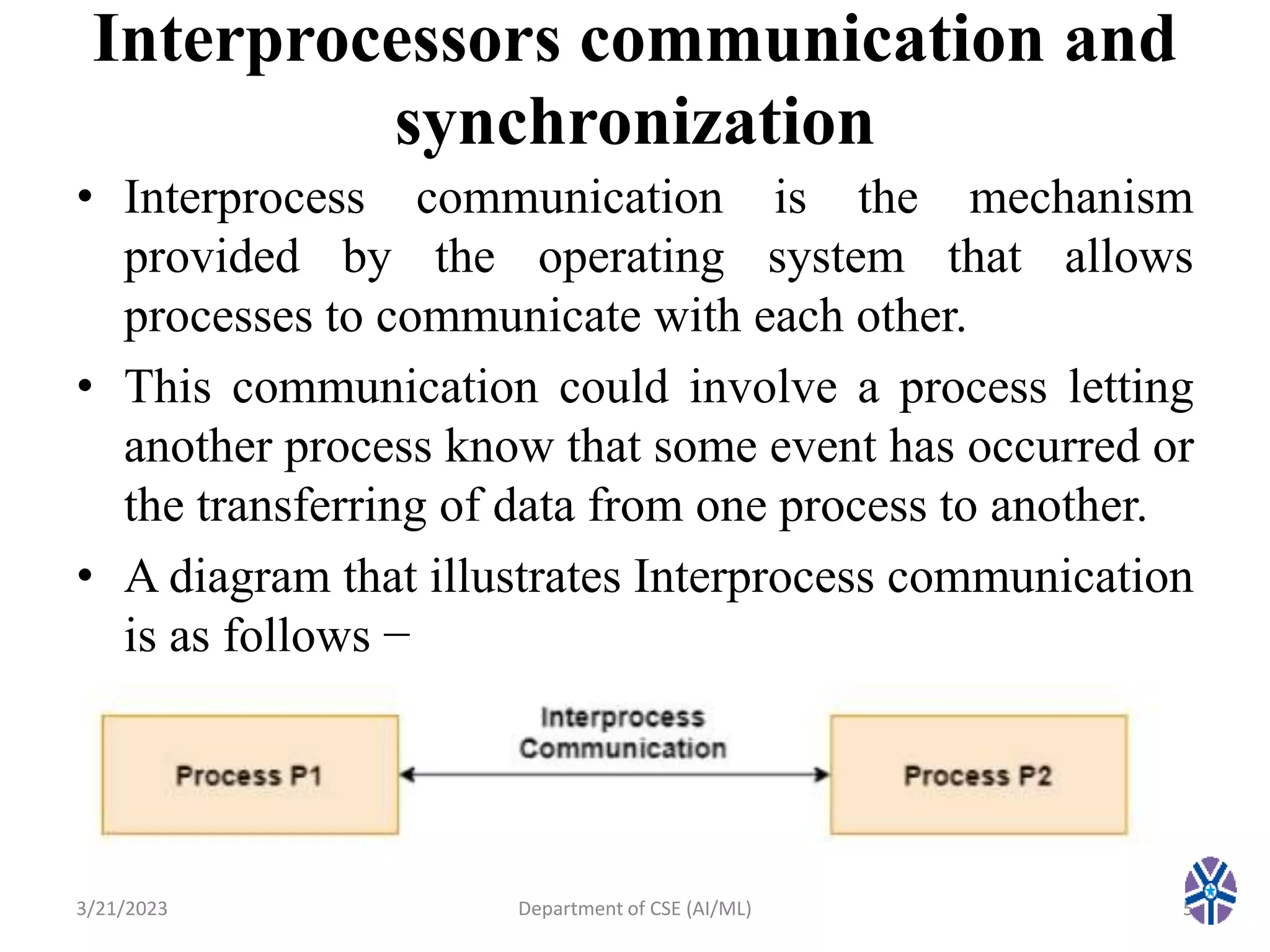
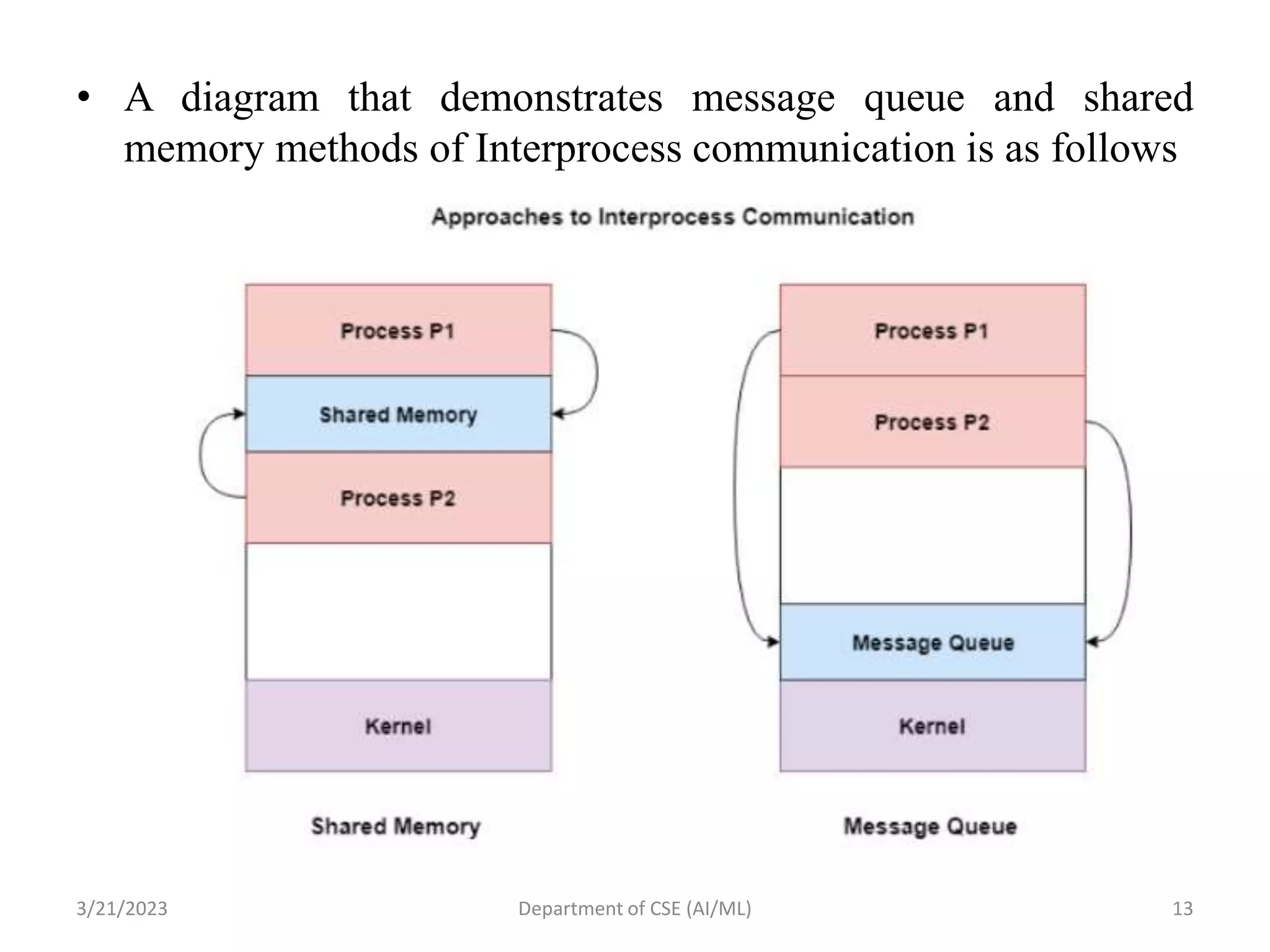
The document outlines a computer organization and architecture course focusing on key topics such as reduced instruction set computers, pipeline and vector processing, and interprocess communication mechanisms. It discusses synchronization methods including semaphores, mutual exclusion, and barriers, as well as approaches to interprocess communication like pipes, sockets, shared memory, and message queues. The document also previews the topics to be covered in the next session.