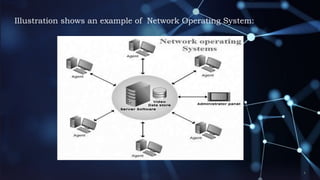
This document defines and compares the two major types of network operating systems (NOS): peer-to-peer and client/server. A NOS is an operating system designed to support sharing of resources like files, printers, and applications between computers in a network. In a peer-to-peer NOS, all computers have equal abilities to access shared resources without a central server. In a client/server NOS, functions are centralized on dedicated file servers that provide resources to individual workstations or clients. Examples of each type and their relative advantages and disadvantages are provided.