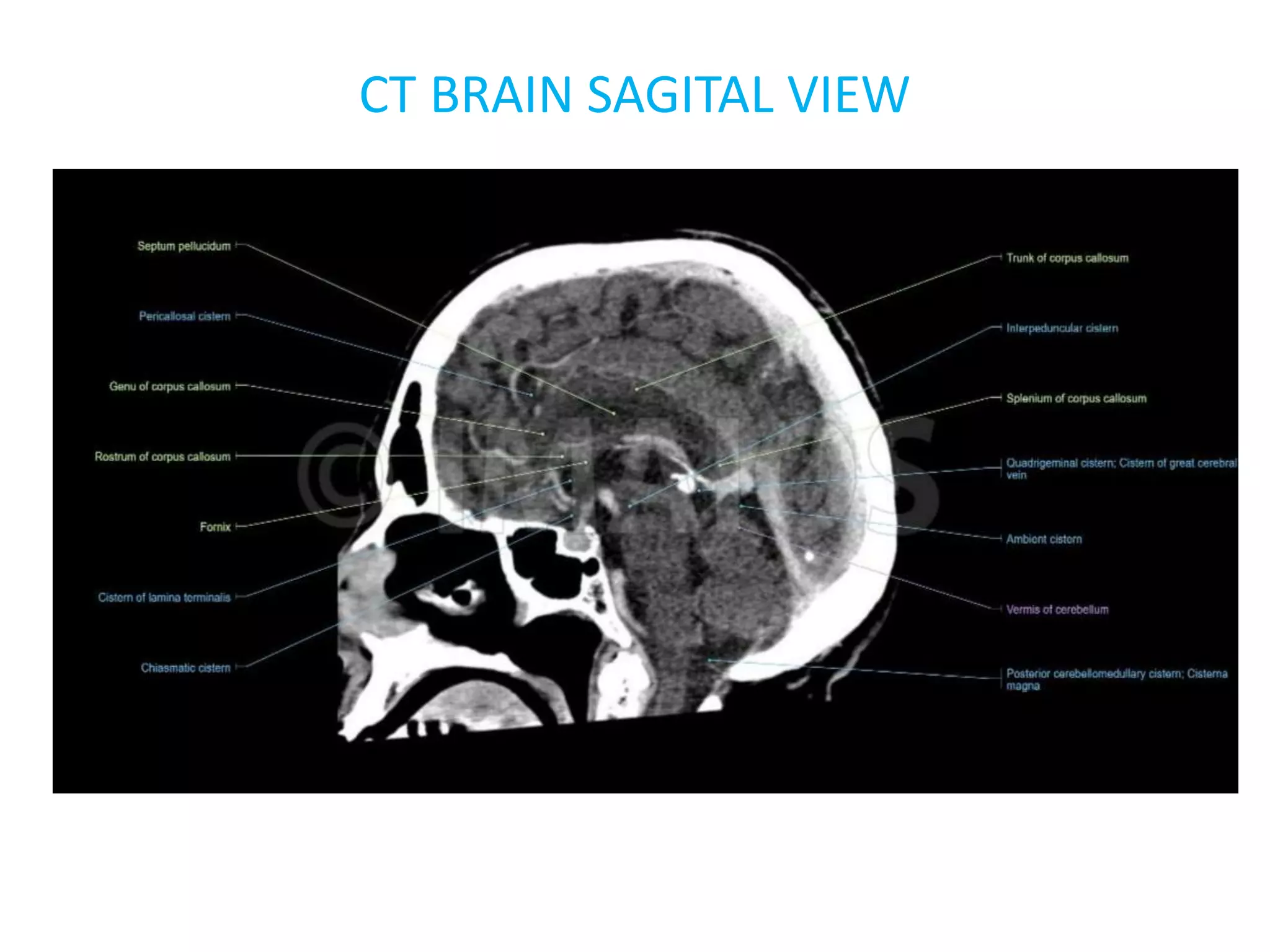
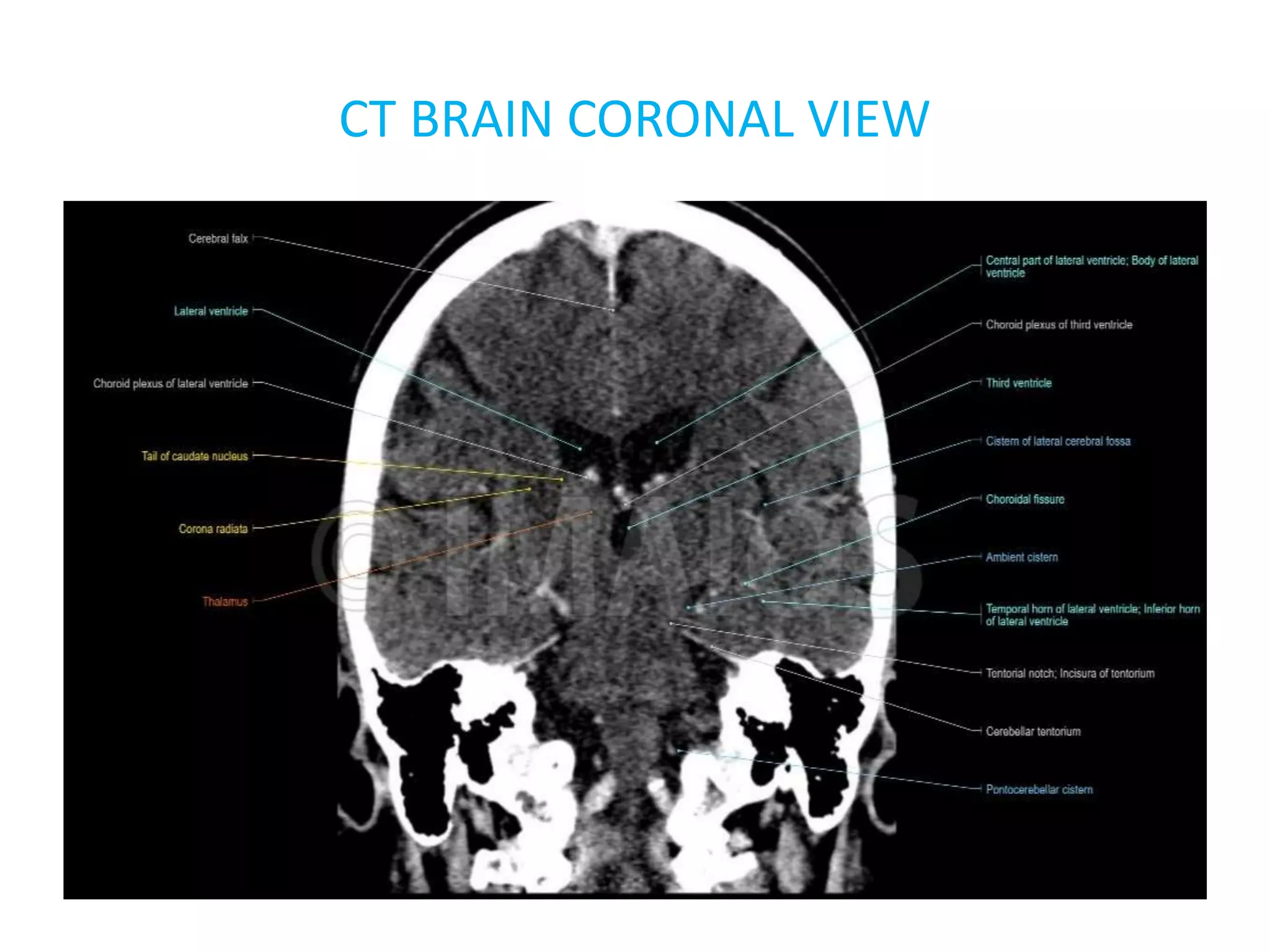
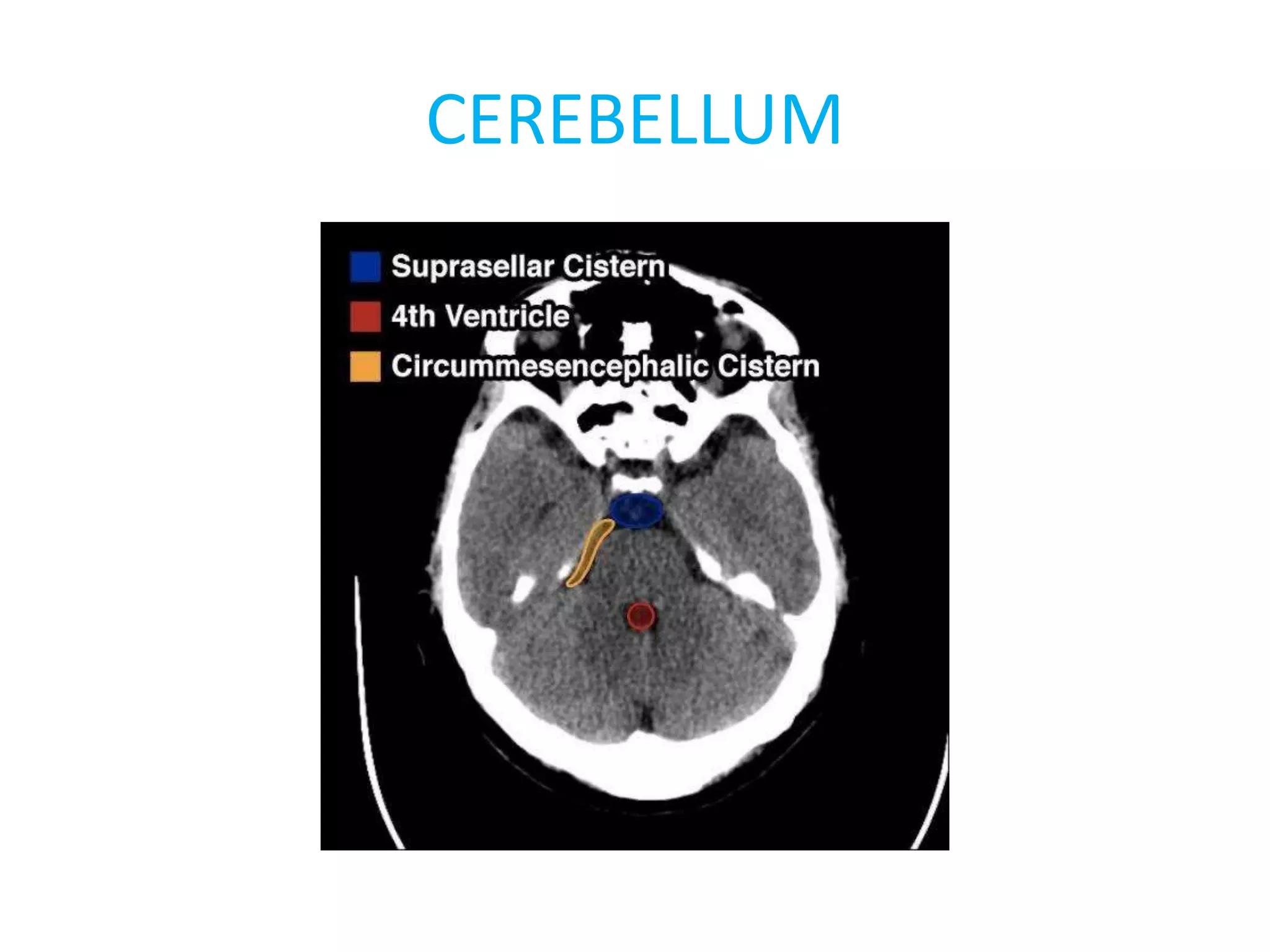
