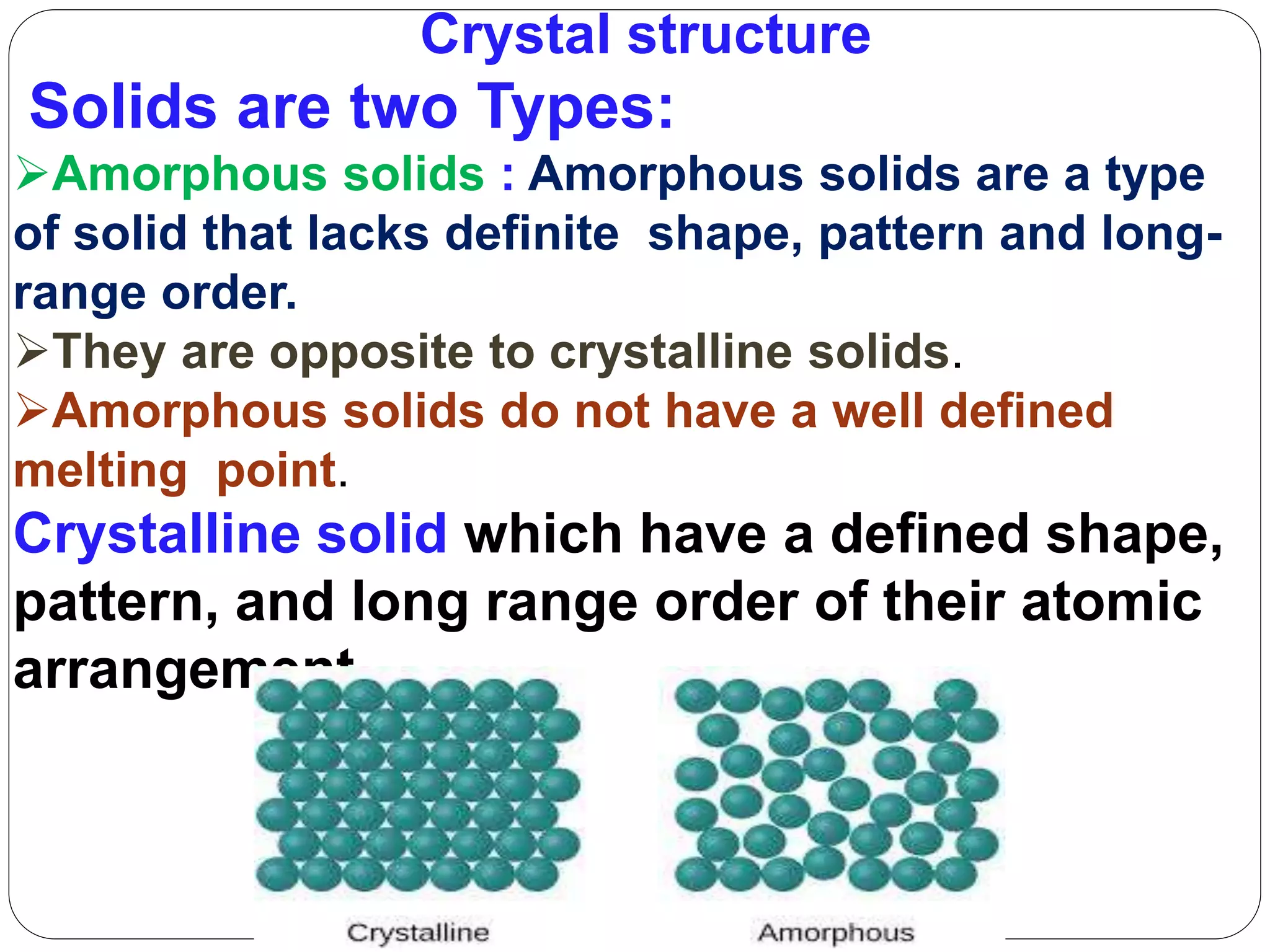
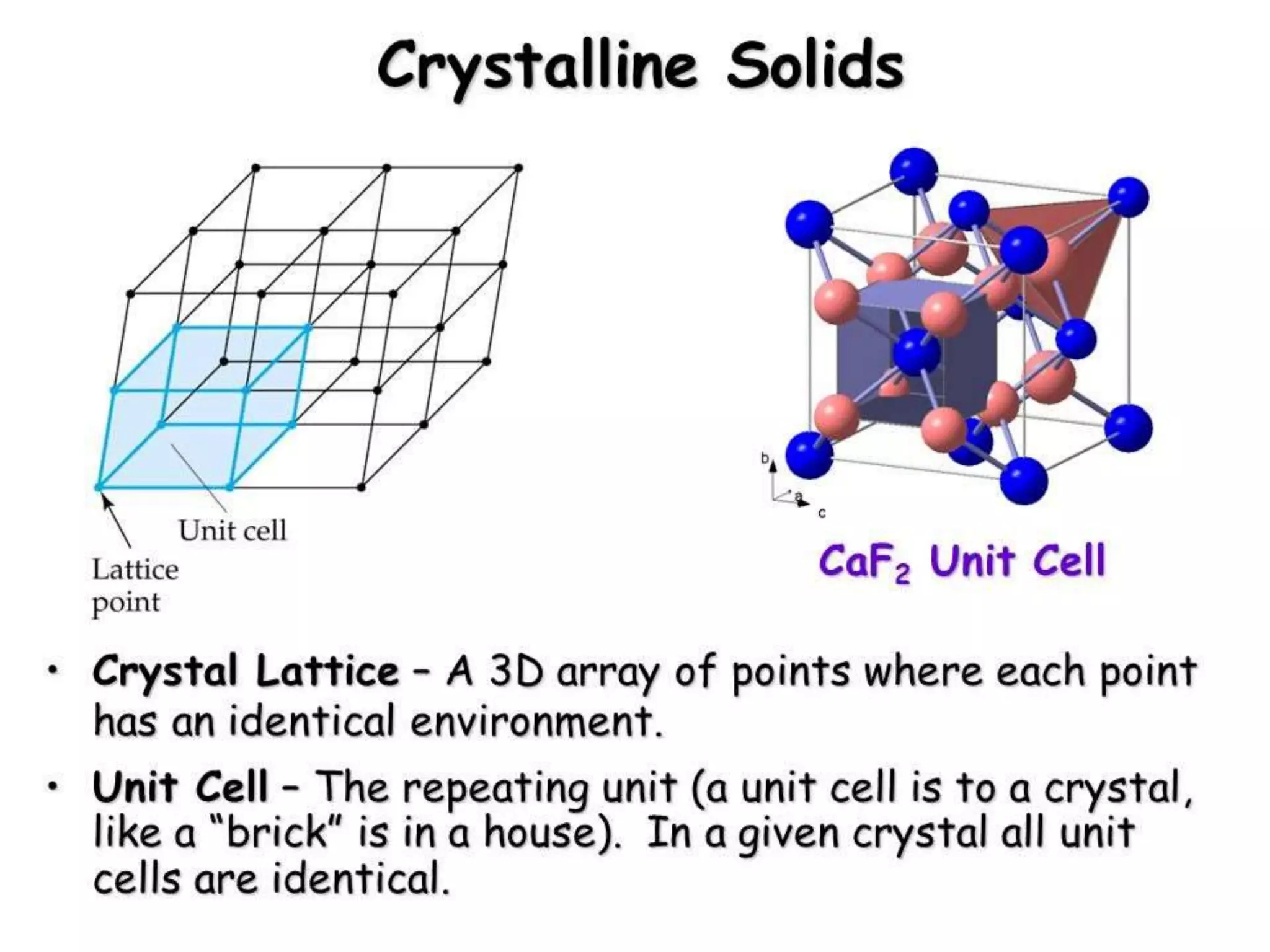
This document discusses the differences between amorphous and crystalline solids. Amorphous solids lack a definite shape or order of atomic arrangement, while crystalline solids have a defined shape and long-range order. Crystalline solids are anisotropic, meaning their properties vary with direction, because their atomic structure is ordered, whereas amorphous solids are isotropic with uniform properties in all directions due to their irregular atomic arrangement. The document then covers topics such as unit cell types, crystal axes and angles, calculating packing factors, defects in crystalline structures, and line defects.