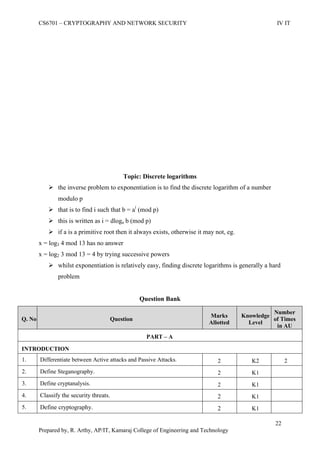
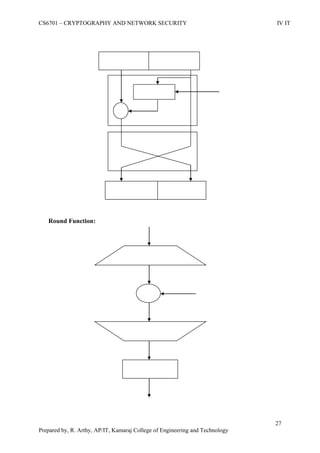
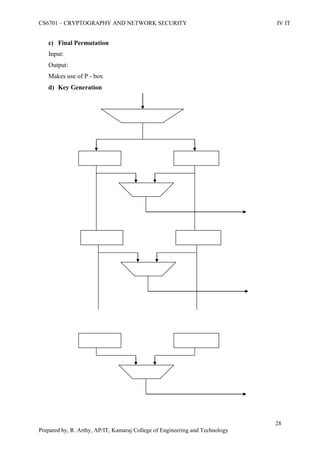
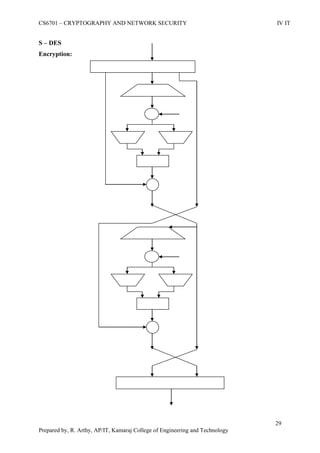
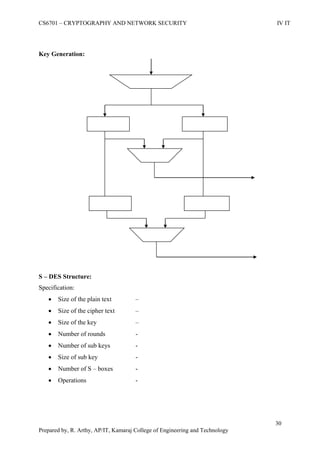
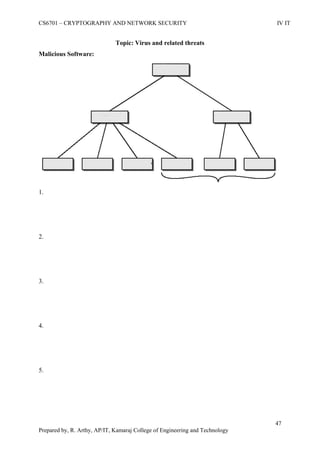
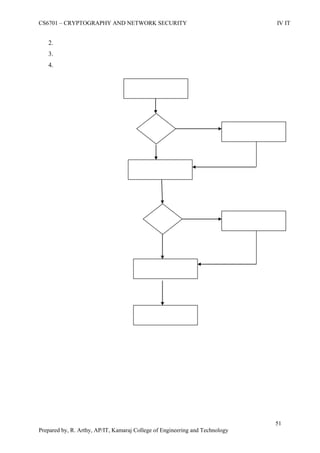
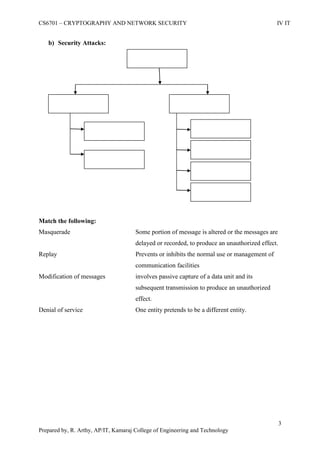
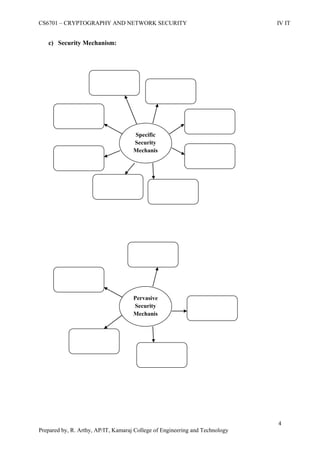
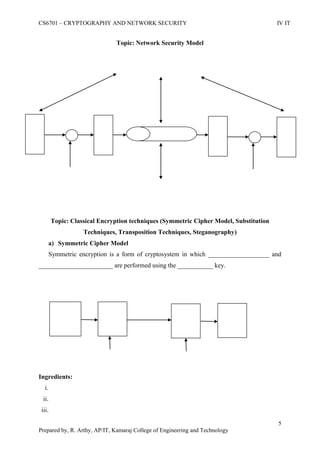
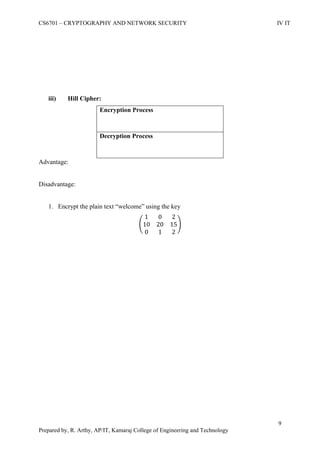
This document is a worksheet for a cryptography and network security course. It contains definitions of key terms like cryptography, encryption, decryption, and types of attacks. It also outlines classical encryption techniques like the Caesar cipher, Playfair cipher, Hill cipher, Vigenere cipher, and transposition techniques. Finally, it covers number theory topics such as prime numbers, factorization, Fermat's theorem, Euler's theorem, and primitive roots as they relate to cryptography.











![CS6701 – CRYPTOGRAPHY AND NETWORK SECURITY IV IT
16
Prepared by, R. Arthy, AP/IT, Kamaraj College of Engineering and Technology
Topic: Modular arithmetic- Euclid’s algorithm
Modular Arithmetic:
Modular arithmetic is 'clock arithmetic' b mod n says when divided by n have a remainder r
a = qn + r
a and b are congruent if; a mod n = b mod n
Properties:
i. [(a mod n) + (b mod n)] mod n = (a + b) mod n
ii. [(a mod n) - (b mod n)] mod n = (a - b) mod n
iii. [(a mod n) * (b mod n)] mod n = (a * b) mod n
Euclid’s Algorithm:
To find the GCD of two numbers
GCD (a,b) = GCD(b, a mod b)
Euclid(a, b):
if(b == 0)
return a;
else
return Euclid(b, a mod b);
1. Determine the gcd (24140, 16762)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/workbook-200920123548/85/Cryptography-Workbook-16-320.jpg)