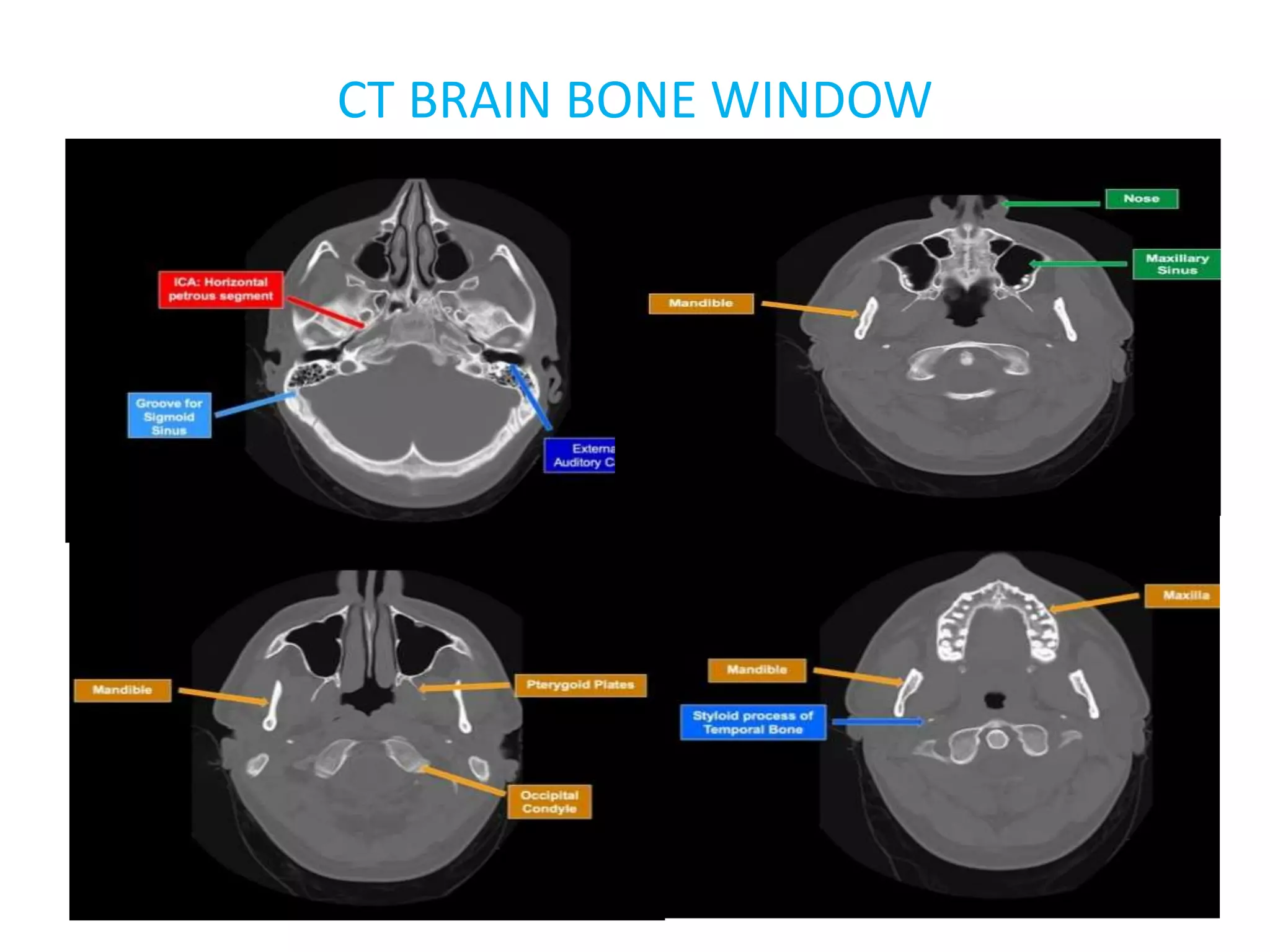
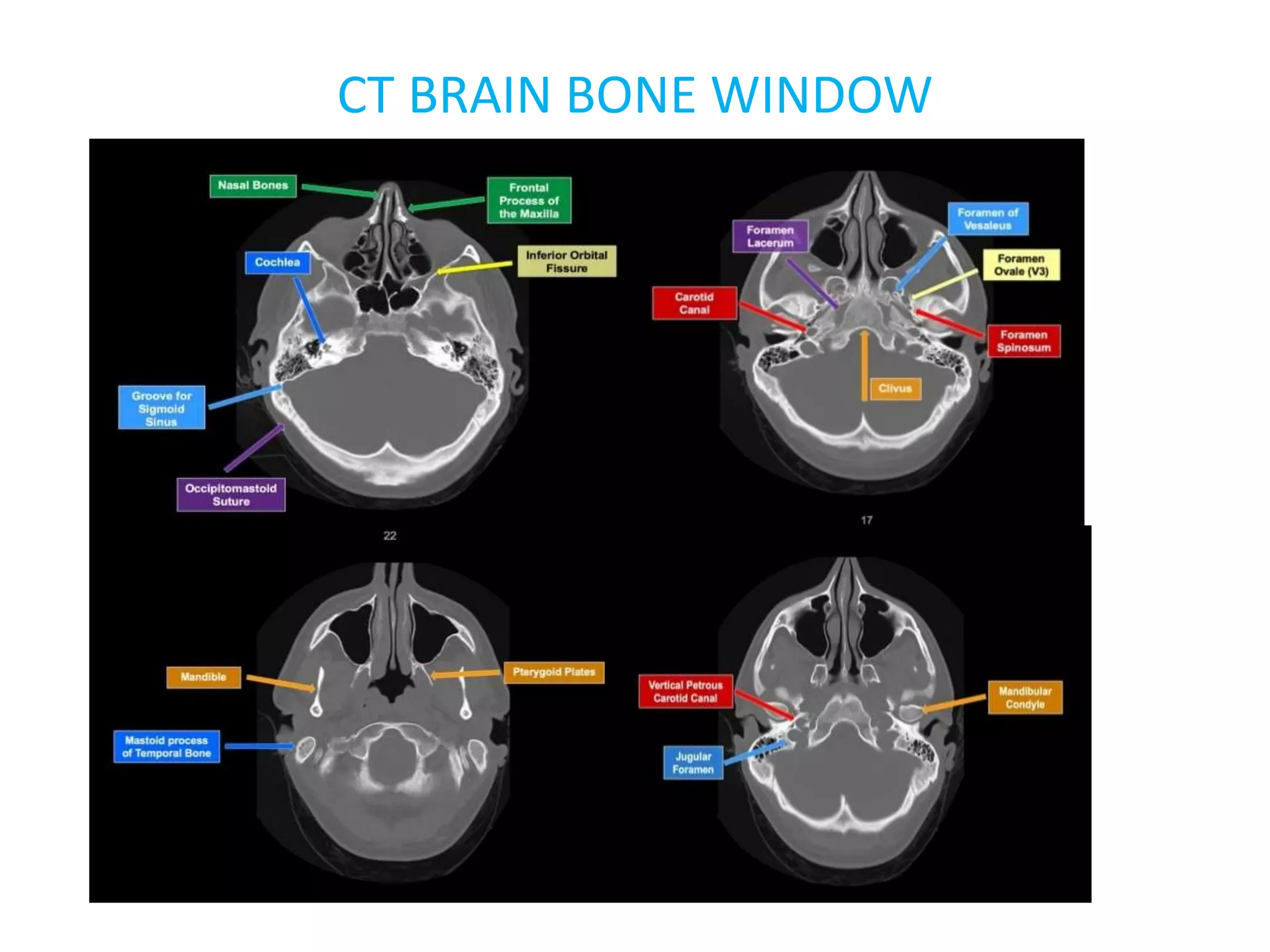
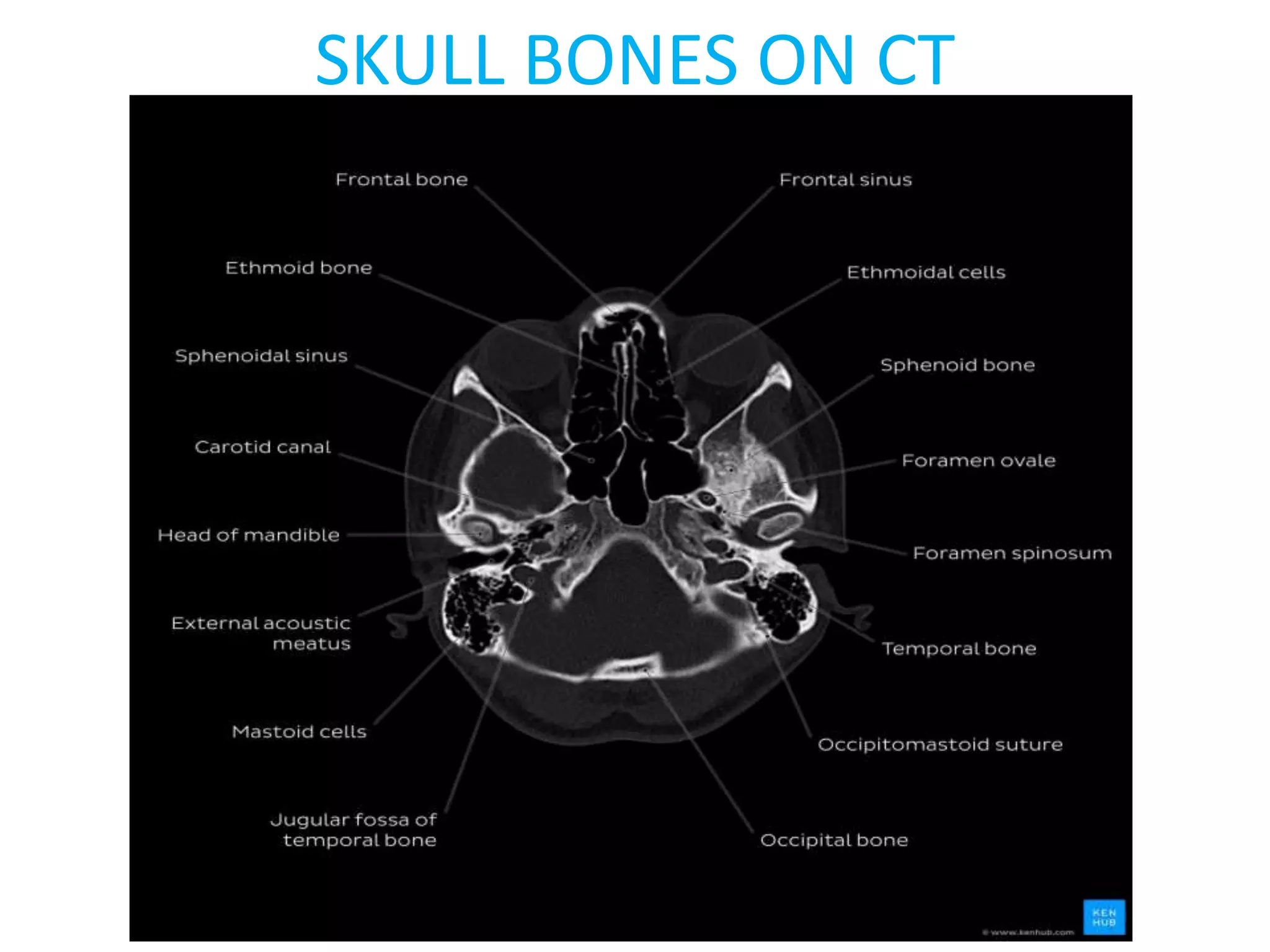
