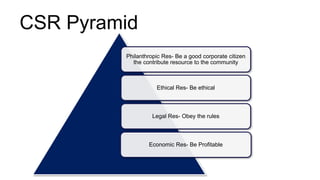
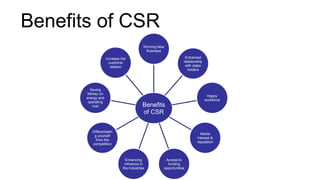
Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) refers to corporate initiatives to assess and take responsibility for a company's effects on the environment and impact on social welfare. CSR involves companies integrating economic, social, and environmental concerns into their business operations. The legal mandate in India requires companies with a net worth over 500 crore INR, turnover over 1000 crore INR, or net profit over 5 crore INR to spend on CSR activities classified as education, healthcare, rural development, and more. Benefits of CSR include winning new business, enhancing stakeholder relationships, and improving reputation. Many Indian companies actively engage in CSR programs focused on areas like education, community support, and socio-economic development.