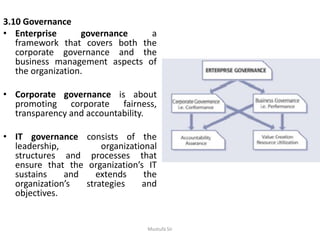
This document discusses key principles of Continual Service Improvement (CSI) including focusing on efficiency, effectiveness, and cost optimization. It emphasizes organizational change management, defining roles like the CSI manager, and addressing both external drivers like regulations and internal drivers like culture. The Deming Cycle of plan-do-check-act is recommended. Service measurement, knowledge management, benchmarks, governance, and service level management are also identified as important aspects of successful CSI.