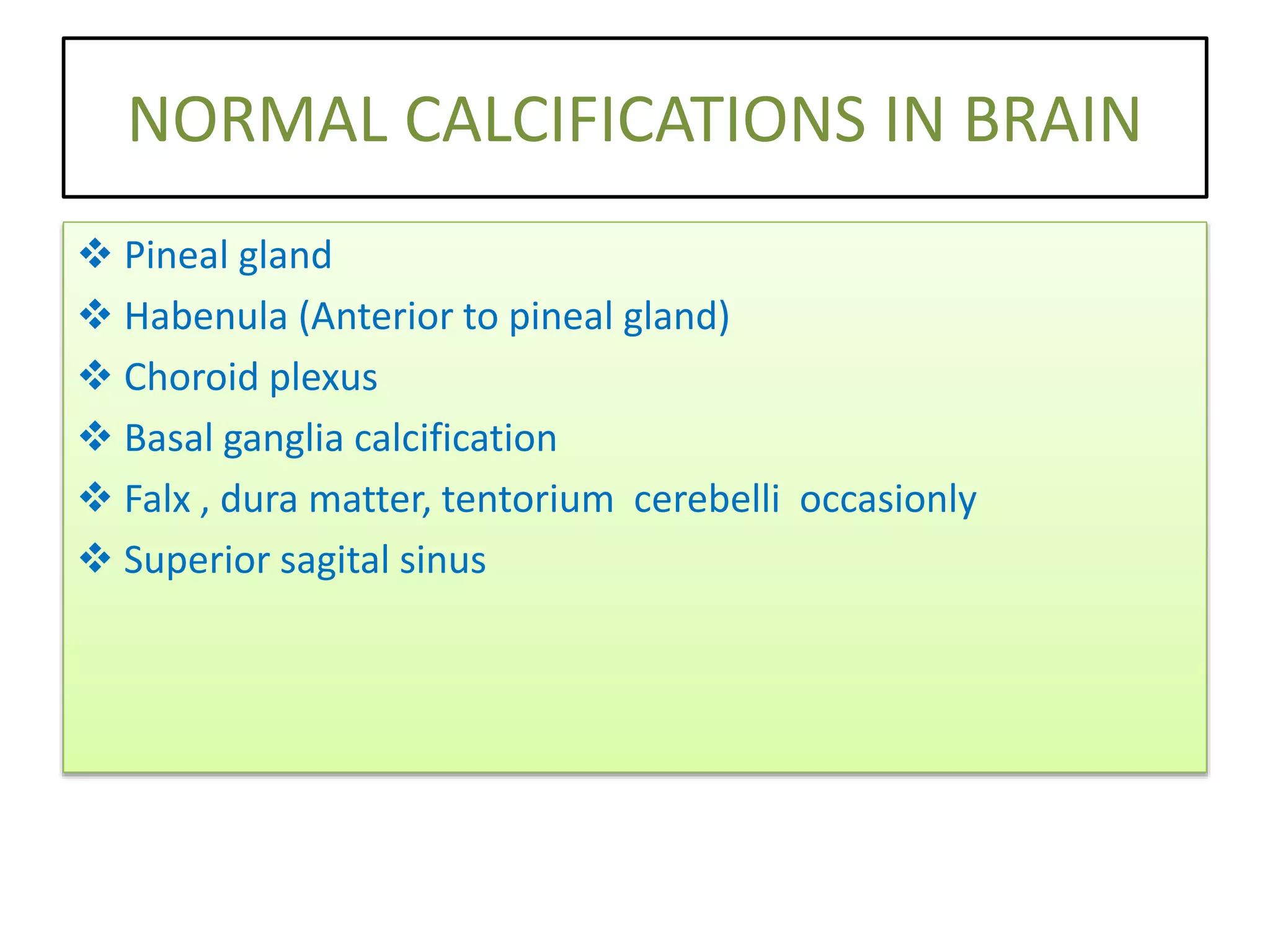
The document discusses indications for CT brain scans, including acute stroke, head injury, suspected hydrocephalus, and mental status changes. It describes how CT scans use Hounsfield units to represent radiodensity in images and how window width and level settings can be adjusted. Certain tissues appear hyperdense or hypodense on CT scans, such as blood appearing bright while CSF appears dark. The document outlines sections of the brain visible on CT and different windows used. It identifies cisterns, sulci, and fissures seen on scans and provides examples of normal brain calcifications.